Nonhormonal contraception refers to mechanisms that prevent pregnancy without affecting the reproductive hormones in the user. Nonhormonal contraception includes physiologic methods, barrier methods, surgical methods, or the use of a copper intrauterine device (IUD). Efficacy levels vary significantly between methods. Most physiologic methods are associated with high failure rates, while, on the other hand, surgical methods are permanent and highly effective. The copper IUD is the most effective reversible method. Some barrier methods can prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) and, in addition, provide contraceptive coverage.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Nonhormonal contraception can be classified into:
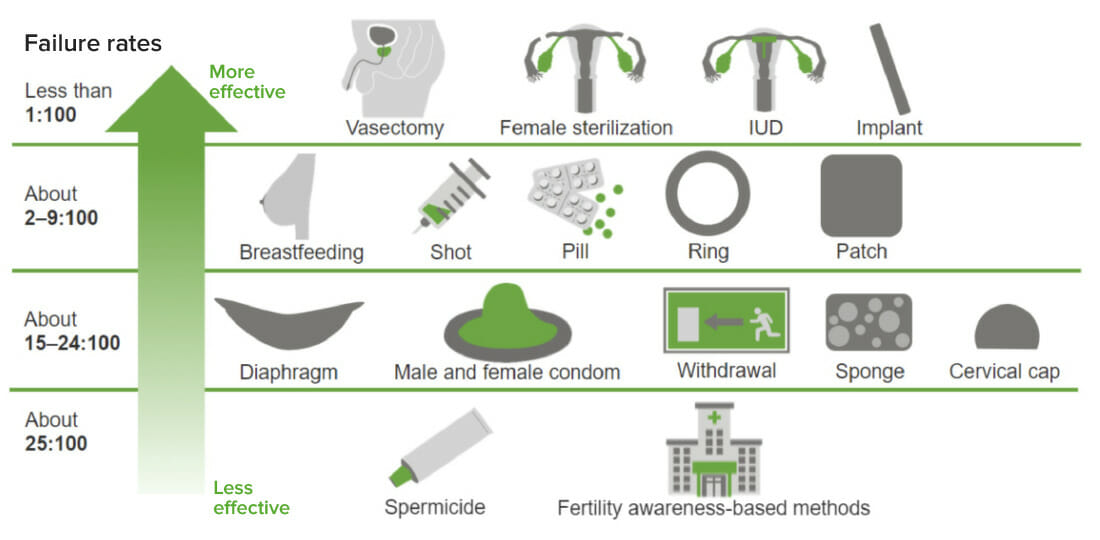
Comparison of the effectiveness of hormonal and nonhormonal contraceptive methods
Image by Lecturio.Rhythm method (calendar method)
Basal body temperature Body Temperature The measure of the level of heat of a human or animal. Heatstroke method
Cervical mucus method
Mechanism:
Male condom:
Female condom:
Advantages:
Disadvantages:
A partially unrolled male condom
Image: “An unrolled male condom” by Béa. License: Public Domain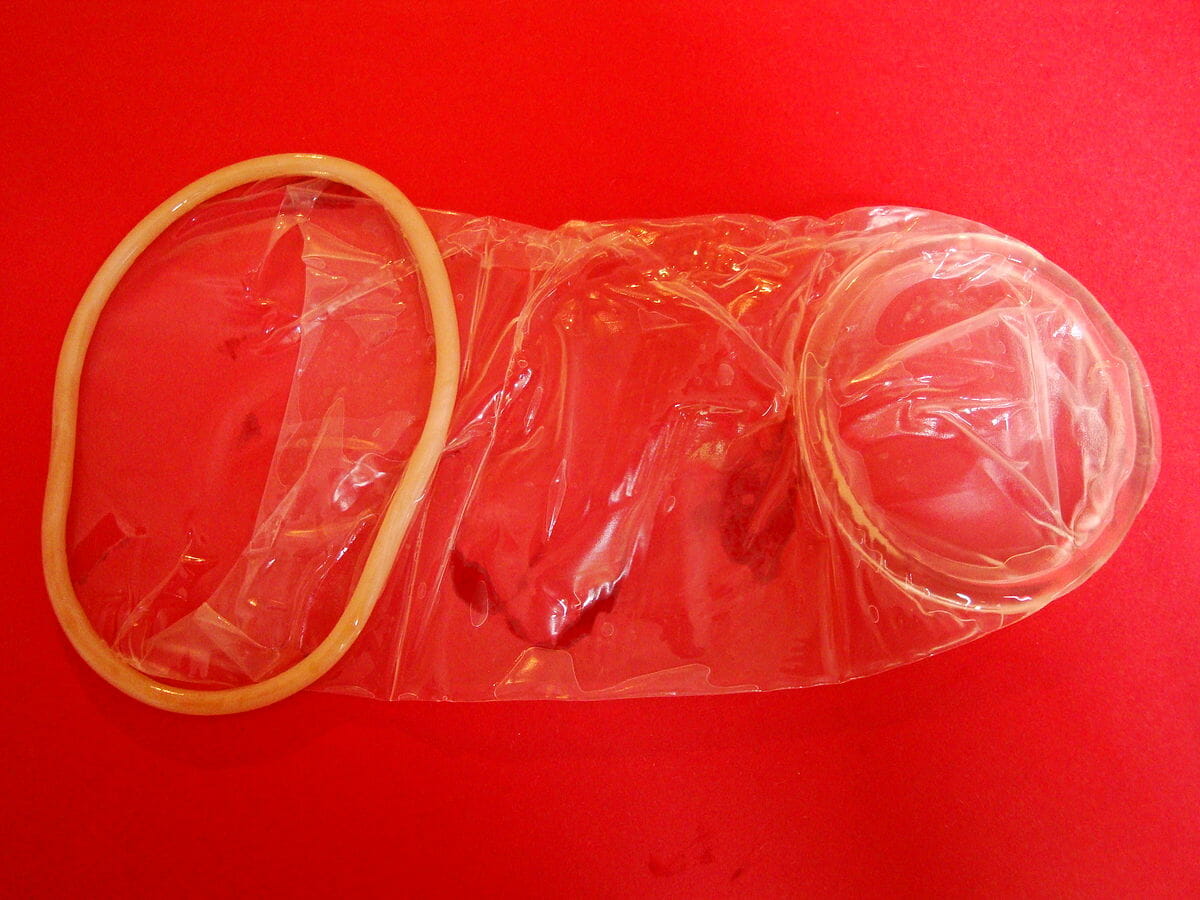
A female condom
Image: “Female condom” by Anka Grzywacz. License: Public Domain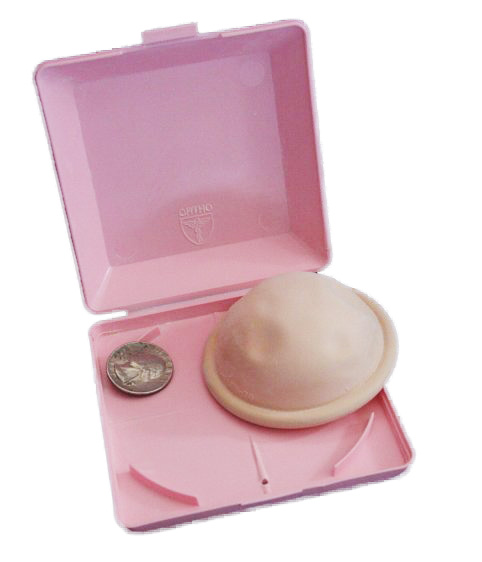
A contraceptive diaphragm
Image: “A contraceptive diaphragm” by Axefan2. License: Public DomainThe copper Copper A heavy metal trace element with the atomic symbol cu, atomic number 29, and atomic weight 63. 55. Trace Elements IUD is the only nonhormonal long-acting, reversible contraceptive available. In the United States, the copper Copper A heavy metal trace element with the atomic symbol cu, atomic number 29, and atomic weight 63. 55. Trace Elements IUD is sold under the brand name Paragard®.
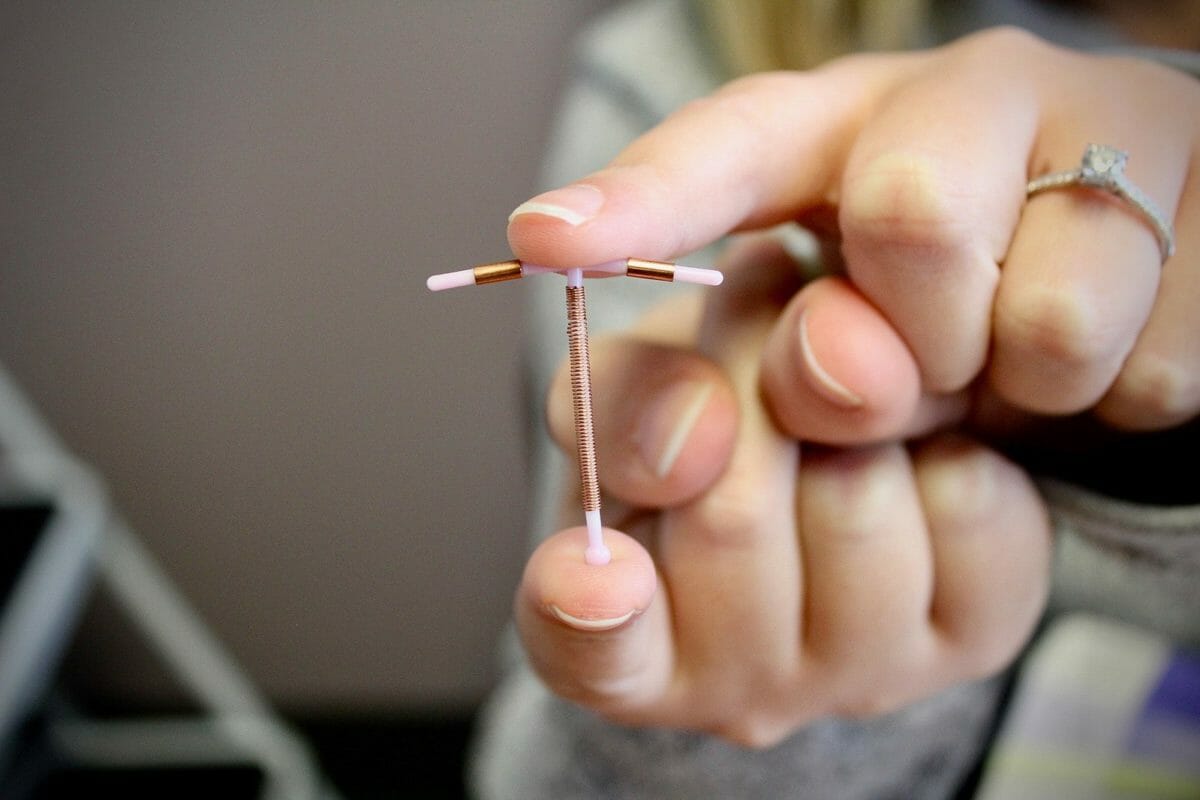

Image of a copper IUD
Image: “Example of IUD” by Robin Marty. License: CC BY 2.0Mechanism:
Indications and contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation:
Complications:
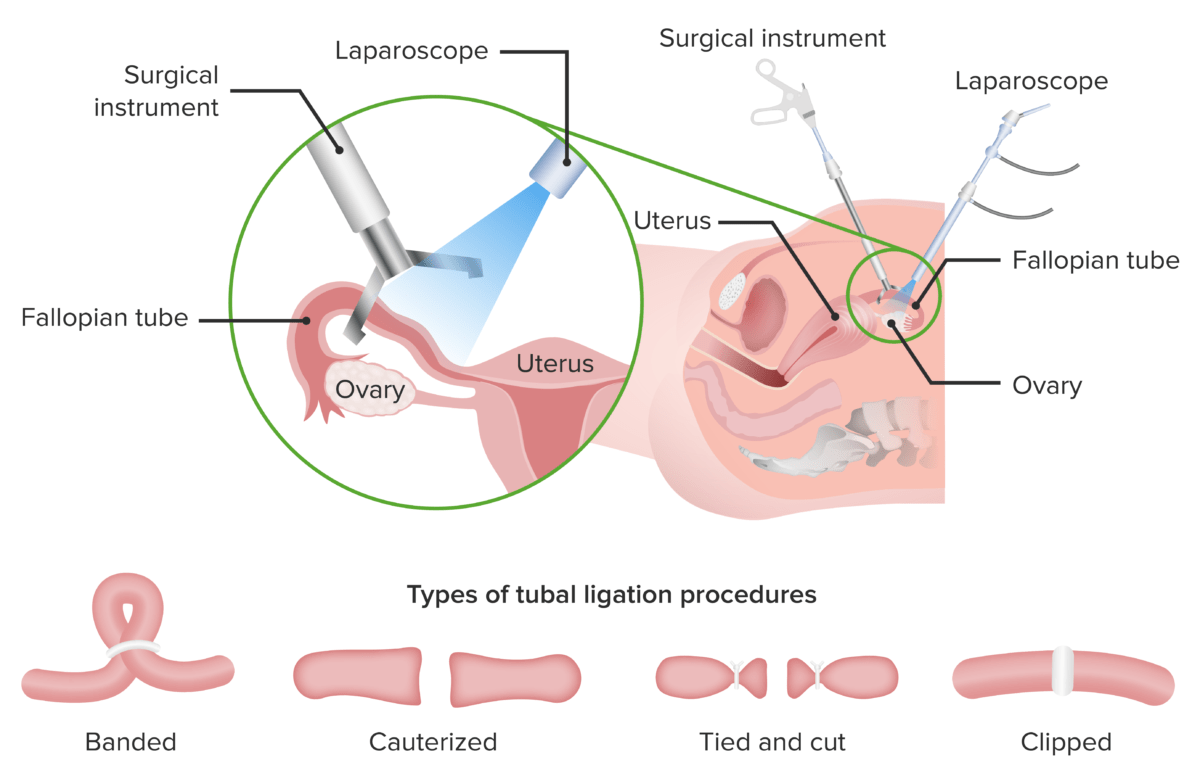
Tubal ligation is a method of surgical contraception for women.
There are 4 different tubal ligation procedures:
1. Banding of the tubes
2. Cauterization of the tubes
3. Tie and cut method (the tube is tied with 2 strings placed slightly apart and a cut is made in the space between the strings)
4. Clipping of the tubes
Mechanism:
Indications and contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation:
Complications:
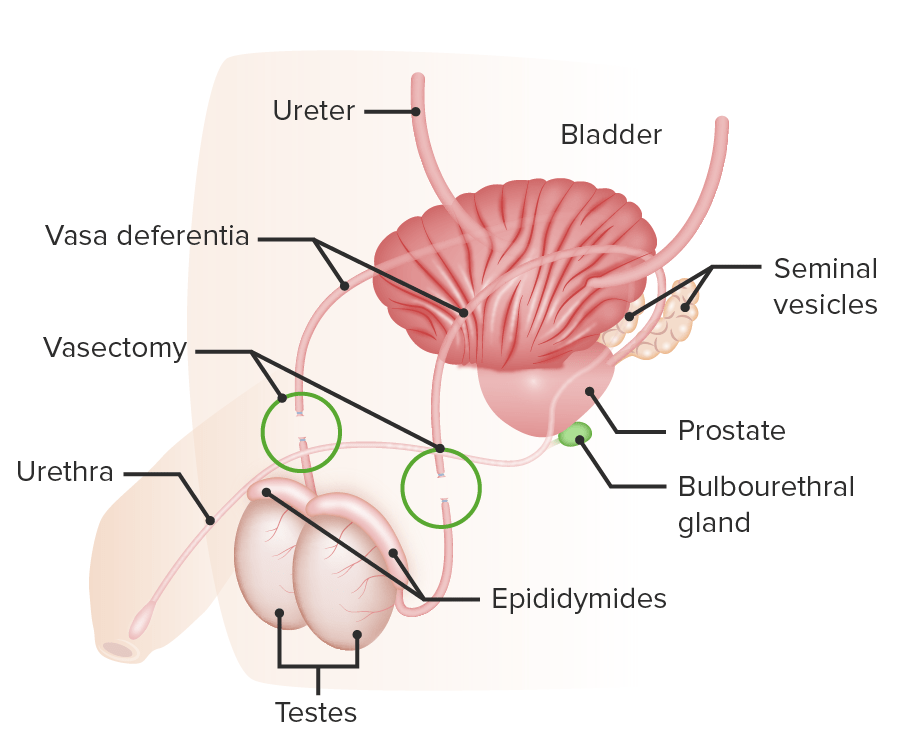
Vasectomy is a type of non-hormonal contraception in men:
The patency of the vas deferens is disrupted.