Osgood-Schlatter disease, or apophysitis of the tibial tubercle, is a common orthopedic condition seen in children between 10 and 15 years of age. The disease is caused by the repetitive application of mechanical forces on the knee, leading to microtrauma on the ossification Ossification The process of bone formation. Histogenesis of bone including ossification. Bones: Development and Ossification center at the site of insertion of the distal patellar ligament. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship present with localized knee pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, tenderness, and swelling Swelling Inflammation at the proximal anterior tibia Tibia The second longest bone of the skeleton. It is located on the medial side of the lower leg, articulating with the fibula laterally, the talus distally, and the femur proximally. Knee Joint: Anatomy. Diagnosis is clinical and treatment is focused on symptomatic relief. Osgood-Schlatter disease is a self-limiting Self-Limiting Meningitis in Children condition that resolves with skeletal maturity.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Osgood-Schlatter disease is an apophysitis, a painful traction injury, of the cartilage Cartilage Cartilage is a type of connective tissue derived from embryonic mesenchyme that is responsible for structural support, resilience, and the smoothness of physical actions. Perichondrium (connective tissue membrane surrounding cartilage) compensates for the absence of vasculature in cartilage by providing nutrition and support. Cartilage: Histology and bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types on the anterior, proximal tibial tubercle, where the distal patella Patella The flat, triangular bone situated at the anterior part of the knee. Knee Joint: Anatomy tendon inserts.
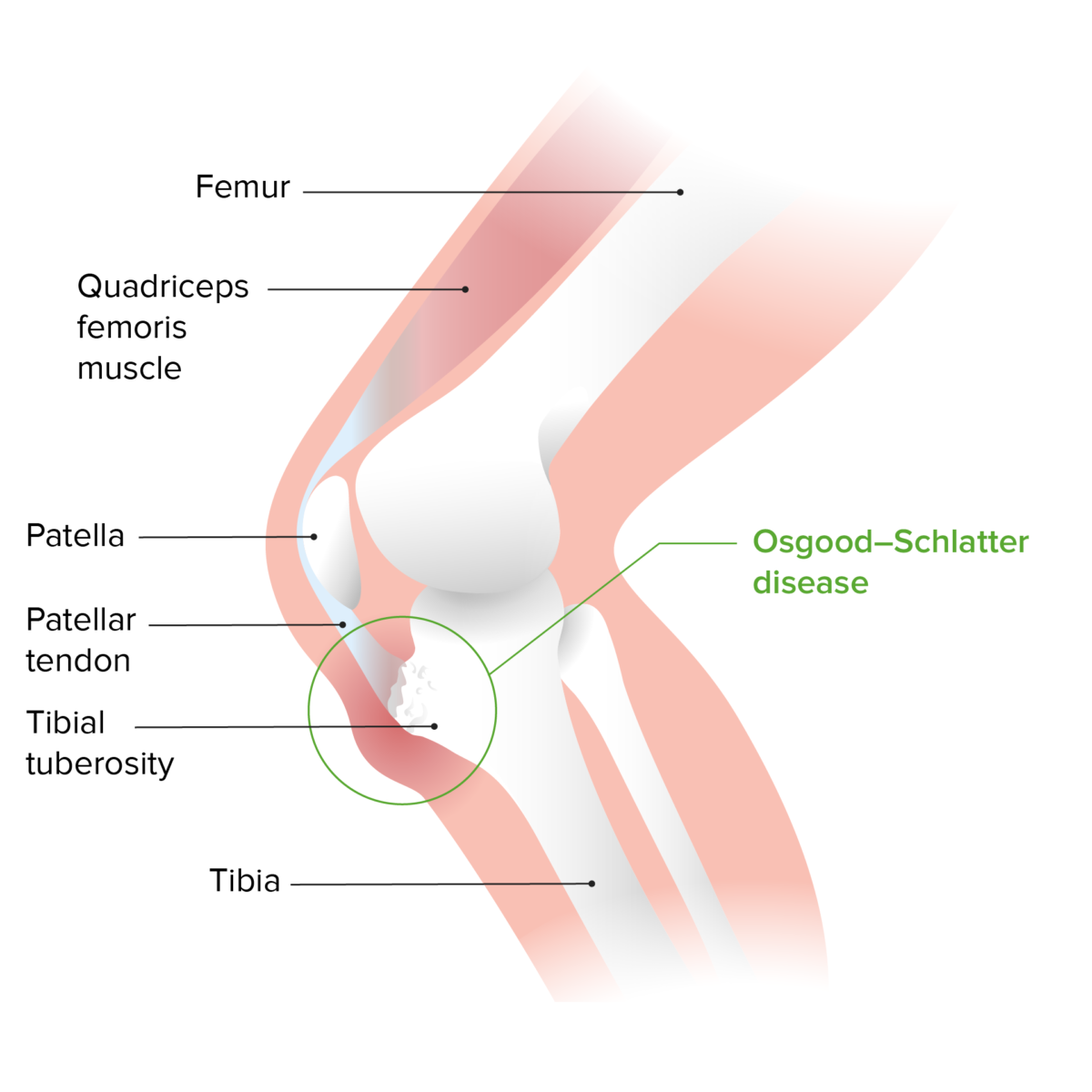
Osgood-Schlatter disease: a painful inflammation of the tibial tuberosity caused by repetitive traction by the patellar tendon due to repetitive exertion, such as running or jumping
Image by Lecturio.Osgood-Schlatter disease occurs due to overuse injury.
Osgood-Schlatter disease typically presents during early adolescence with the chief complaint of knee pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways.
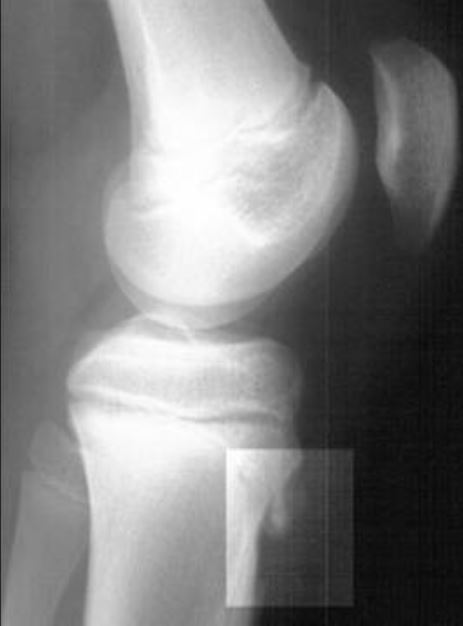
Osgood-Schlatter disease: lateral radiograph of the knee demonstrating fragmentation of the tibial tubercle with overlying soft tissue swelling
Image: “Review for the generalist: evaluation of anterior knee pain” by Houghton KM. License: CC BY 2.0Most cases are treated successfully with relative rest and symptom management.
The majority of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are asymptomatic after cessation of growth. Uncommon sequelae include: