Geriatric care includes the prevention and diagnosis of diseases, as well as the management of diseases, disabilities, and other health concerns in individuals ≥ 65 years of age. Special consideration is given when addressing multiple aspects that are specific to aging. Preventive measures such as vaccinations as well as cancer and disease screening Screening Preoperative Care are essential in this age group because of the high risk for infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease and developing cancer and chronic diseases. A majority of older individuals have at least 1 chronic medical condition, which increases the likelihood of polypharmacy and adverse drug reactions. Vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam, hearing, cognitive function, gait Gait Manner or style of walking. Neurological Examination, and balance are among the functions that decline in the geriatric population. These disease- and age-related factors affect the activities of daily living. Assessing the financial and social resources of older adults is also important, given the direct impact of these factors on their health. A multidisciplinary approach involving various professionals in the healthcare field is important in achieving comprehensive care for older adults.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Care for older adults is a team-based approach that involves various professionals (e.g., physicians Physicians Individuals licensed to practice medicine. Clinician–Patient Relationship, social workers, nutritionists, physical therapists) working together to assess the following:
| Medications | Side effects |
|---|---|
| Antipsychotics |
|
| Glyburide | Long-acting sulfonylurea associated with a high risk of hypoglycemia Hypoglycemia Hypoglycemia is an emergency condition defined as a serum glucose level ≤ 70 mg/dL (≤ 3.9 mmol/L) in diabetic patients. In nondiabetic patients, there is no specific or defined limit for normal serum glucose levels, and hypoglycemia is defined mainly by its clinical features. Hypoglycemia |
| Benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines work on the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor to produce inhibitory effects on the CNS. Benzodiazepines do not mimic GABA, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in humans, but instead potentiate GABA activity. Benzodiazepines | Increased risk of delirium Delirium Delirium is a medical condition characterized by acute disturbances in attention and awareness. Symptoms may fluctuate during the course of a day and involve memory deficits and disorientation. Delirium, sedation, and falls |
| Opioids Opioids Opiates are drugs that are derived from the sap of the opium poppy. Opiates have been used since antiquity for the relief of acute severe pain. Opioids are synthetic opiates with properties that are substantially similar to those of opiates. Opioid Analgesics | Increased risk of delirium Delirium Delirium is a medical condition characterized by acute disturbances in attention and awareness. Symptoms may fluctuate during the course of a day and involve memory deficits and disorientation. Delirium, sedation, falls, constipation Constipation Constipation is common and may be due to a variety of causes. Constipation is generally defined as bowel movement frequency < 3 times per week. Patients who are constipated often strain to pass hard stools. The condition is classified as primary (also known as idiopathic or functional constipation) or secondary, and as acute or chronic. Constipation, urinary retention Urinary retention Inability to empty the urinary bladder with voiding (urination). Delirium, and respiratory depression |
| Anticholinergics Anticholinergics Anticholinergic drugs block the effect of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine at the muscarinic receptors in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Anticholinergic agents inhibit the parasympathetic nervous system, resulting in effects on the smooth muscle in the respiratory tract, vascular system, urinary tract, GI tract, and pupils of the eyes. Anticholinergic Drugs (includes some antidepressants and antihistamines Antihistamines Antihistamines are drugs that target histamine receptors, particularly H1 and H2 receptors. H1 antagonists are competitive and reversible inhibitors of H1 receptors. First-generation antihistamines cross the blood-brain barrier and can cause sedation. Antihistamines) | Increased risk of delirium Delirium Delirium is a medical condition characterized by acute disturbances in attention and awareness. Symptoms may fluctuate during the course of a day and involve memory deficits and disorientation. Delirium, sedation, falls, constipation Constipation Constipation is common and may be due to a variety of causes. Constipation is generally defined as bowel movement frequency < 3 times per week. Patients who are constipated often strain to pass hard stools. The condition is classified as primary (also known as idiopathic or functional constipation) or secondary, and as acute or chronic. Constipation, and urinary retention Urinary retention Inability to empty the urinary bladder with voiding (urination). Delirium |
| NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches |
|
| α-Blockers | Increased risk of hypotension Hypotension Hypotension is defined as low blood pressure, specifically < 90/60 mm Hg, and is most commonly a physiologic response. Hypotension may be mild, serious, or life threatening, depending on the cause. Hypotension |
| Proton pump Pump ACES and RUSH: Resuscitation Ultrasound Protocols inhibitors (PPIs) |
|
Screenings in the older population should consider risk factors beyond merely the individual’s age. The elderly individual and/or caregivers should be involved in decision-making about pursuing screening Screening Preoperative Care. Most screenings are generally not indicated if the life expectancy Life expectancy Based on known statistical data, the number of years which any person of a given age may reasonably expected to live. Population Pyramids is < 5 years.
Men between 65 and 75 years of age with a history of tobacco use should undergo abdominal ultrasound screening Screening Preoperative Care once.
Based on the US Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF):
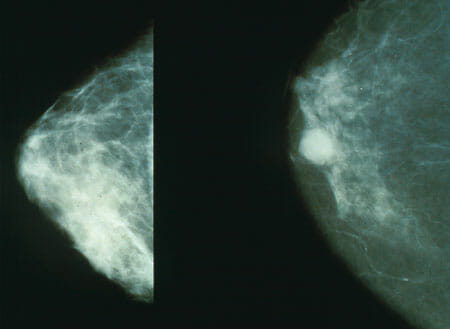
The 1st image shows mammography of normal breast tissue; the 2nd image shows cancerous breast tissue. Mammography is done for early detection of breast cancer.
Image: “Mammo breast cancer” by National Cancer Institute. License: Public Domain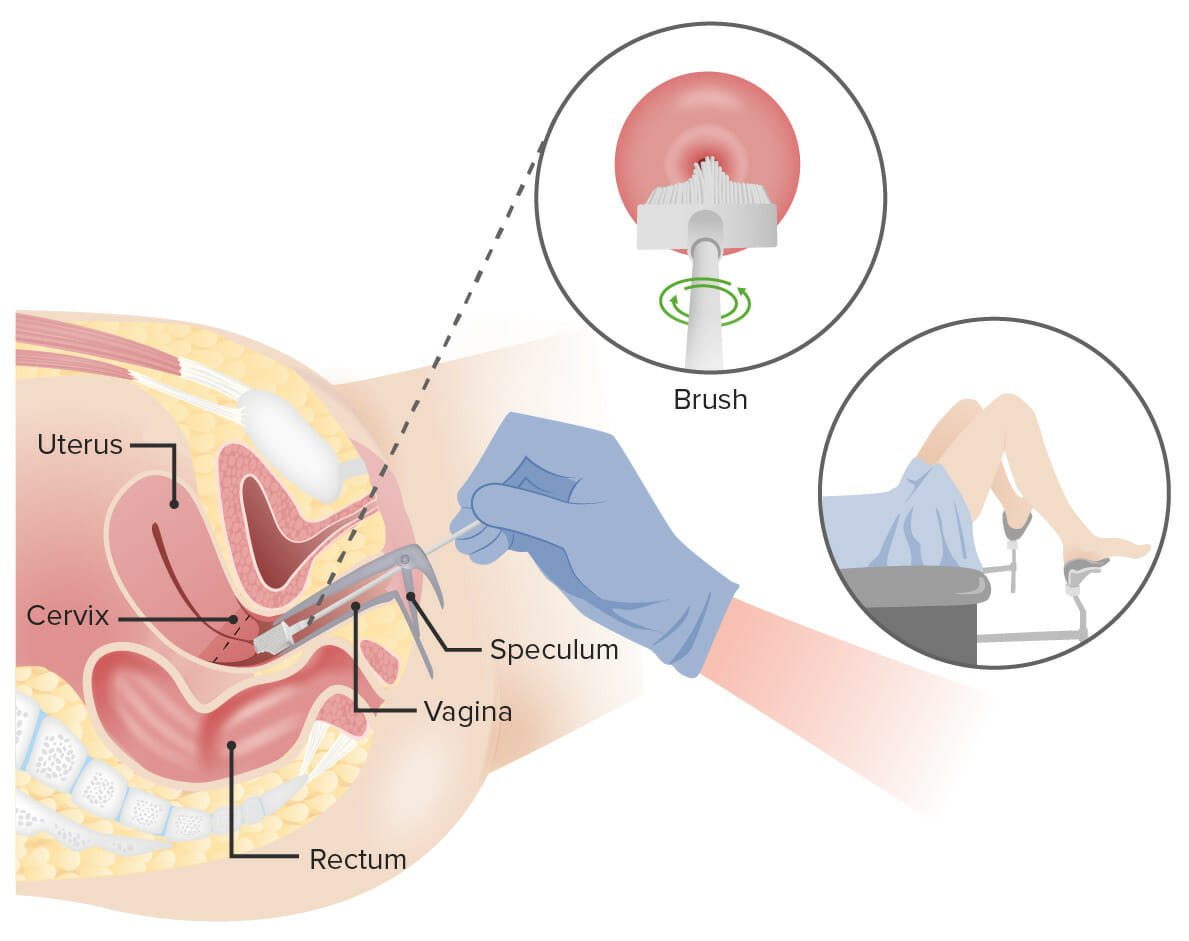
Pap test:
A speculum is inserted into the vagina to widen the area. Next, a brush is inserted into the vagina to collect cells from the cervix. The cells are checked under a microscope for signs of disease.
