Osmotic diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication increase tubular fluid osmolarity Osmolarity The concentration of osmotically active particles in solution expressed in terms of osmoles of solute per liter of solution. Osmolality is expressed in terms of osmoles of solute per kilogram of solvent. Hypernatremia, pulling water into the collecting tubules Collecting tubules Straight tubes commencing in the radiate part of the kidney cortex where they receive the curved ends of the distal convoluted tubules. In the medulla the collecting tubules of each pyramid converge to join a central tube (duct of Bellini) which opens on the summit of the papilla. Kidneys: Anatomy and preventing water reabsorption, which results in osmotic diuresis Osmotic diuresis Volume Depletion and Dehydration. The primary osmotic diuretic used clinically is mannitol. The primary indication for mannitol is to treat cases of increased intracranial or intraocular pressure Intraocular Pressure The pressure of the fluids in the eye. Ophthalmic Exam, which can have significant effects on fluid volume and sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals. It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Hyponatremia concentration, so caution must be exercised when using these agents.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
An osmotic diuretic is an osmotically active agent that is filtered into the renal tubules but not reabsorbed. The presence of this substance in the renal tubules keeps water in the tubules, resulting in diuresis.
Mannitol is a nonabsorbable 6-carbon simple sugar alcohol.
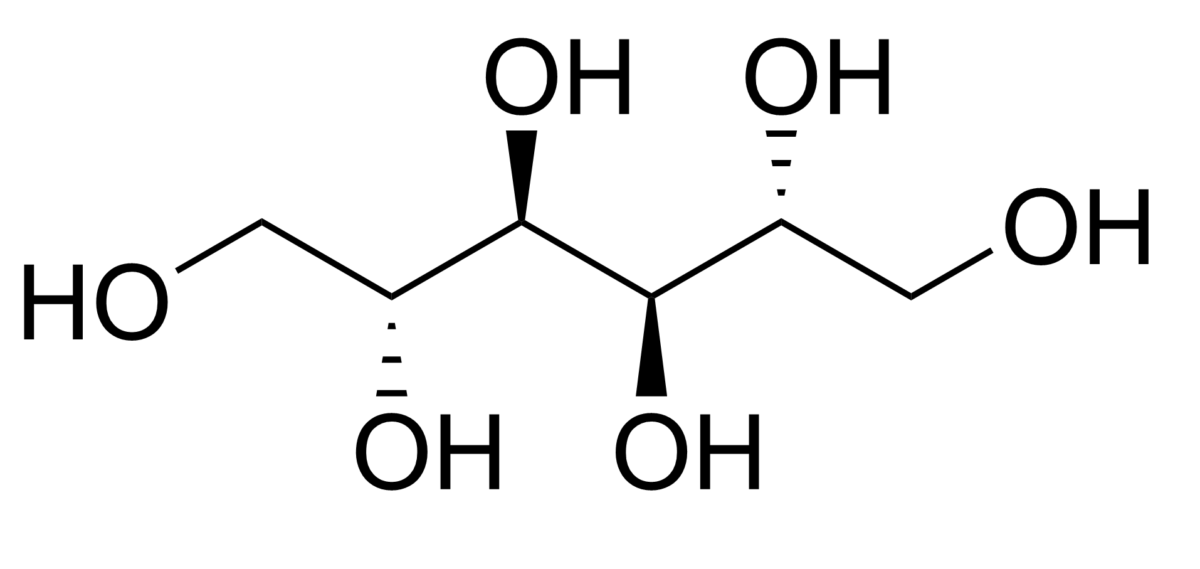
Chemical structure of mannitol
Image: “Chemical Structure of Mannitol” by Edgar181. License: Public Domain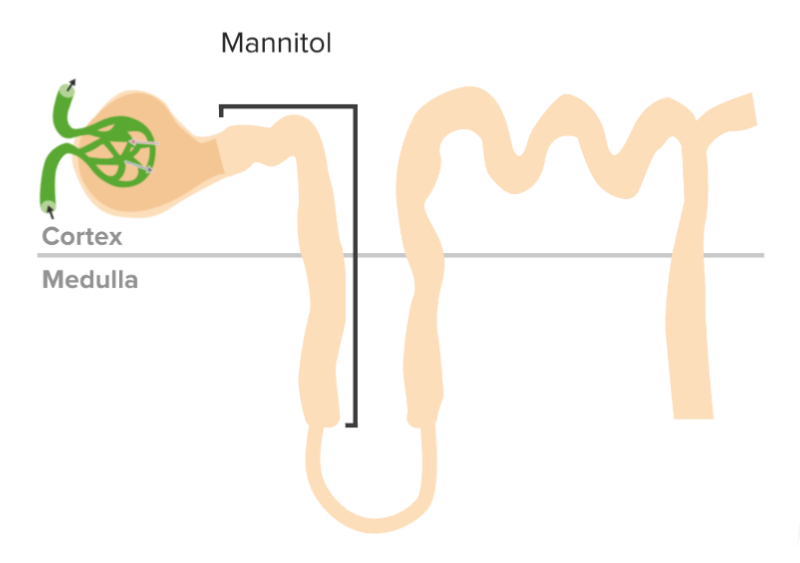
Mechanism of action of osmotic diuretics
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0The primary indications for the use of mannitol include:
Some of the other most common diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication include thiazide Thiazide Heterocyclic compounds with sulfur and nitrogen in the ring. This term commonly refers to the benzothiadiazines that inhibit sodium-potassium-chloride symporters and are used as diuretics. Hyponatremia diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication (e.g., hydrochlorothiazide Hydrochlorothiazide A thiazide diuretic often considered the prototypical member of this class. It reduces the reabsorption of electrolytes from the renal tubules. This results in increased excretion of water and electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, chloride, and magnesium. It is used in the treatment of several disorders including edema, hypertension, diabetes insipidus, and hypoparathyroidism. Thiazide Diuretics), loop diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication (e.g., furosemide Furosemide A benzoic-sulfonamide-furan. It is a diuretic with fast onset and short duration that is used for edema and chronic renal insufficiency. Loop Diuretics), potassium-sparing diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication (e.g., spironolactone Spironolactone A potassium sparing diuretic that acts by antagonism of aldosterone in the distal renal tubules. It is used mainly in the treatment of refractory edema in patients with congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, or hepatic cirrhosis. Its effects on the endocrine system are utilized in the treatments of hirsutism and acne but they can lead to adverse effects. Potassium-sparing Diuretics), and carbonic anhydrase Carbonic anhydrase A family of zinc-containing enzymes that catalyze the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. They play an important role in the transport of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lung. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors inhibitors (e.g., acetazolamide Acetazolamide One of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitors that is sometimes effective against absence seizures. It is sometimes useful also as an adjunct in the treatment of tonic-clonic, myoclonic, and atonic seizures, particularly in women whose seizures occur or are exacerbated at specific times in the menstrual cycle. However, its usefulness is transient often because of rapid development of tolerance. Its antiepileptic effect may be due to its inhibitory effect on brain carbonic anhydrase, which leads to an increased transneuronal chloride gradient, increased chloride current, and increased inhibition. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors).
| Medication | Mechanism | Physiologic effect | Indication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thiazide Thiazide Heterocyclic compounds with sulfur and nitrogen in the ring. This term commonly refers to the benzothiadiazines that inhibit sodium-potassium-chloride symporters and are used as diuretics. Hyponatremia diuretic: Hydrochlorothiazide Hydrochlorothiazide A thiazide diuretic often considered the prototypical member of this class. It reduces the reabsorption of electrolytes from the renal tubules. This results in increased excretion of water and electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, chloride, and magnesium. It is used in the treatment of several disorders including edema, hypertension, diabetes insipidus, and hypoparathyroidism. Thiazide Diuretics | ↓ Reabsorption of NaCl in the DCT through the inhibition of Na+/Cl– cotransporter |
|
|
| Loop diuretic: Furosemide Furosemide A benzoic-sulfonamide-furan. It is a diuretic with fast onset and short duration that is used for edema and chronic renal insufficiency. Loop Diuretics | Inhibits the luminal Na+/K+/Cl– cotransporter in the thick ascending limb Thick ascending limb Renal Sodium and Water Regulation of the loop of Henle Loop of Henle The U-shaped portion of the renal tubule in the kidney medulla, consisting of a descending limb and an ascending limb. It is situated between the proximal kidney tubule and the distal kidney tubule. Tubular System |
|
|
| Potassium-sparing diuretic: Spironolactone Spironolactone A potassium sparing diuretic that acts by antagonism of aldosterone in the distal renal tubules. It is used mainly in the treatment of refractory edema in patients with congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, or hepatic cirrhosis. Its effects on the endocrine system are utilized in the treatments of hirsutism and acne but they can lead to adverse effects. Potassium-sparing Diuretics |
|
|
|
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor Glaucoma: Acetazolamide Acetazolamide One of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitors that is sometimes effective against absence seizures. It is sometimes useful also as an adjunct in the treatment of tonic-clonic, myoclonic, and atonic seizures, particularly in women whose seizures occur or are exacerbated at specific times in the menstrual cycle. However, its usefulness is transient often because of rapid development of tolerance. Its antiepileptic effect may be due to its inhibitory effect on brain carbonic anhydrase, which leads to an increased transneuronal chloride gradient, increased chloride current, and increased inhibition. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors | Inhibits both the hydration of CO2 in the PCT epithelial cells and the dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration of H2CO3 in the PCT lumen; results in ↑ HCO3– and Na+ excretion |
|
|
| Osmotic diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication: Mannitol | ↑ Osmotic pressure Osmotic pressure The pressure required to prevent the passage of solvent through a semipermeable membrane that separates a pure solvent from a solution of the solvent and solute or that separates different concentrations of a solution. It is proportional to the osmolality of the solution. Intravenous Fluids in the glomerular filtrate → ↑ tubular fluid and prevents water reabsorption |
|
|
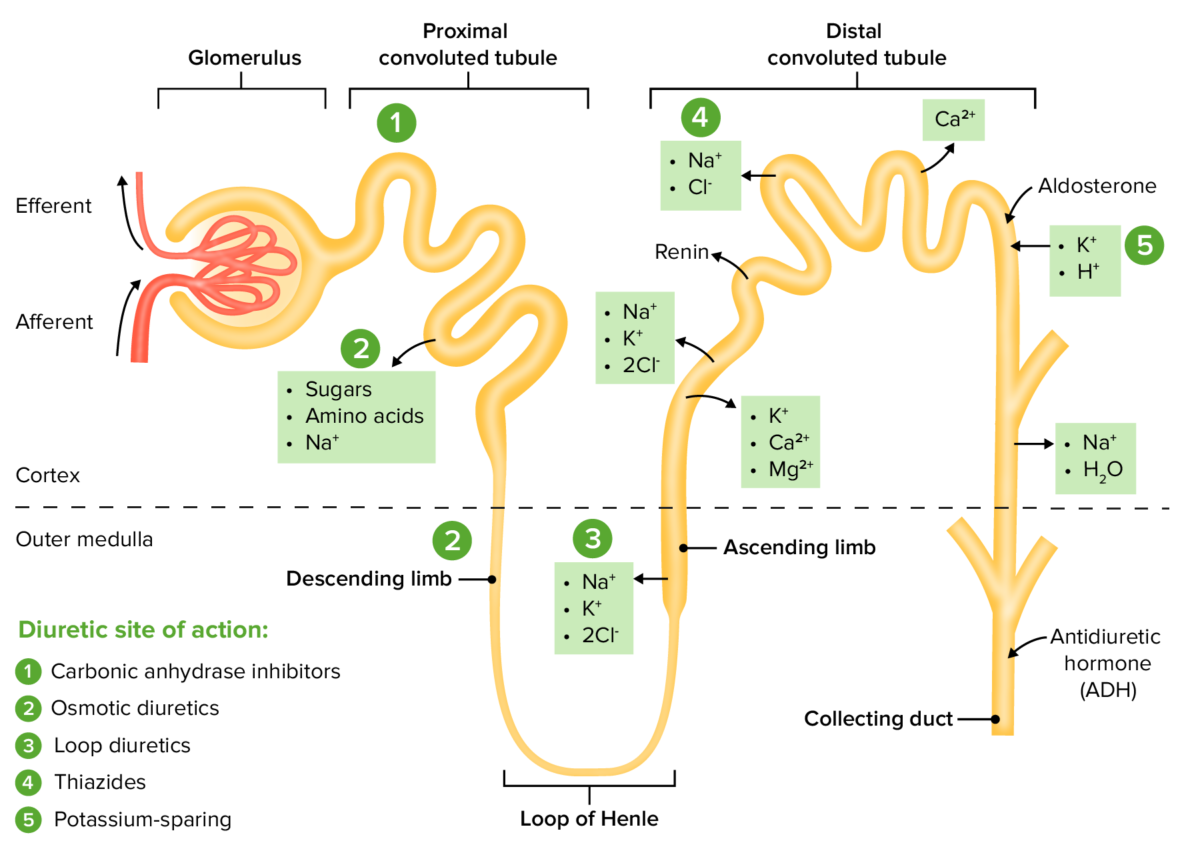
The sites of action within the nephron for the diuretic drug classes
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0