Labor can be extremely painful, and adequate pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways management during labor and delivery is an important part of obstetric care. Appropriate therapy should be administered based on patient preference and medical need. Both pharmacological and non-pharmacological pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways control options are available. Maternal request alone is sufficient indication for pharmacologic pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways management. Options include systemic analgesics, including inhaled nitrous oxide Nitrous oxide Nitrogen oxide (N2O). A colorless, odorless gas that is used as an anesthetic and analgesic. High concentrations cause a narcotic effect and may replace oxygen, causing death by asphyxia. Inhaled Anesthetics and opioids Opioids Opiates are drugs that are derived from the sap of the opium poppy. Opiates have been used since antiquity for the relief of acute severe pain. Opioids are synthetic opiates with properties that are substantially similar to those of opiates. Opioid Analgesics, as well as local and regional techniques, including pudendal nerve Pudendal nerve A nerve which originates in the sacral spinal cord (s2 to s4) and innervates the perineum, the external genitalia, the external anal sphincter and the external urethral sphincter. It has three major branches: the perineal nerve, inferior anal nerves, and the dorsal nerve of penis or clitoris. Gluteal Region: Anatomy blocks, epidural, and spinal anesthesia Spinal anesthesia Procedure in which an anesthetic is injected directly into the spinal cord. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts. In truly emergent situations requiring urgent cesarean delivery Cesarean Delivery Cesarean delivery (CD) is the operative delivery of ≥ 1 infants through a surgical incision in the maternal abdomen and uterus. Cesarean deliveries may be indicated for a number of either maternal or fetal reasons, most commonly including fetal intolerance to labor, arrest of labor, a history of prior uterine surgery, fetal malpresentation, and placental abnormalities. Cesarean Delivery, general anesthesia General anesthesia Procedure in which patients are induced into an unconscious state through use of various medications so that they do not feel pain during surgery. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts can also be used.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Obstetric pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways management refers to the pharmacological and non-pharmacological options available to help manage discomfort during labor and delivery. Such options include spontaneous vaginal deliveries and cesarean deliveries.
According to the American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology (ACOG), “There is no other circumstance in which it is considered acceptable for an individual to experience untreated severe pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways that is amenable to safe intervention while the individual is under a physician’s care.”
The 1st stage of labor 1st stage of labor Period from the onset of true obstetric labor to the complete dilatation of the cervix uteri. Normal and Abnormal Labor begins with the onset of regular Regular Insulin uterine contractions causing cervical change and ends when the patient’s cervix Cervix The uterus, cervix, and fallopian tubes are part of the internal female reproductive system. The most inferior portion of the uterus is the cervix, which connects the uterine cavity to the vagina. Externally, the cervix is lined by stratified squamous cells; however, the cervical canal is lined by columnar epithelium. Uterus, Cervix, and Fallopian Tubes: Anatomy is fully dilated at 10 cm.
Pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways in the 1st stage of labor 1st stage of labor Period from the onset of true obstetric labor to the complete dilatation of the cervix uteri. Normal and Abnormal Labor is:
The 2nd stage of labor 2nd stage of labor The period of obstetric labor that is from the complete dilatation of the cervix uteri to the expulsion of the fetus. Normal and Abnormal Labor begins when the cervix Cervix The uterus, cervix, and fallopian tubes are part of the internal female reproductive system. The most inferior portion of the uterus is the cervix, which connects the uterine cavity to the vagina. Externally, the cervix is lined by stratified squamous cells; however, the cervical canal is lined by columnar epithelium. Uterus, Cervix, and Fallopian Tubes: Anatomy is fully dilated at 10 cm and ends with expulsion of the fetus.
Systemic analgesics can be used during labor but are not adequate for cesarean deliveries. They are commonly chosen by women for management of earlier labor, prior to getting an epidural.