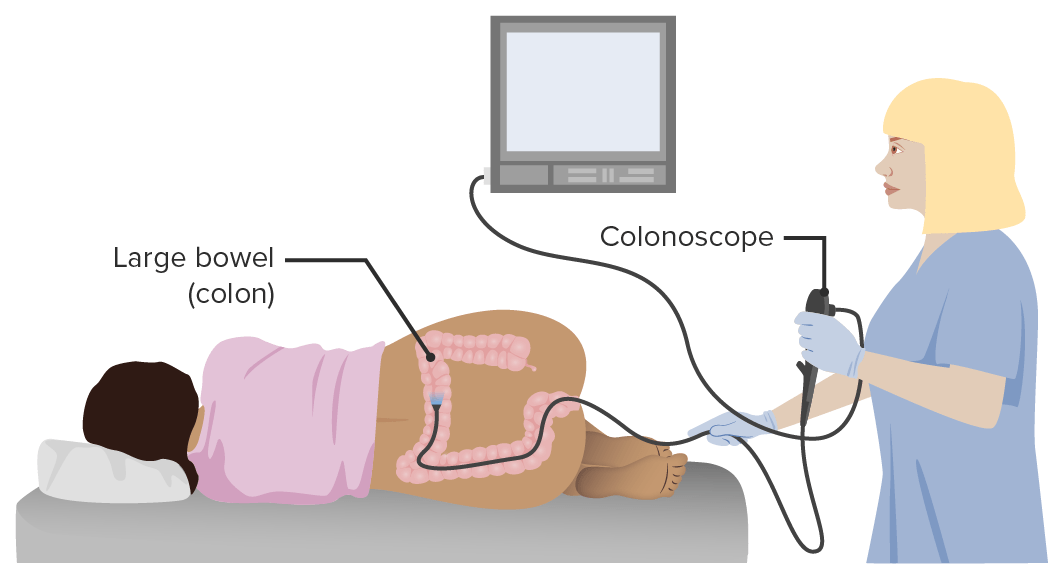
Representation of a colonoscopy
Image by Lecturio.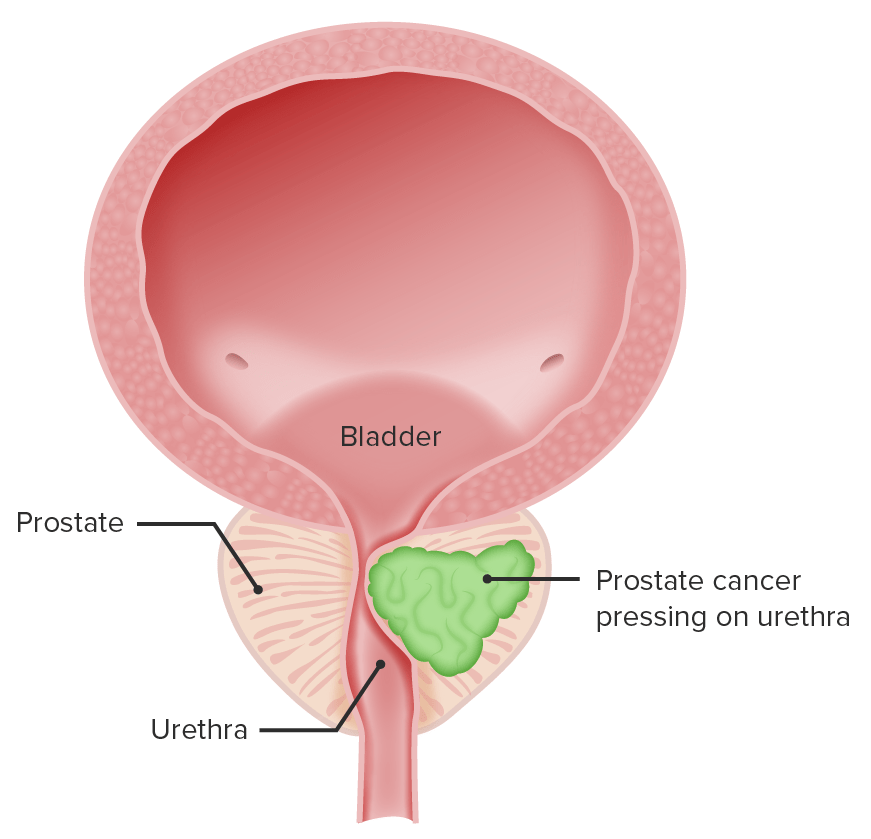
Depiction of prostate cancer pressing on the urethra (urinary symptoms result)
Image by Lecturio.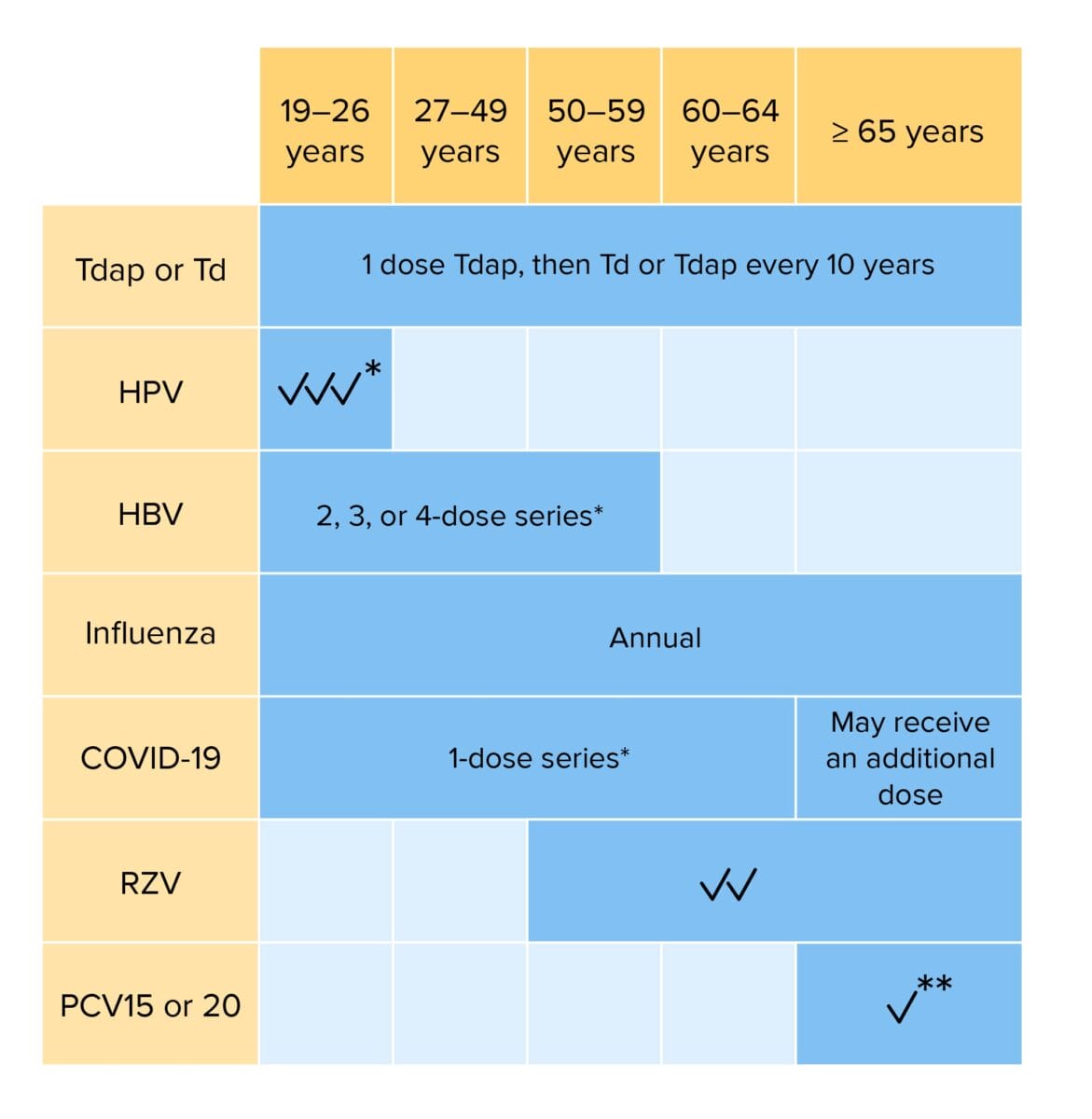
Routine vaccination for adults:
Individuals with risk factors may require additional vaccinations or alterations in dosing schedule.
Tdap: tetanus, diphtheria, and acellular pertussis vaccination
Td: tetanus and diphtheria vaccination
HPV: human papillomavirus vaccination
HBV: hepatitis B virus vaccination
COVID-19: coronavirus disease 2019 vaccination (bivalent)
RZV: recombinant zoster vaccination
PCV: pneumococcal conjugate vaccination
*If not previously vaccinated
**If PCV15 is given, should be followed PPSV23 (pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination)