Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, and is due to cartilage Cartilage Cartilage is a type of connective tissue derived from embryonic mesenchyme that is responsible for structural support, resilience, and the smoothness of physical actions. Perichondrium (connective tissue membrane surrounding cartilage) compensates for the absence of vasculature in cartilage by providing nutrition and support. Cartilage: Histology destruction and changes of the subchondral bone Subchondral Bone Osteochondritis Dissecans. The risk of developing this disorder increases with age, obesity Obesity Obesity is a condition associated with excess body weight, specifically with the deposition of excessive adipose tissue. Obesity is considered a global epidemic. Major influences come from the western diet and sedentary lifestyles, but the exact mechanisms likely include a mixture of genetic and environmental factors. Obesity, and repetitive joint use or trauma. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship develop gradual joint pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, stiffness lasting < 30 minutes, and decreased range of motion Range of motion The distance and direction to which a bone joint can be extended. Range of motion is a function of the condition of the joints, muscles, and connective tissues involved. Joint flexibility can be improved through appropriate muscle strength exercises. Examination of the Upper Limbs. Physical exam may reveal crepitus with joint motion and osteophyte formation (Heberden and Bouchard nodes). The diagnosis is clinical and supported with radiographic joint findings. Management includes conservative measures, analgesic medications, glucocorticoid intra-articular injections, and surgery for advanced disease.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
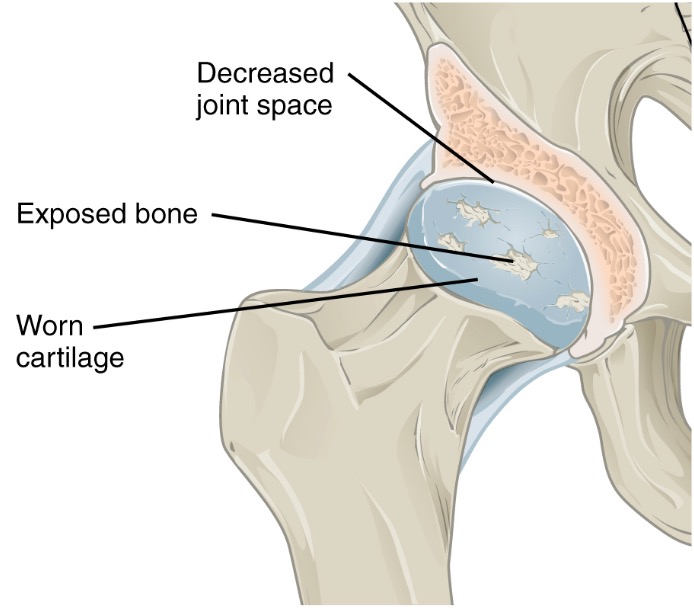
Pathology of osteoarthritis
Destruction of cartilage leads to decreased joint space. With severe destruction, bone becomes denuded.
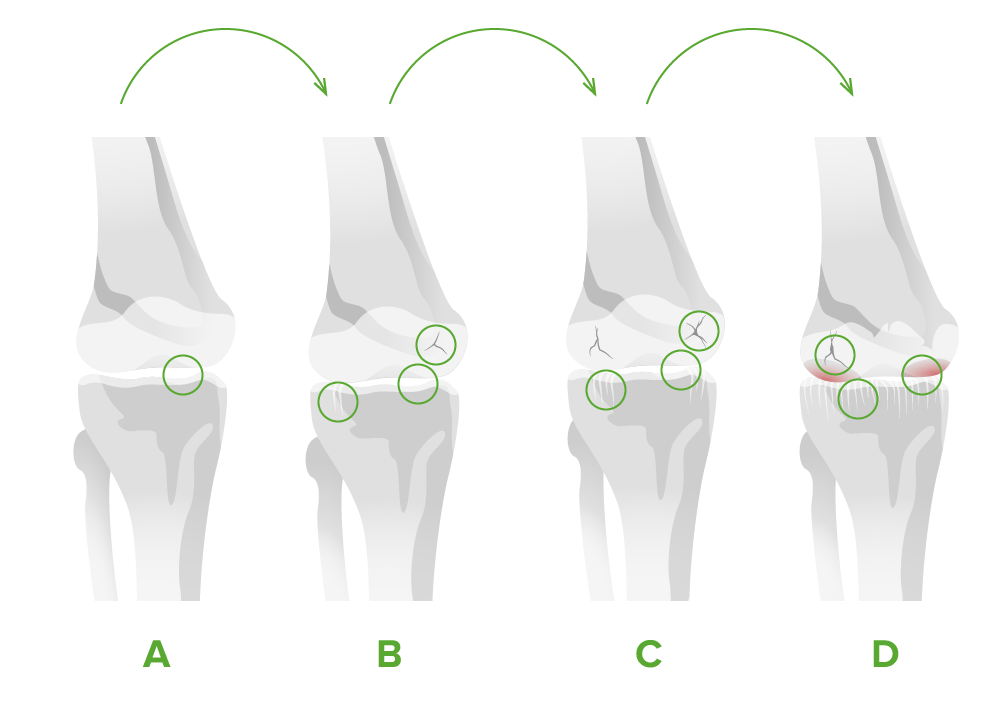
Stages of osteoarthritis of the knee joint:
A. There is minimal disruption and approximately 10% cartilage loss.
B. Narrowing of the joint space is seen, cartilage begins to break down, and osteophytes develop.
C. There is moderate reduction of the joint space. Gaps in the cartilage can expand until the bone is reached.
D. The joint space is greatly reduced and approximately 60% of the cartilage is lost. Large osteophytes are seen.
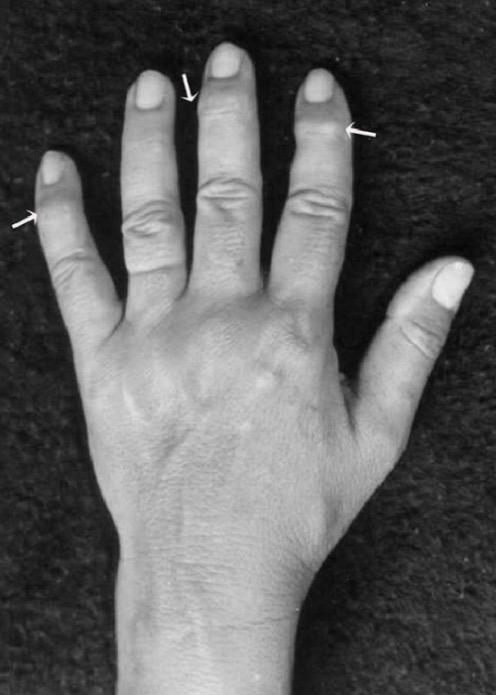
Heberden’s nodes in osteoarthritis: bony growth spurs at the DIP joints due to osteophytes
Image: “Bony growth spurts” by School of Dentistry, Franciscan University Center, Andradas Street, 1614, 97010-032 Santa Maria, RS, Brazil. License: CC BY 3.0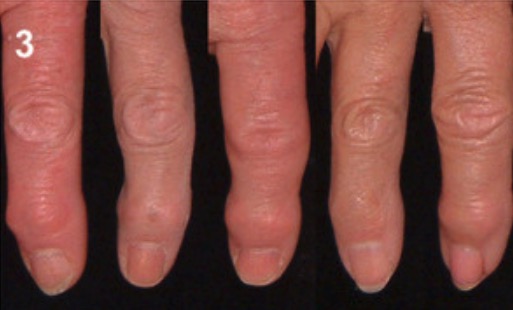
Bouchard’s nodes in osteoarthritis: osteophytes of the PIP joints
Image: “Grading of osteoarthritis” by Landspitalinn University Hospital, University of Iceland, IS-108 Fossvogur, Reykjavik, ICELAND. License: CC BY 2.0, edited by Lecturio.Osteoarthritis is a clinical diagnosis that is confirmed with imaging.