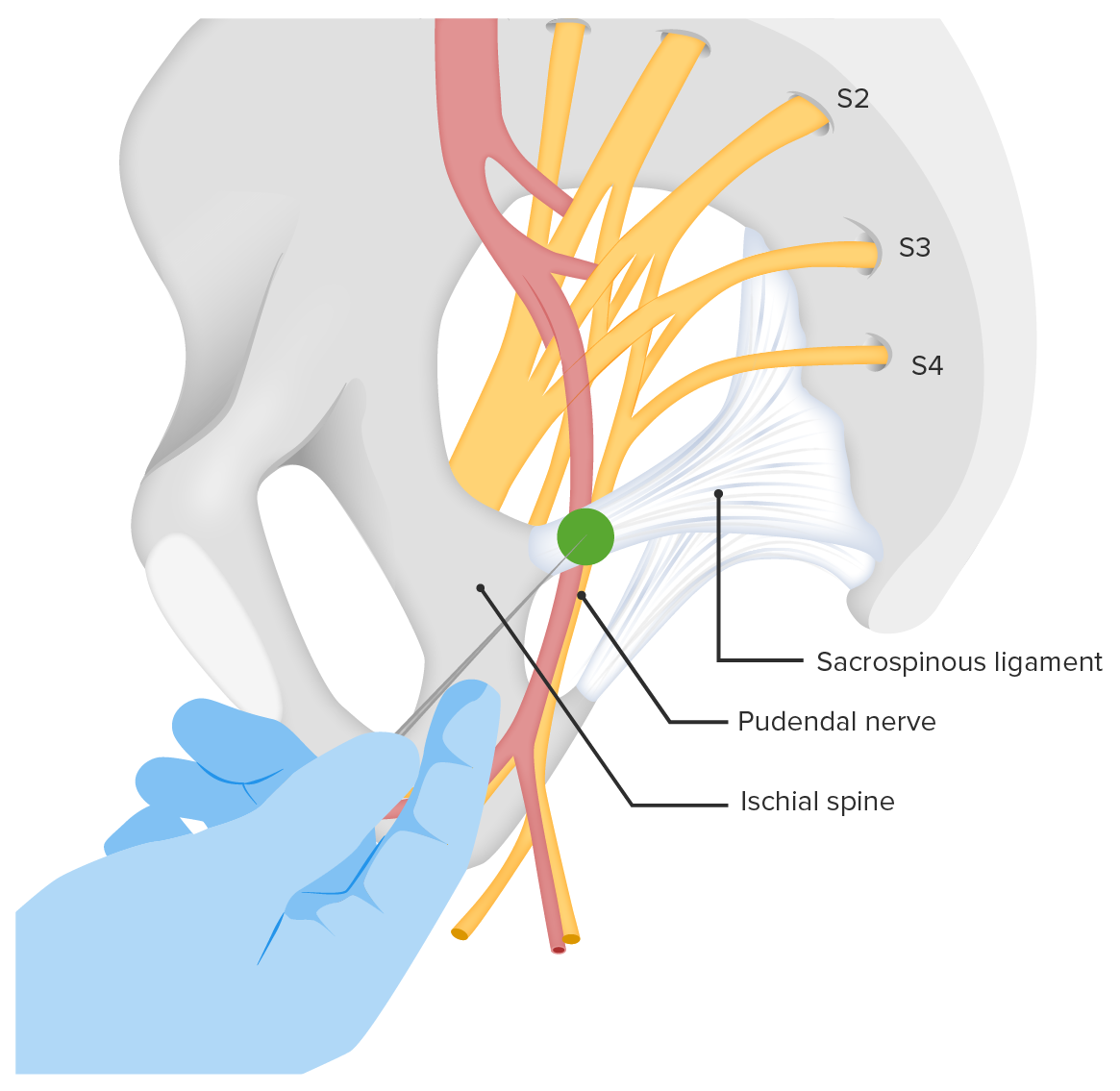
Site of injection for a pudendal nerve block
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0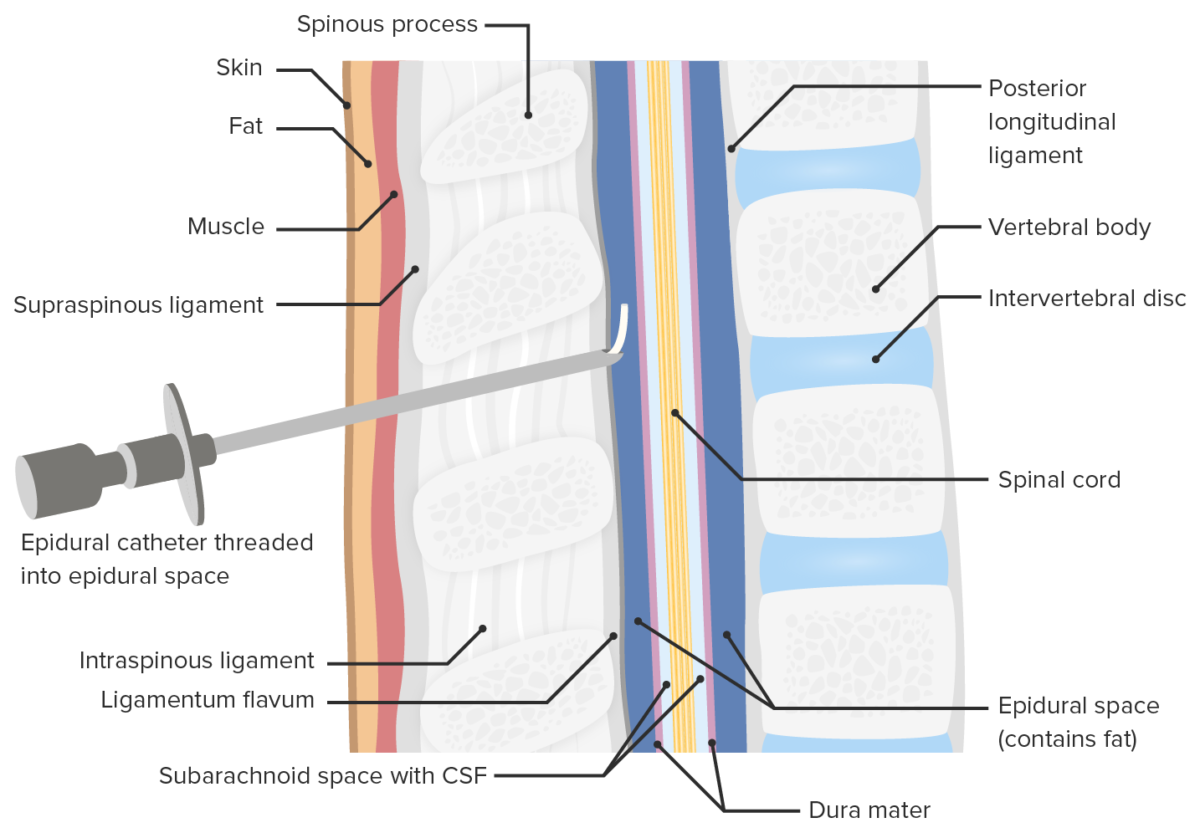
Location of epidural catheter placement
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0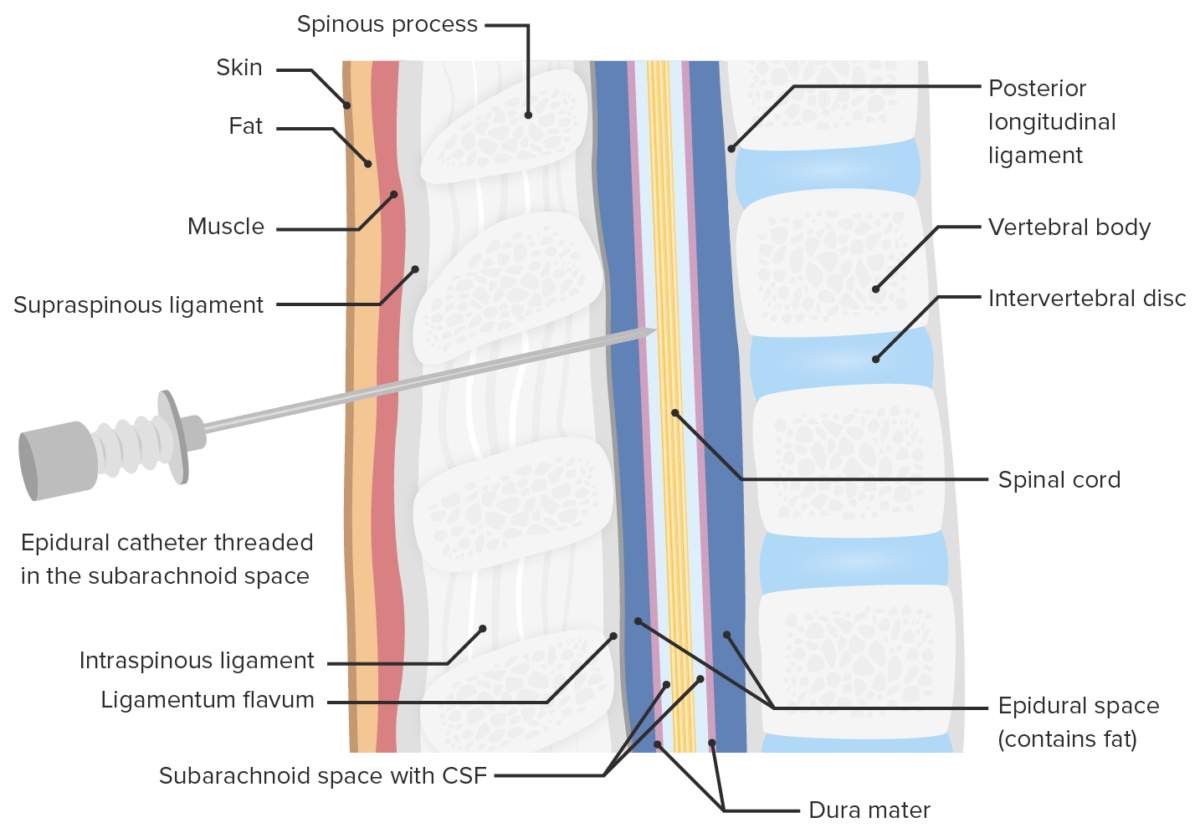
Location of opioid injection during spinal anesthesia
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Epidural anesthesia Epidural anesthesia Procedure in which an anesthetic is injected into the epidural space. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts | Spinal anesthesia Spinal anesthesia Procedure in which an anesthetic is injected directly into the spinal cord. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts | |
|---|---|---|
| Site of injection | Epidural space Epidural space Space between the dura mater and the walls of the vertebral canal. Epidural Hemorrhage | Subarachnoid space Subarachnoid space The space between the arachnoid membrane and pia mater, filled with cerebrospinal fluid. It contains large blood vessels that supply the brain and spinal cord. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage |
| Level of injection | T8 | T10 |
| Duration of pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways relief | Continuous while catheter remains in place | 2–4 hours |
| Side effects | Hypotension Hypotension Hypotension is defined as low blood pressure, specifically < 90/60 mm Hg, and is most commonly a physiologic response. Hypotension may be mild, serious, or life threatening, depending on the cause. Hypotension | Hypotension Hypotension Hypotension is defined as low blood pressure, specifically < 90/60 mm Hg, and is most commonly a physiologic response. Hypotension may be mild, serious, or life threatening, depending on the cause. Hypotension and bradycardia Bradycardia Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias |