Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is a potentially reversible neurologic disorder caused by impaired cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) dynamics featuring enlarged ventricles with normal opening pressures on lumbar puncture. Clinically, the condition is characterized by the triad of gait Gait Manner or style of walking. Neurological Examination abnormalities, dementia Dementia Major neurocognitive disorders (NCD), also known as dementia, are a group of diseases characterized by decline in a person's memory and executive function. These disorders are progressive and persistent diseases that are the leading cause of disability among elderly people worldwide. Major Neurocognitive Disorders, and urinary urgency or incontinence. Normal pressure hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage can be either idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis or secondary to intraventricular or subarachnoid hemorrhage Subarachnoid Hemorrhage Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) is a type of cerebrovascular accident (stroke) resulting from intracranial hemorrhage into the subarachnoid space between the arachnoid and the pia mater layers of the meninges surrounding the brain. Most SAHs originate from a saccular aneurysm in the circle of Willis but may also occur as a result of trauma, uncontrolled hypertension, vasculitis, anticoagulant use, or stimulant use. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Symptoms may be similar to those of Alzheimer and Parkinson's diseases. Diagnosis of NPH is clinical, in addition to lumbar puncture Lumbar Puncture Febrile Infant testing and neuroimaging Neuroimaging Non-invasive methods of visualizing the central nervous system, especially the brain, by various imaging modalities. Febrile Infant. Management is with surgical shunt placement to drain excess CSF from the cerebral ventricles.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Normal pressure hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid within the cranium which may be associated with dilation of cerebral ventricles, intracranial. Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (NPH) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the triad of dementia Dementia Major neurocognitive disorders (NCD), also known as dementia, are a group of diseases characterized by decline in a person’s memory and executive function. These disorders are progressive and persistent diseases that are the leading cause of disability among elderly people worldwide. Major Neurocognitive Disorders, progressive gait Gait Manner or style of walking. Neurological Examination abnormalities, and urinary urgency or incontinence.
The pathophysiology of NPH is still unclear.
Family members or caretakers may report personality and/or behavioral changes and frequent urination or incontinence.
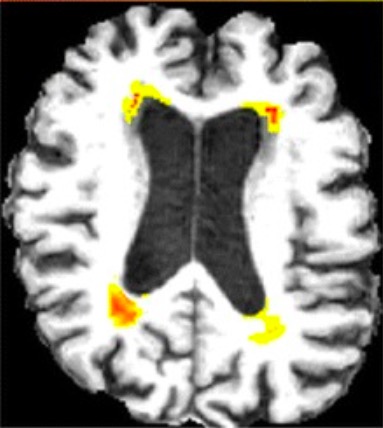
MRI of normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH):
Note the widening of the ventricles, which is out of proportion to the degree of cerebral atrophy.
The treatment of NPH is with an implanted ventricular shunt.