An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphic representation of the electrical activity of the heart plotted against time. Electrocardiograms are simple, inexpensive, noninvasive, and readily obtained. Adhesive electrodes are affixed to the skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions surface allowing measurement of cardiac impulses from many angles. The ECG provides 3-dimensional information about the conduction system of the heart, the myocardium Myocardium The muscle tissue of the heart. It is composed of striated, involuntary muscle cells connected to form the contractile pump to generate blood flow. Heart: Anatomy, and other cardiac structures. In the healthy state, an ECG records predictable, reproducible waves and complexes, which correspond to electromechanically coupled physiologic events in the heart. Under pathologic conditions, the ECG can detect arrhythmias, ischemia Ischemia A hypoperfusion of the blood through an organ or tissue caused by a pathologic constriction or obstruction of its blood vessels, or an absence of blood circulation. Ischemic Cell Damage, inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation, and more.
Last updated: May 16, 2024
In 1902 the electrocardiogram (ECG) was invented by Willem Einthoven, a Dutch physician. Einthoven received the 1924 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the invention.
Electrocardiogram is abbreviated/referred to as:
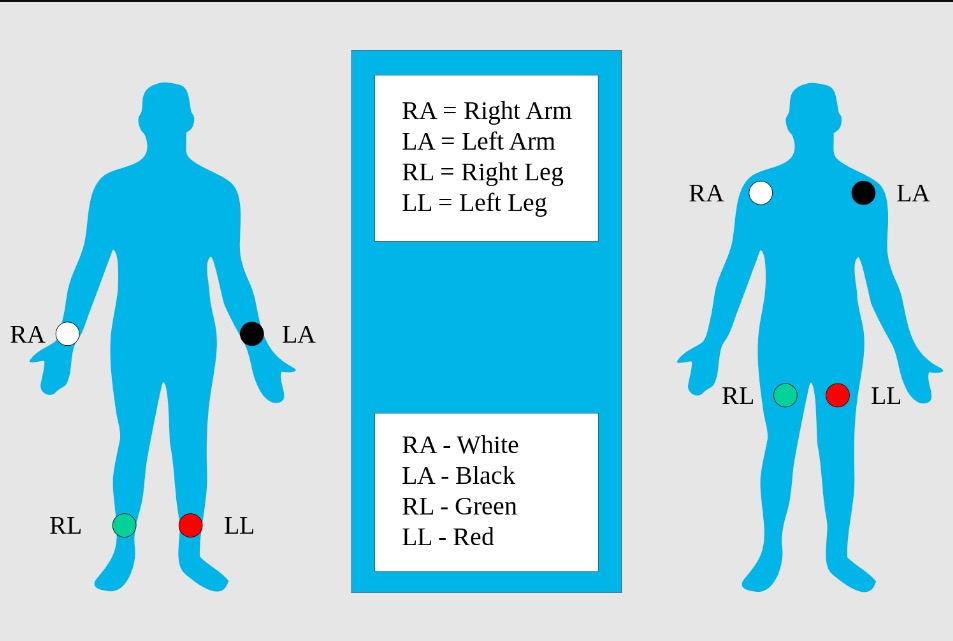
Limb electrodes: standard placement of the limb electrodes (left image) and modified placement (right image) for ECG
Image: “Limb leads, standard placement of the limb leads for electrocardiography” by MoodyGroove. License: Public Domain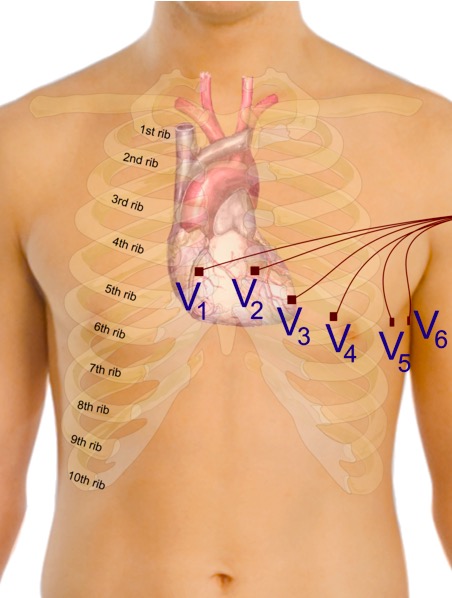
Proper placement of the precordial electrodes for ECG
Image: “Precordial leads in ECG” by Mikael Häggström. License: CC0 1.0
Einthoven triangle
Image: “Einthoven triangle” by Katrin Litzkow. License: Public Domain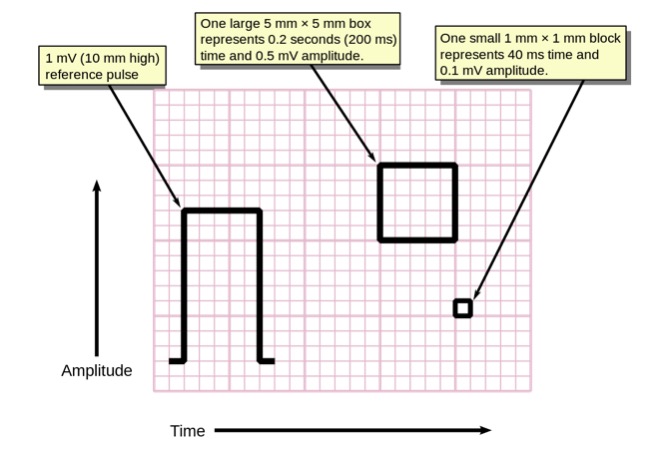
ECG voltage pulse and size of squares
Image: “Measuring time and voltage with ECG graph paper” by Markus Kuhn. License: Public DomainA normal ECG tracing will have several predictable and reproducible components corresponding to electromechanical events in the cardiac cycle Cardiac cycle The cardiac cycle describes a complete contraction and relaxation of all 4 chambers of the heart during a standard heartbeat. The cardiac cycle includes 7 phases, which together describe the cycle of ventricular filling, isovolumetric contraction, ventricular ejection, and isovolumetric relaxation. Cardiac Cycle.
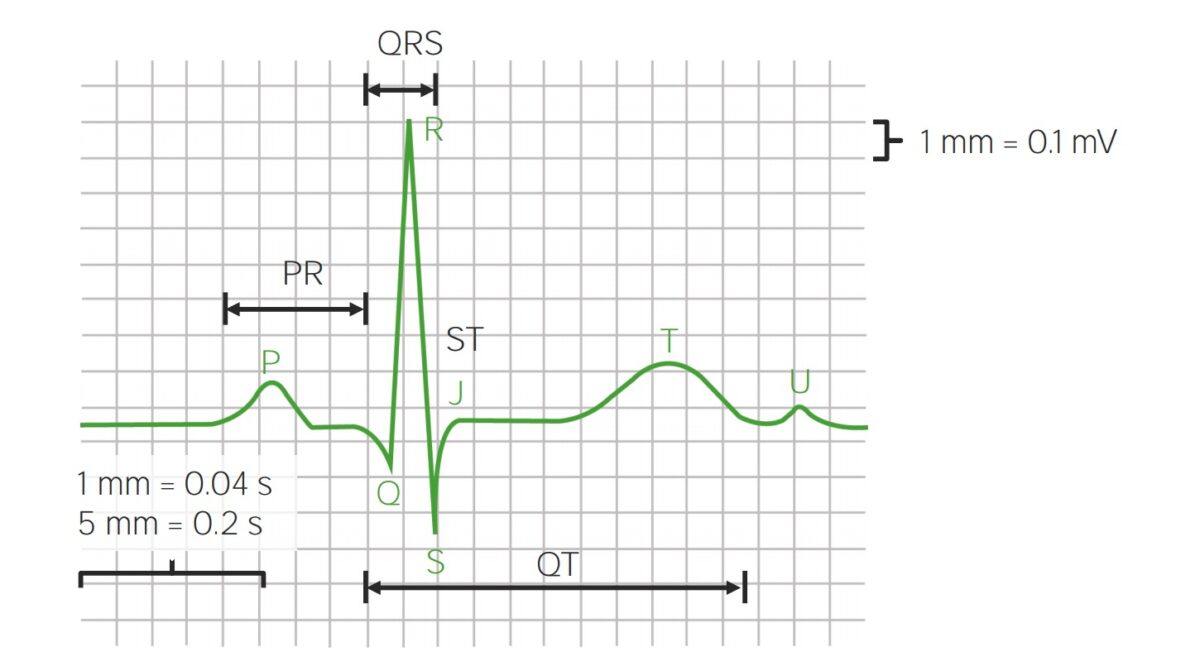
Parts of ECG waveforms and intervals
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0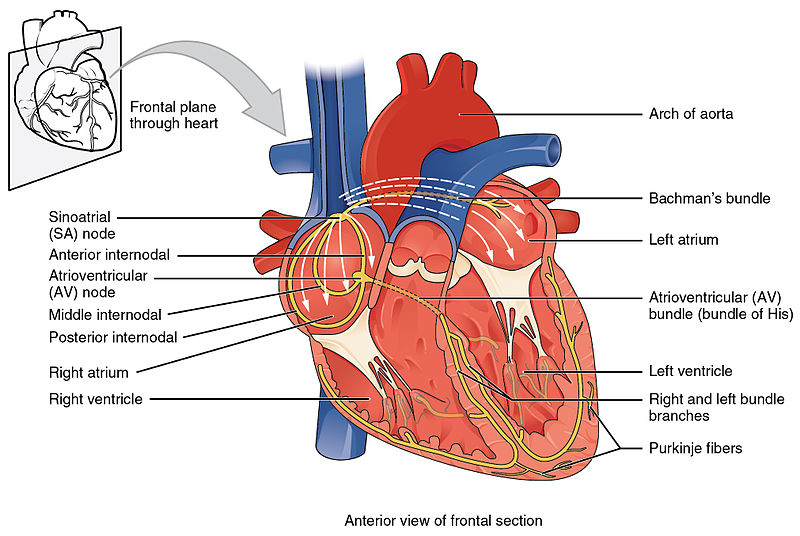
Cross-section of the heart showing the conduction system
Image: “Conduction System of Heart” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 3.0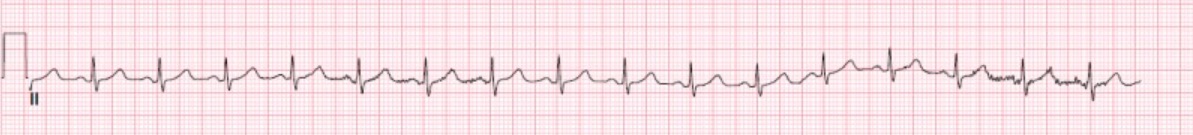
Normal lead II rhythm strip with standard voltage bar
Image: “Normal EKG” by StatPearls Publishing LLC. License: CC BY 4.0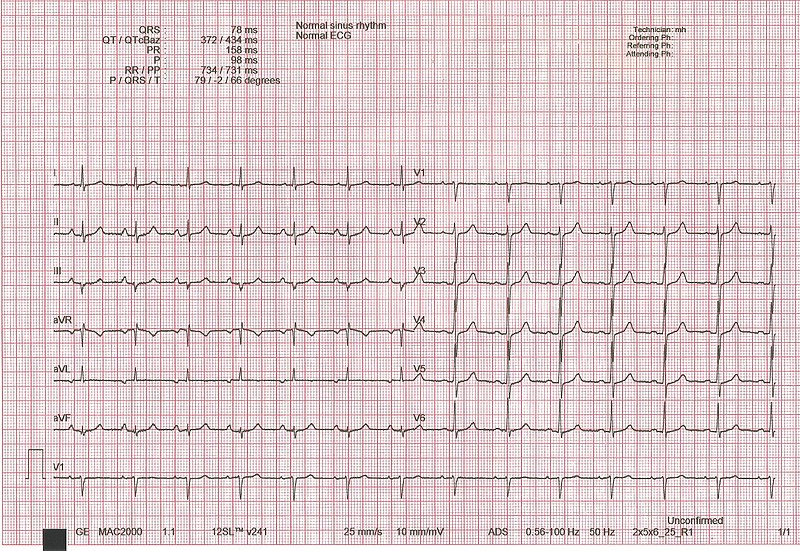
Normal ECG: 12-lead tracing with a V1 rhythm strip displayed at the bottom
Image: “ECG interpretation” by Rodhullandemu. License: Public Domain