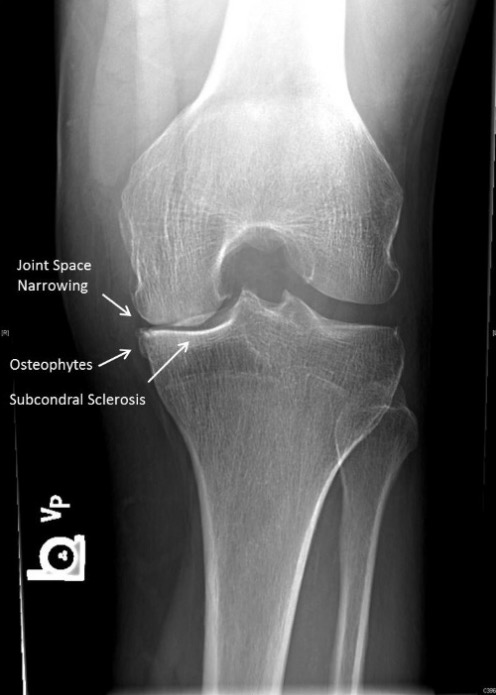
Radiographic features of osteoarthritis: This image shows joint space narrowing, osteophytes, and subchondral sclerosis (arrows).
Image: “Examples of JSN” by Center for Hip and Knee Replacement (CHKR), Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, NewYork-Presbyterian Hospital, Columbia University Medical Center, 622 W. 168th Street, PH 1155, New York, NY 10032, USA. License: CC BY 4.0
Radiographic features of osteoarthritis: Close-up imaging shows a subchondral cyst on distal clavicle. This signals osteoarthritis of the acromioclavicular joint.
Image: “Case presentation” by Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Japanese Red Cross Sendai Hospital, Yagiyama Honcyo, Taihaku-Ku, Sendai, Miyagi, Japan. License: CC BY 2.5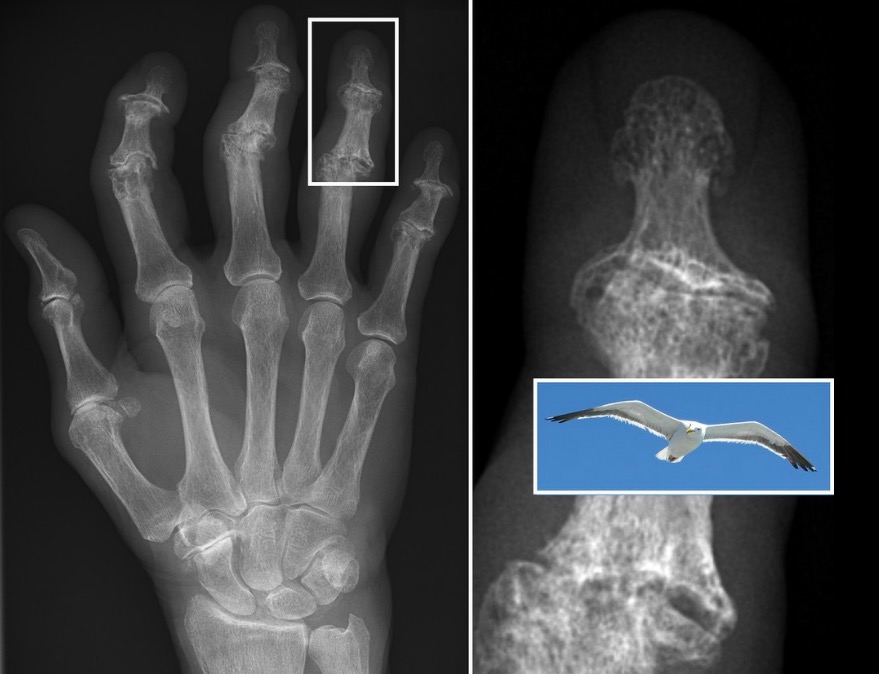
Radiographic features of erosive osteoarthritis: Central subchondral erosions give the DIP joint a “seagull wing” appearance.
Image: “X-ray of erosive osteoarthritis of the fingers” by Rennett Stowe and Mikael Häggström . License: CC BY 4.0The following tests are not used for the diagnosis of OA, but are used to exclude other causes of arthritis.
The goals of management include alleviating pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways and minimizing the loss of physical function.
