Obesity is a condition associated with excess body weight, specifically with the deposition of excessive adipose tissue Adipose tissue Adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that has both structural and highly complex metabolic functions, including energy storage, glucose homeostasis, and a multitude of endocrine capabilities. There are three types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue, brown adipose tissue, and beige or "brite" adipose tissue, which is a transitional form. Adipose Tissue: Histology. Obesity is considered a global epidemic. Major influences come from the western diet and sedentary lifestyles, but the exact mechanisms likely include a mixture of genetic and environmental factors. Several conditions are associated with obesity, including diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus, hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, and heart disease, all of which contribute to significant healthcare costs. Diagnosis is most commonly based on BMI measurement, wherein obesity is defined as BMI > 30. Management includes lifestyle changes, medications, or, in severe cases, bariatric surgery Bariatric surgery Bariatric surgery refers to a group of invasive procedures used to surgically reduce the size of the stomach to produce early satiety, decrease food intake (restrictive type) and/or alter digestion, and artificially induce malabsorption of nutrients (malabsorptive type). The ultimate goal of bariatric surgery is drastic weight loss. Bariatric Surgery.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Obesity is a condition associated with excess body weight, specifically with excessive adipose tissue Adipose tissue Adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that has both structural and highly complex metabolic functions, including energy storage, glucose homeostasis, and a multitude of endocrine capabilities. There are three types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue, brown adipose tissue, and beige or “brite” adipose tissue, which is a transitional form. Adipose Tissue: Histology deposition.
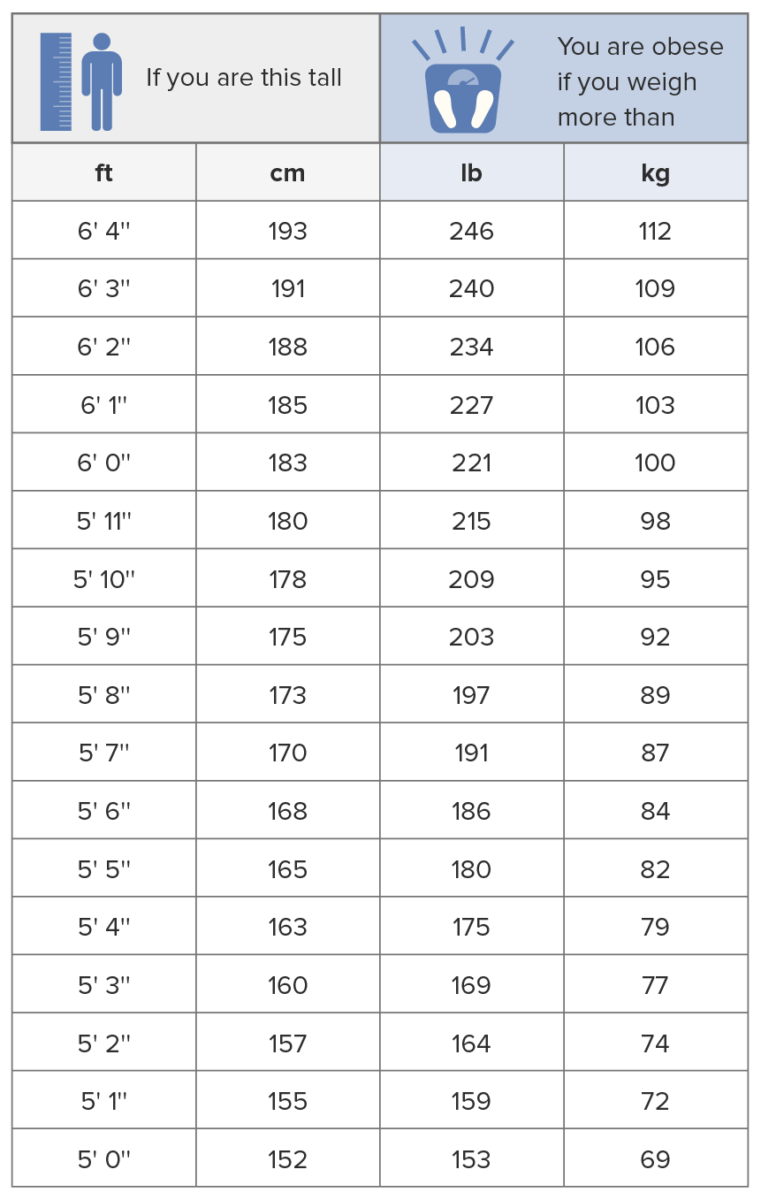
Body mass index chart
Image by Lecturio.The nature of obesity is believed to be multifactorial. Sedentary lifestyle and increased caloric intake appear to be the most common causes.
Causes can be further categorized by:
Medications associated with weight gain include:
Obesity is associated with increased mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status and negatively impacts almost every organ system. Abdominal obesity is specifically associated with increased cardiovascular risks.
Commonly observed effects include:
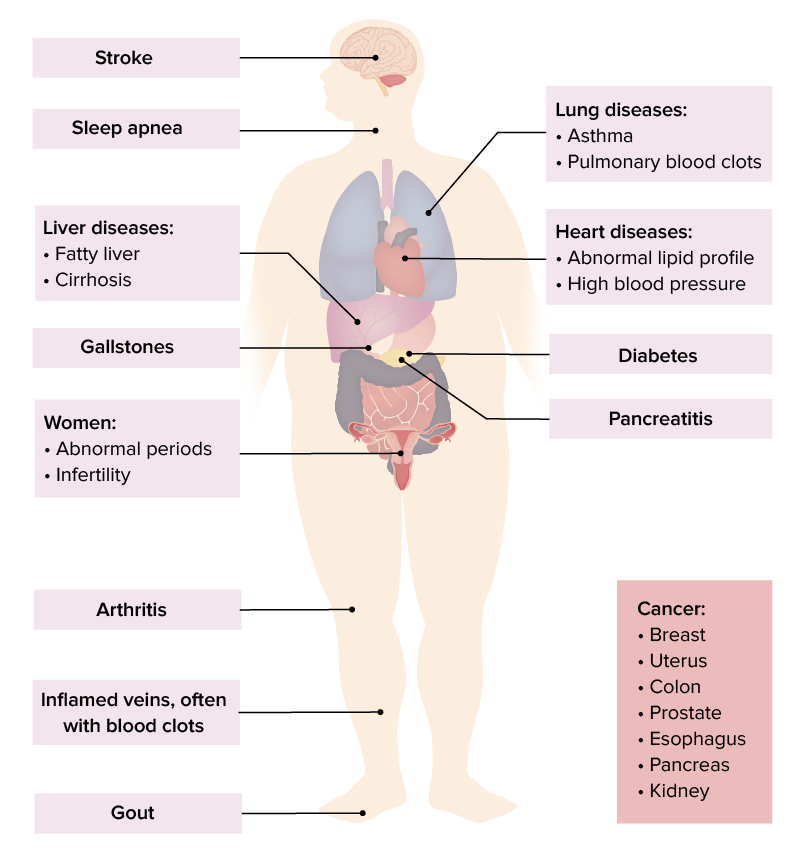
A sample of complications of obesity
Image by Lecturio.
Abdominal obesity
Image: “Belly of an obese teenage boy” by OctoMocto. License: Public DomainWeight-loss medications are reserved for patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship who have:
Considerations and results:
Duration:
Medications may also be needed to manage comorbidities Comorbidities The presence of co-existing or additional diseases with reference to an initial diagnosis or with reference to the index condition that is the subject of study. Comorbidity may affect the ability of affected individuals to function and also their survival; it may be used as a prognostic indicator for length of hospital stay, cost factors, and outcome or survival. St. Louis Encephalitis Virus such as hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and depression: