Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone that results from the spread of microorganisms from the blood (hematogenous), nearby infected tissue, or open wounds (non-hematogenous). Infections are most commonly caused by Staphylococcus aureus, but a variety of organisms have been linked to osteomyelitis. The majority of patients present with pain, redness, and swelling of the affected site, and may have associated symptoms such as fever and chills. Laboratory values will demonstrate elevated WBC, CRP, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate ( ESR ESR Soft Tissue Abscess) in most cases. The most sensitive and specific imaging modality to diagnose osteomyelitis is MRI. Management may require long-term antibiotics and potential surgical debridement Debridement The removal of foreign material and devitalized or contaminated tissue from or adjacent to a traumatic or infected lesion until surrounding healthy tissue is exposed. Stevens-Johnson Syndrome.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Osteomyelitis is classified based on the route of infection.
Non-hematogenous osteomyelitis (80% of cases):
Hematogenous Hematogenous Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases osteomyelitis (20% of cases):
| Risk factors | Infectious agents |
|---|---|
| No specific risk factor | S. aureus S. aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Staphylococcus |
| Prosthetic joint replacement Prosthetic Joint Replacement Septic Arthritis |
|
| Sickle cell anemia Sickle cell anemia A disease characterized by chronic hemolytic anemia, episodic painful crises, and pathologic involvement of many organs. It is the clinical expression of homozygosity for hemoglobin S. Sickle Cell Disease |
|
| Chronic granulomatous disease Granulomatous disease A defect of leukocyte function in which phagocytic cells ingest but fail to digest bacteria, resulting in recurring bacterial infections with granuloma formation. When chronic granulomatous disease is caused by mutations in the cybb gene, the condition is inherited in an X-linked recessive pattern. When chronic granulomatous disease is caused by cyba, ncf1, ncf2, or ncf4 gene mutations, the condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) |
|
| Vertebral osteomyelitis |
|
| Sexually active, no other risk factors | N. gonorrhoeae N. gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria (more likely to cause septic arthritis Arthritis Acute or chronic inflammation of joints. Osteoarthritis than osteomyelitis) |
| Cat or dog bite | Pasteurella multocida Pasteurella Multocida A species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria normally found in the flora of the mouth and respiratory tract of animals and birds. It causes shipping fever; hemorrhagic bacteremia; and intestinal disease in animals. In humans, disease usually arises from a wound infection following a bite or scratch from domesticated animals. Dog and Cat Bites |
| IV drug use or immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis |
|
Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types that results from hematogenous Hematogenous Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases or non-hematogenous spread of infectious organisms.
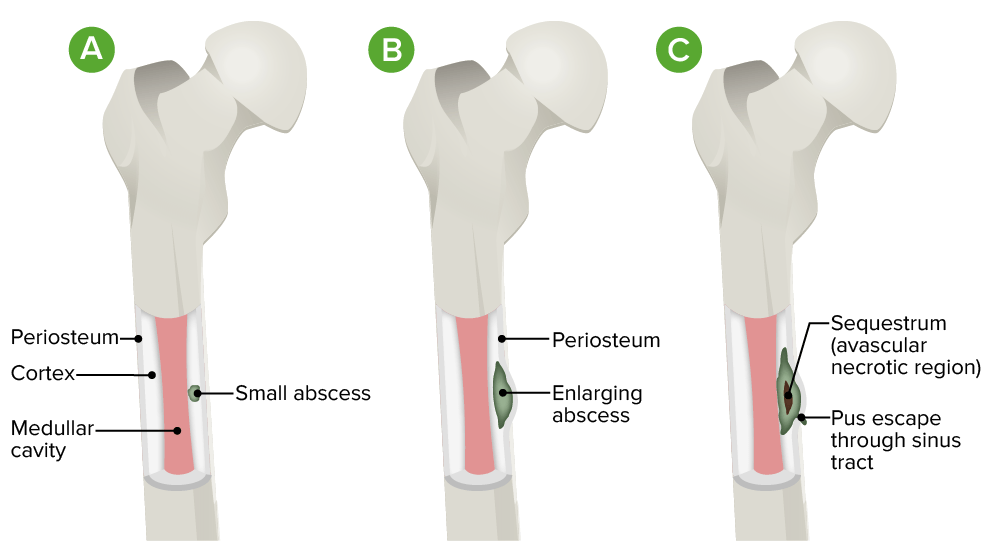
Pathophysiology of osteomyelitis:
A. Initial infection is localized to the cortical region.
B. There is progression into the subperiosteal space with lifting of the periosteum.
C. Diffuse infection occurs with sequestrum (avascular necrotic region) and sinus tract formation.
Vertebral osteomyelitis:
Sternoclavicular and pelvic osteomyelitis:
Long bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types osteomyelitis:
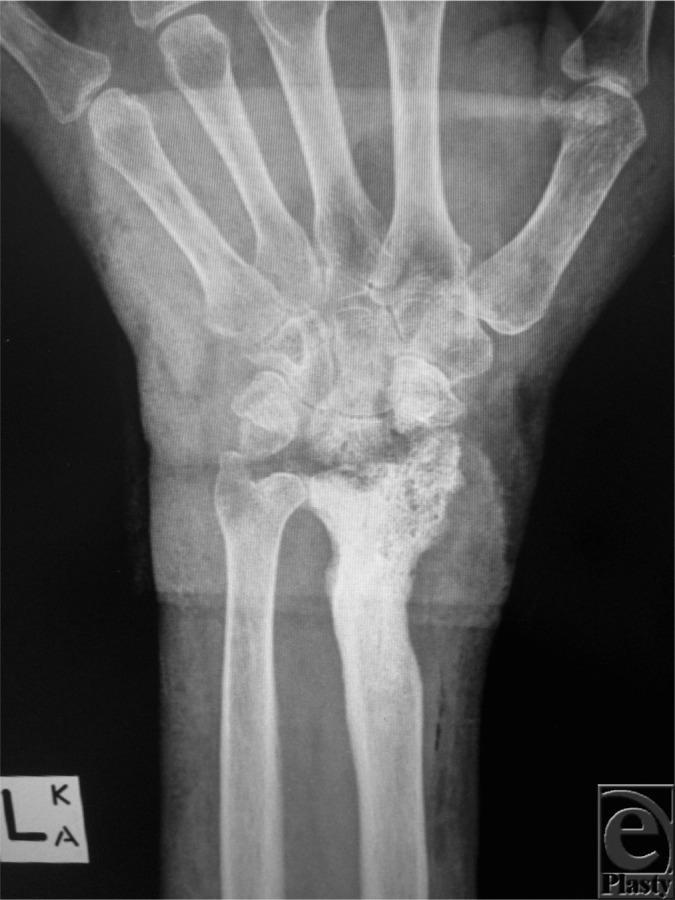
X-ray of the hand showing chronic osteomyelitis:
Note the bony destruction at the radiocarpal joint.
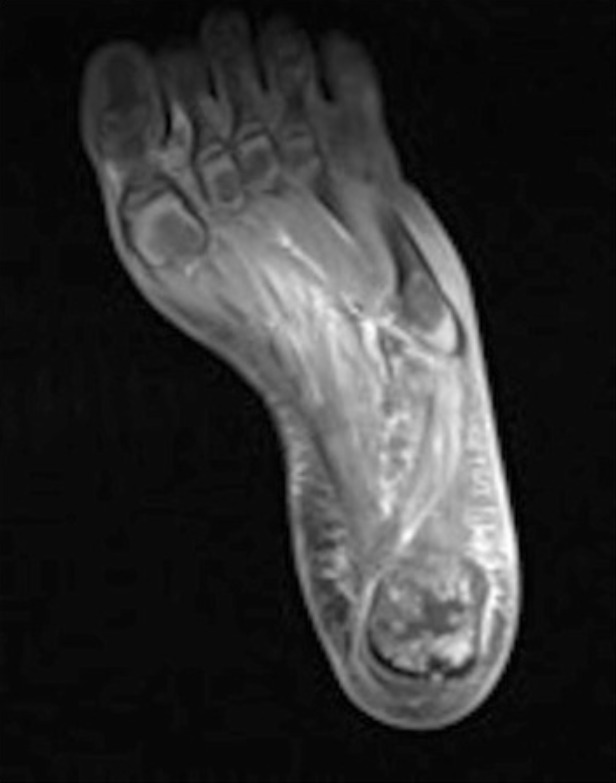
An MRI of the left foot with osseous changes of the calcaneus consistent with osteomyelitis
Image: “Delayed recognition of pediatric calcaneal osteomyelitis: a case report” by Mallia AJ, Ashwood N, Arealis G, Bindi F, Zamfir G, Galanopoulos I. License: CC BY 4.0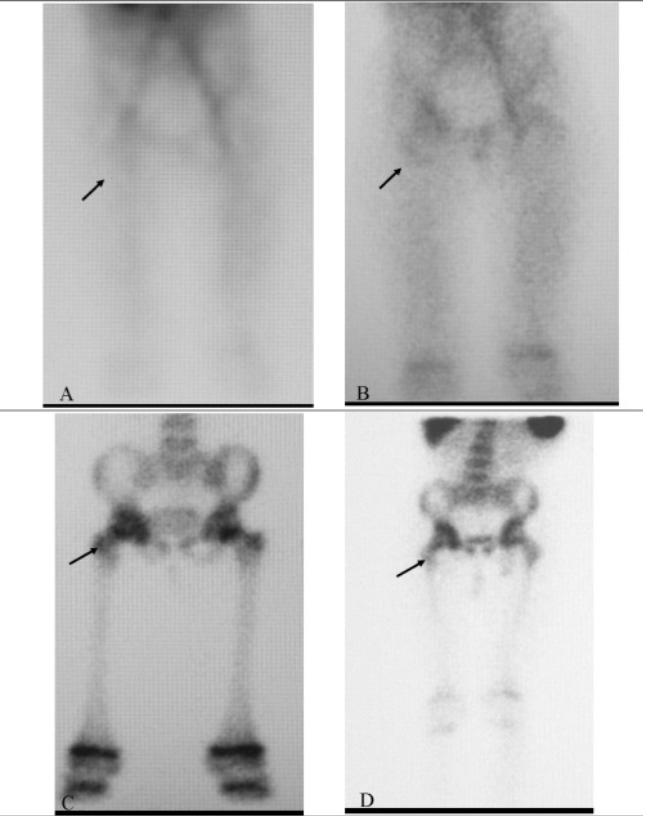
A 3-phase bone scan showing positive uptake in the region of the right hip (arrow) in a patient with osteomyelitis
Image: “Tc-99m Labeled HMPAO white Blood Cell Scintigraphy in Pediatric Patients” by Aydın F, Kın Cengiz A, Güngör F. License: CC BY 2.5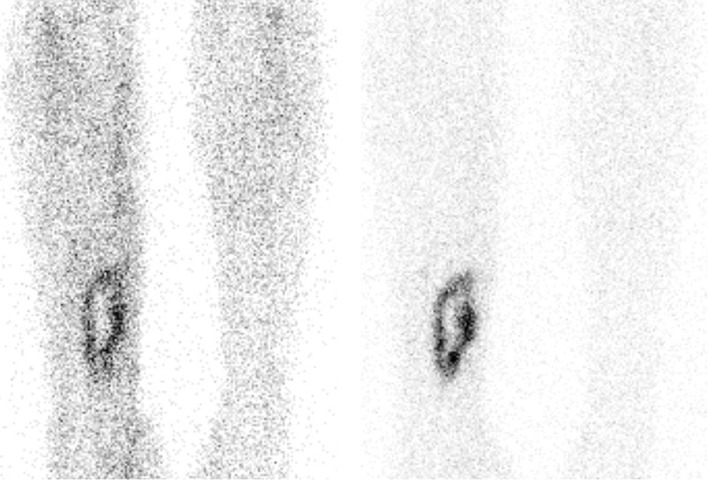
An example of a positive tagged WBC scan in a patient with osteomyelitis of the right tibia.
Increased uptake is seen in the right tibia, compared with the background uptake.
Left image: anterior view 4 hours after injection
Right image: anterior view 24 hours after injection.