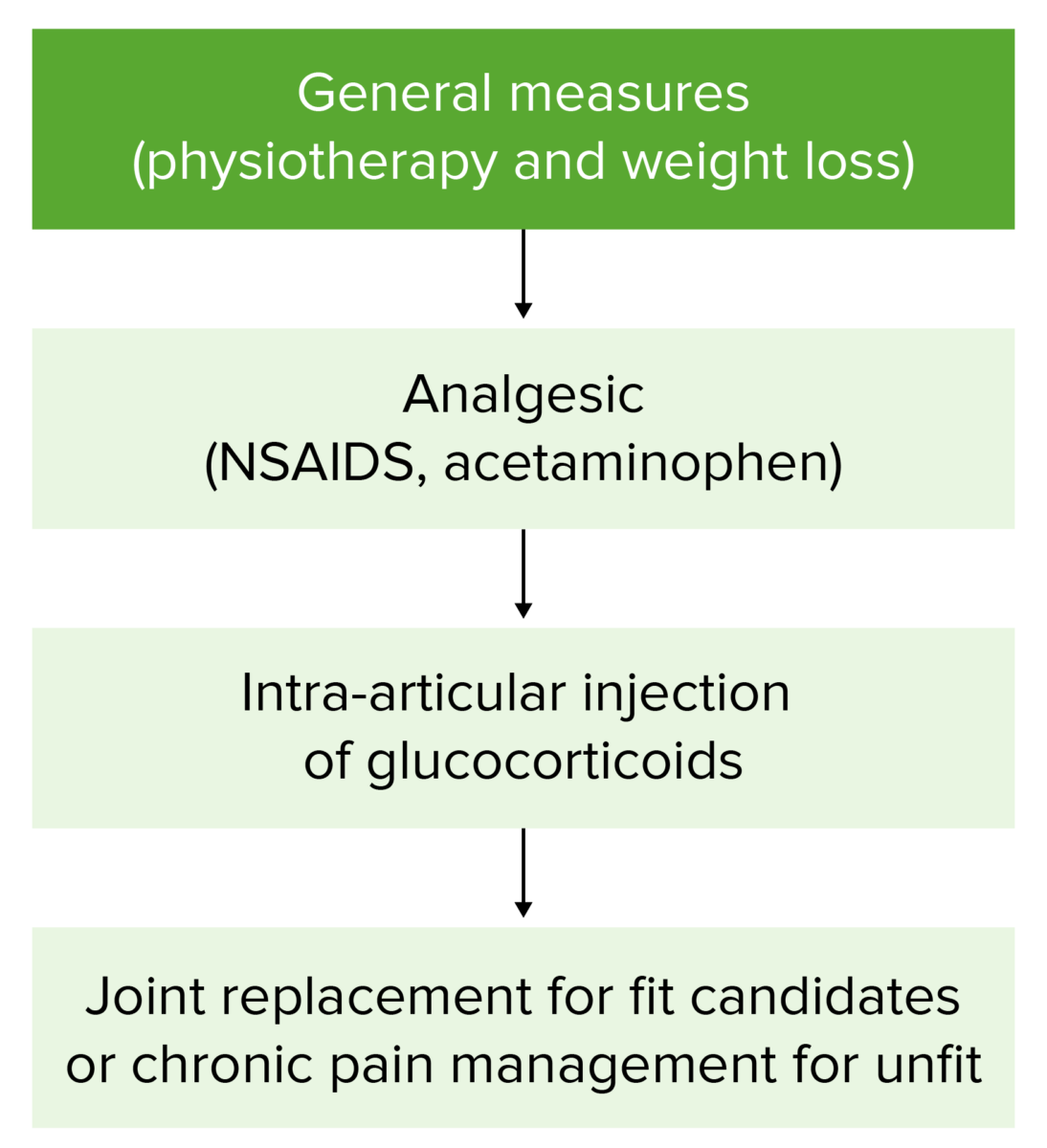
Osteoarthritis management flowchart
Patients start with conservative measures (weight loss and physical therapy). If symptoms do not improve, or if they worsen, management progresses through this flowchart. Surgery is reserved for patients with severe, unrelenting disease.