Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI), or “brittle bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types disease,” is a rare genetic connective tissue Connective tissue Connective tissues originate from embryonic mesenchyme and are present throughout the body except inside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of connective tissues is to provide structural support to organs. Connective tissues consist of cells and an extracellular matrix. Connective Tissue: Histology disorder characterized by severe bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types fragility. Although OI is considered a single disease, OI includes over 20 genotypes and clinical phenotypes with differing symptom severity. Of these, types I–IV are the most common. Because of the rarity of OI, OI is considered an “orphan disease” in the United States. Diagnosis is made clinically, through history and examination, and is confirmed by radiologic findings and DNA analysis DNA analysis Biochemical identification of mutational changes in a nucleotide sequence. Hyper-IgM Syndrome. While there is no definitive cure, treatment is supportive, usually involving bisphosphonates Bisphosphonates Bisphosphonates are pyrophosphate analogs most well-known for treating osteoporosis by preventing bone loss. Bisphosphonates end in the suffix "-dronate" or "-dronic acid" (e.g., alendronate, risedronate, pamidronate) and bind to hydroxyapatite crystals in bone, inhibiting osteoclast-induced bone resorption. Bisphosphonates, and is focused on reducing pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, reducing fracture Fracture A fracture is a disruption of the cortex of any bone and periosteum and is commonly due to mechanical stress after an injury or accident. Open fractures due to trauma can be a medical emergency. Fractures are frequently associated with automobile accidents, workplace injuries, and trauma. Overview of Bone Fractures frequency, reducing bony deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs, and increasing ambulation. The prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables, depending on the OI type.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Osteogenesis imperfecta (OI) is an inherited connective tissue Connective tissue Connective tissues originate from embryonic mesenchyme and are present throughout the body except inside the brain and spinal cord. The main function of connective tissues is to provide structural support to organs. Connective tissues consist of cells and an extracellular matrix. Connective Tissue: Histology disorder characterized by impaired bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types formation and severe bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types fragility.
| Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mutated gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics | COL1A1, COL1A2 ( collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy alpha 1 and 2 chains) | COL1A1, COL1A2, and CRTAP (cartilage-associated protein) | COL1A1, COL1A2 | COL1A1, COL1A2 |
| Inheritance modality | Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance | Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance AND autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance | Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance | Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance |
| Defect | Frameshift mutations in collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy alpha 1 and 2 chains leading to decreased amounts of normal collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology | Disrupted formation of the collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology triple helix structure, leading to little or no normal collagen Collagen A polypeptide substance comprising about one third of the total protein in mammalian organisms. It is the main constituent of skin; connective tissue; and the organic substance of bones (bone and bones) and teeth (tooth). Connective Tissue: Histology | Mutations causing structural protein defects leading to severe pathology | Mutations causing structural protein defects leading to minimal or mild pathology |
| Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Description | Non-deforming with blue sclerae | Perinatally lethal | Progressively deforming | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables with normal sclerae |
| Severity | Mild | Perinatal lethal | Severe | Mild to moderate |
| Fractures | < 100 | > 100 | > 100 | > 100 |
| Bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs | Uncommon | Severe | Moderate to severe | Mild to moderate |
| Stature | Normal to mildly reduced | Severely reduced | Reduced | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables |
| Dentogenesis imperfecta | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables | Common | Common | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables |
| Color of sclerae | Blue | Dark blue | Blue | Normal to gray |
| Hearing loss Hearing loss Hearing loss, also known as hearing impairment, is any degree of impairment in the ability to apprehend sound as determined by audiometry to be below normal hearing thresholds. Clinical presentation may occur at birth or as a gradual loss of hearing with age, including a short-term or sudden loss at any point. Hearing Loss | Present in approximately 50% | — | Frequent | Variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables |
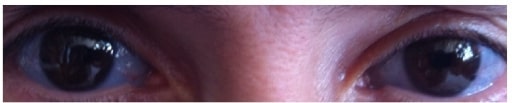
Blue-colored sclera associated with OI
Image: “Blue sclera” by the Department of Medical Oncology, Ankara University School of Medicine, 06300 Ankara, Turkey. License: CC BY 3.0.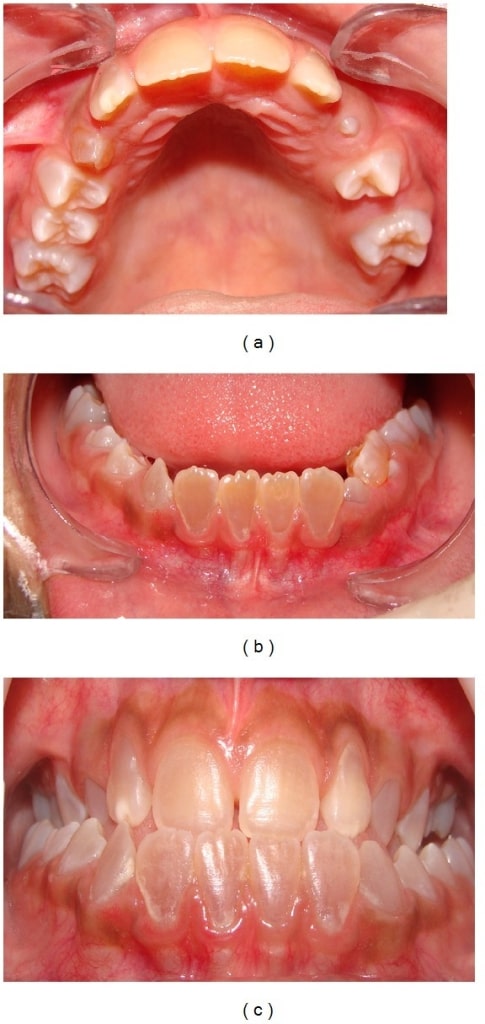
Dentinogenesis imperfecta:
Anterior teeth show a brownish discoloration (upper dental arch (a), lower arch (b), and dental occlusion(c)).
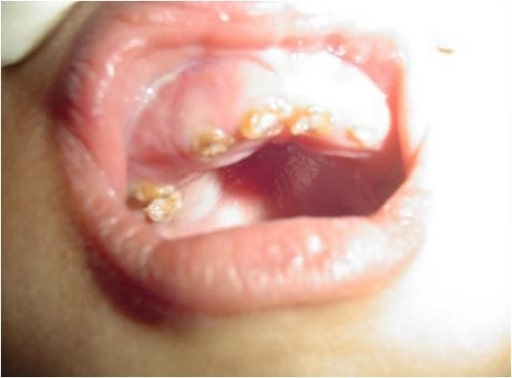
Intraoral photograph showing yellowish discoloration and chipping of the dentition: A 4-year-old male child with OI (type IV)
Image: “Chipping of the dentition” by the Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, AB Shetty Memorial Institute of Dental Sciences, Nitte University, Mangalore 575018, India. License: CC BY 3.0.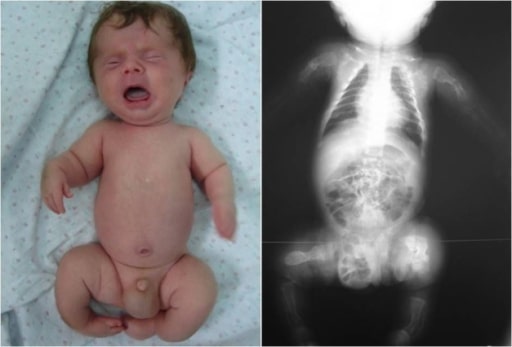
Infant with OI: Notice the deformity of the limbs, an indication of possible fractures during inspection.
Image: “Congenita A type of osteogenesis imperfecta” by the Maria Sklodowska Curie Clinical Emergency Hospital for Children, Bucharest, Romania. License: CC BY 2.0.| Type I | Type II | Type III | Type IV | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Skull Skull The skull (cranium) is the skeletal structure of the head supporting the face and forming a protective cavity for the brain. The skull consists of 22 bones divided into the viscerocranium (facial skeleton) and the neurocranium. Skull: Anatomy radiographic findings | Intra-sutural bones | Undermineralization; calcified areas | Intra-sutural bones | Intra-sutural bones (sometimes) |
| Spine Spine The human spine, or vertebral column, is the most important anatomical and functional axis of the human body. It consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and 5 lumbar vertebrae and is limited cranially by the skull and caudally by the sacrum. Vertebral Column: Anatomy radiographic findings | Biconcave vertebrae (adults) | Widened vertebral bodies (platyspondyly) | Biconcave vertebrae; kyphoscoliosis Kyphoscoliosis Osteomalacia and Rickets | Biconcave vertebrae |
| Extremity radiographic findings | Thin cortices | Severely deformed femurs | Flared metaphyses, bowing, thin cortices | Thin cortices |
| Other radiographic findings | Osteopenia Osteopenia Osteoporosis | Small, beaded ribs Ribs A set of twelve curved bones which connect to the vertebral column posteriorly, and terminate anteriorly as costal cartilage. Together, they form a protective cage around the internal thoracic organs. Chest Wall: Anatomy (pathognomonic) | Thin ribs Ribs A set of twelve curved bones which connect to the vertebral column posteriorly, and terminate anteriorly as costal cartilage. Together, they form a protective cage around the internal thoracic organs. Chest Wall: Anatomy, severe osteoporosis Osteoporosis Osteoporosis refers to a decrease in bone mass and density leading to an increased number of fractures. There are 2 forms of osteoporosis: primary, which is commonly postmenopausal or senile; and secondary, which is a manifestation of immobilization, underlying medical disorders, or long-term use of certain medications. Osteoporosis | Protrusio acetabuli Protrusio Acetabuli Marfan Syndrome in a subset |

Prenatal ultrasound diagnosing OI:
This prenatal ultrasound at 22 weeks’ gestation shows bowing of the femur (the crosshairs show the extremities of the femur).
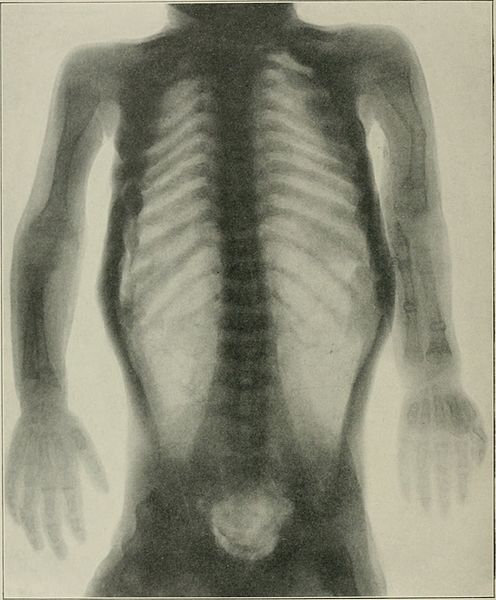
Radiograph showing OI:
periosteal dysplasia, almost complete absence of cortical bone, and numerous fractures
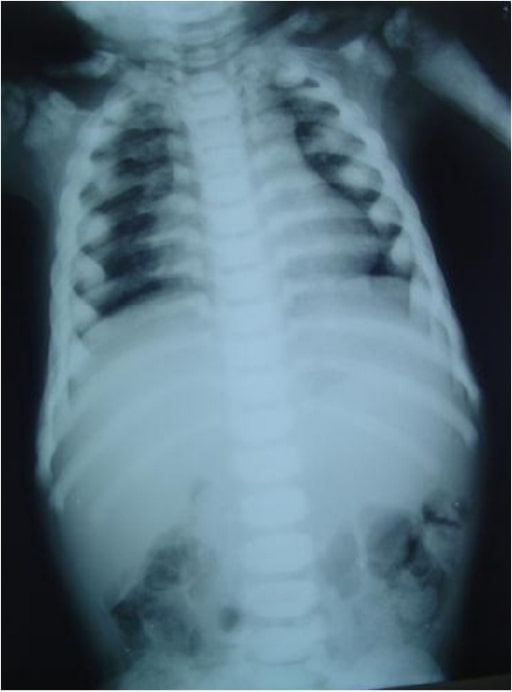
Chest radiograph showing long and narrow thorax (barrel-shaped chest) with anterior compression
Image: “Barrel-shaped chest” by the Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, AB Shetty Memorial Institute of Dental Sciences, Nitte University, Mangalore 575018, India. License: CC BY 3.0.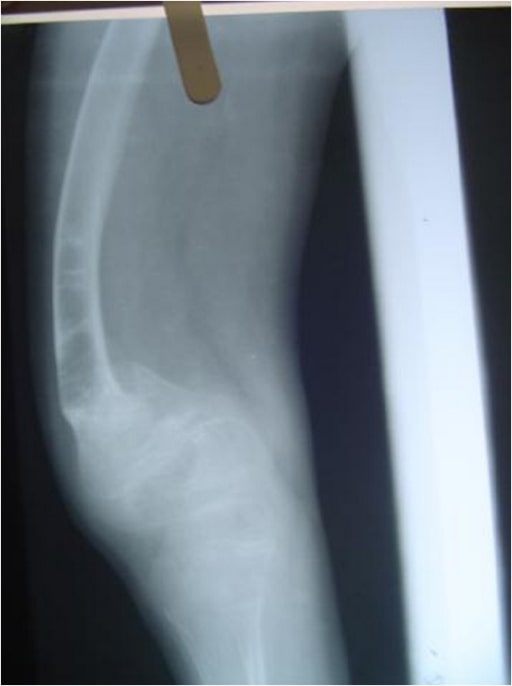
Radiograph of the lower limbs showing bowing of the femur, with widening of the metaphases:
a 4-year-old boy with OI (type IV)
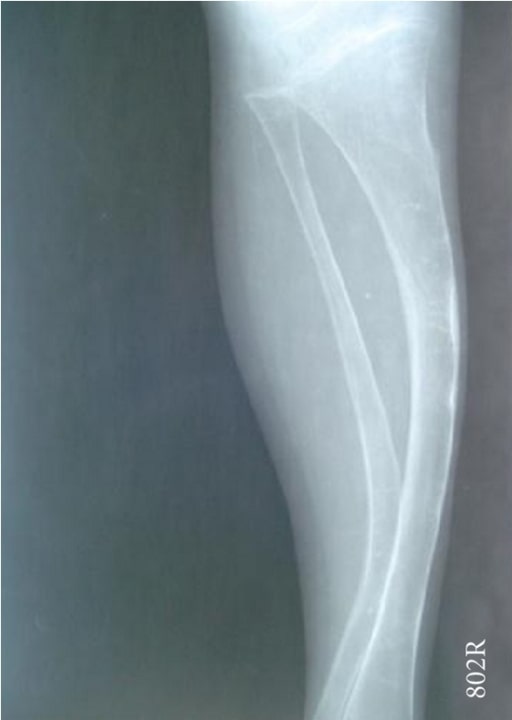
Radiograph showing a bowing tibia and fibula (saber shins):
a 4-year-old boy with OI (type IV)
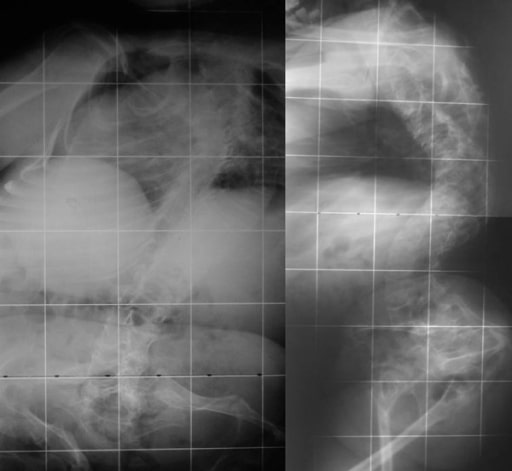
