Oligodendrogliomas are malignant CNS tumors arising from neural glial cell precursors. Oligodendrogliomas often arise in the frontal Frontal The bone that forms the frontal aspect of the skull. Its flat part forms the forehead, articulating inferiorly with the nasal bone and the cheek bone on each side of the face. Skull: Anatomy lobes of the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification and have a generally favorable prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas when compared to other gliomas. Oligodendrogliomas are the 3rd most common CNS tumor Tumor Inflammation. The most frequent presenting symptom is a seizure; other symptoms include headaches, visual loss, and focal neurologic deficits Neurologic Deficits High-Risk Headaches. Diagnosis is established by brain biopsy Brain biopsy JC Virus and BK Virus that demonstrates a classic “fried egg” appearance (round nuclei with clear cytoplasm). Oligodendrogliomas are slow-growing, but because they are life-limiting, they are managed with a combination of surgical resection, radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma, and chemotherapy Chemotherapy Osteosarcoma.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Oligodendrogliomas are malignant neuroepithelial tumors arising from neural glial cell precursors. These tumor Tumor Inflammation cells appear histologically similar to oligodendrocytes, but lack the myelinating ability of oligodendrocytes. Oligodendrogliomas are a type of glioma:
| Categories | Specific tumors |
|---|---|
| Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS |
|
| Meningeal tumors |
|
| Sellar region tumors |
|
| Primary CNS lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum | Primary CNS lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum |
| Metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis to the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification (5× more common than primary brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification tumors) | Most commonly arising from: |
| Peripheral tumors |
|
Oligodendrogliomas are histologically defined tumors that include both isocitrate dehydrogenase Isocitrate dehydrogenase An enzyme of the oxidoreductase class that catalyzes the conversion of isocitrate and NAD+ to yield 2-ketoglutarate, carbon dioxide, and nadh. It occurs in cell mitochondria. The enzyme requires mg2+, mn2+; it is activated by adp, citrate, and Ca2+, and inhibited by nadh, NADPH, and ATP. The reaction is the key rate-limiting step of the citric acid (tricarboxylic) cycle. Citric Acid Cycle (IDH) 1 and 2 mutations and codeletions of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q.
Oligodendrogliomas are classified by the WHO according to their histology and the types of mutations they harbor. (Grade I tumors are considered benign Benign Fibroadenoma, so, unlike astrocytomas, there are no grade I oligodendrogliomas.)
Most of the signs and symptoms depend on the exact location of the tumor Tumor Inflammation. Oligodendrogliomas are slow-growing and often asymptomatic for years prior to diagnosis. The most common presenting symptom is a seizure.
Head MRI is the imaging method of choice when evaluating for brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification tumors.
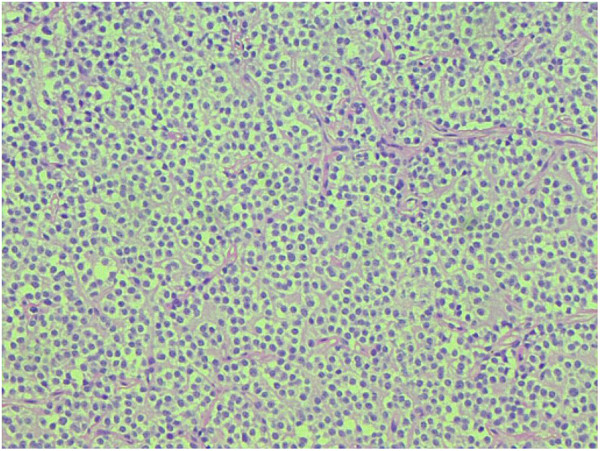
Oligodendroglioma:
Note the fried-egg cells with dark, round nuclei and chicken-wire capillaries throughout the tissue sample.
Oligodendrogliomas are infiltrative tumors that are commonly considered incurable owing to high risk of relapse Relapse Relapsing Fever/recurrence. Optimal management typically involves surgery, radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma, and chemotherapy Chemotherapy Osteosarcoma.