Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches) are a class of medications consisting of aspirin, reversible NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches, and selective NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches. NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches are used as antiplatelet, analgesic, antipyretic Antipyretic Acetaminophen, and antiinflammatory agents. Common side effects include GI irritation, prolonged bleeding, and AKI AKI Acute kidney injury refers to sudden and often reversible loss of renal function, which develops over days or weeks. Azotemia refers to elevated levels of nitrogen-containing substances in the blood that accompany AKI, which include BUN and creatinine. Acute Kidney Injury.
Last updated: Nov 23, 2022
Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches) exert their therapeutic effects by interrupting fatty acid metabolism Fatty acid metabolism Fatty acid metabolism includes the processes of either breaking down fatty acids to generate energy (catabolic) or creating fatty acids for storage or use (anabolic). Besides being a source of energy, fatty acids can also be utilized for cellular membranes or signaling molecules. Synthesis and beta oxidation are almost the reverse of each other, and special reactions are required for variations. Fatty Acid Metabolism, primarily the action of cyclooxygenase (COX) on arachidonic acid ( AA AA Amyloidosis).
NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches are generally very similar:
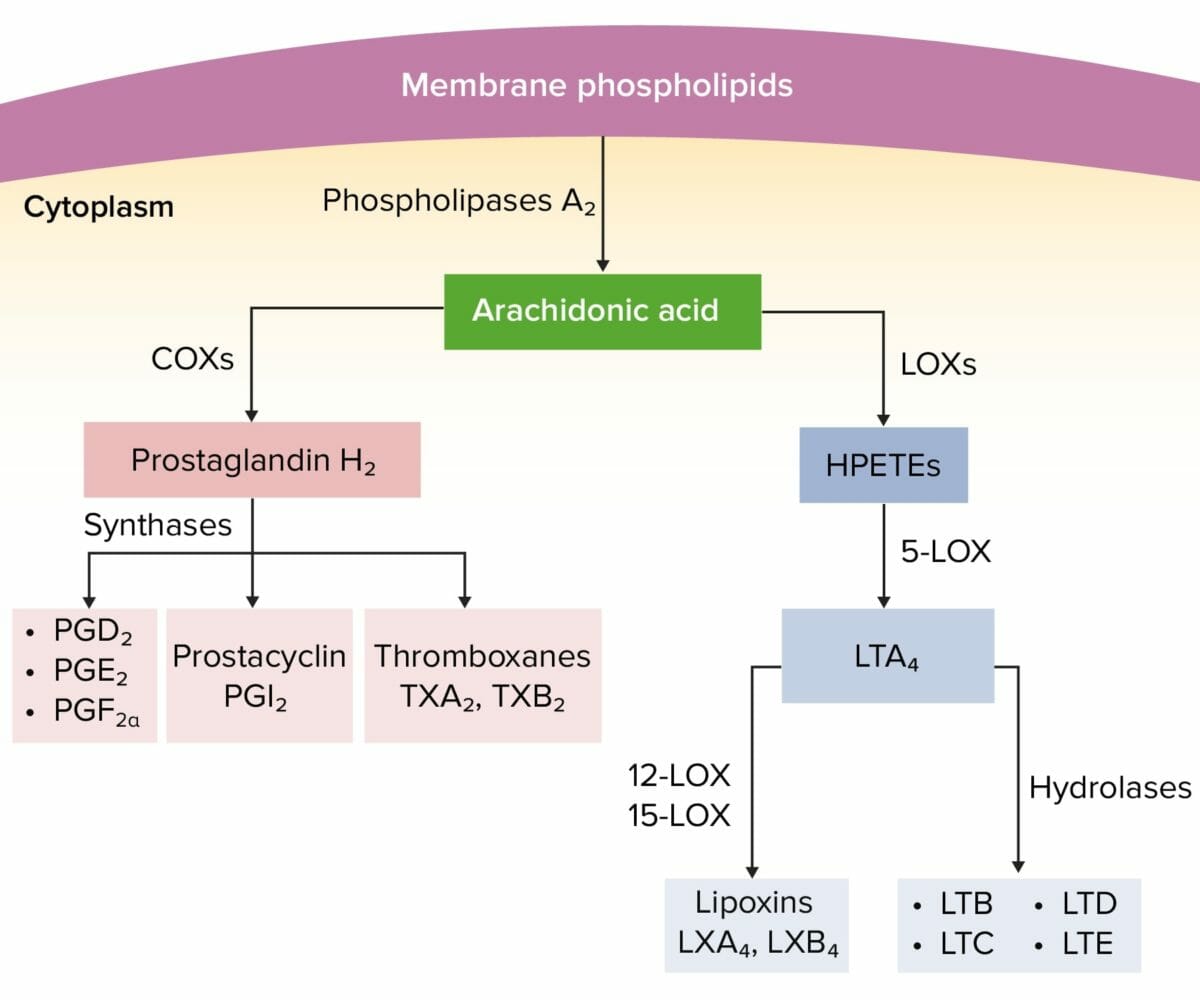
Arachidonic acid pathway
HPETEs: hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acids
LOX: lipoxygenase
LT: leukotriene
NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches can be divided into groups based on their ability to inhibit the isoforms of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Salicylate toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation is a series of symptoms and metabolic disturbances attributable to excessive ingestion of salicylic acid (e.g., aspirin and other over-the-counter (OTC) preparations). Accidental exposure is seen in pediatric patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship, whereas purposeful exposure is more commonly observed in adolescents and young adults (i.e., suicide attempt Suicide attempt The unsuccessful attempt to kill oneself. Suicide).
| Class | Mechanism of action | Clinical use | Side effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reversible NSAIDs NSAIDS Primary vs Secondary Headaches (e.g., ibuprofen, ketorolac, indomethacin) |
|
|
|
| Aspirin |
|
|
|
| COX-2 inhibitors (e.g., celecoxib) |
|
|
|