Biconcave deformities in the lower thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in a 15-year-old patient with OI (“codfish” vertebrae)
Image: “Osteogenesis imperfecta” by the 1st Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, School of Medicine, University of Athens, “Attikon” Hospital, Rimini 1 Haidari 12462, Athens, Greece. License: CC BY 2.0.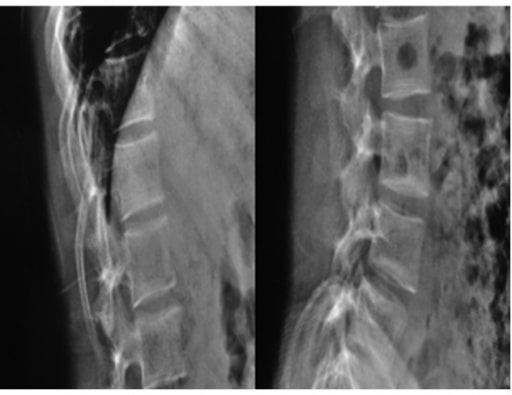
Radiographs of a 19-year-old woman with OI: Fragile bones, short trunk, severe kyphoscoliosis, and platyspondyly are noticed.
Image: “Biconcavity deformities” by the Department of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases, Qilu Hospital, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong 250012, P.R. China. License: CC BY 3.0.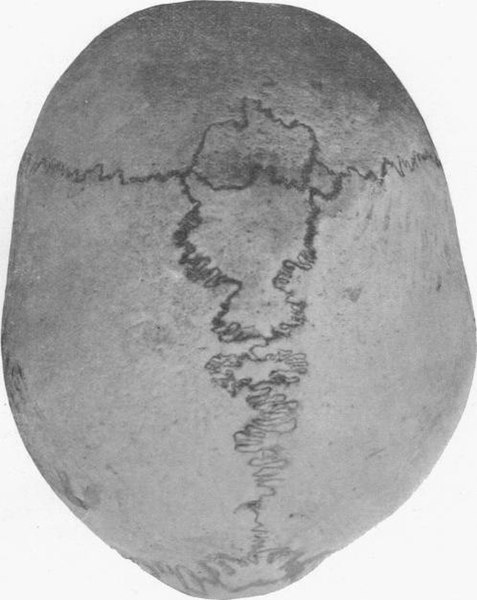
Human skull with wormian bones in a 21-year-old man
Image: “Wormian bones” by E. Barclay-Smith. License: Public domain.There is no definitive cure for OI.