Non-insulinotropic diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus medications are used to treat type 2 diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus by methods other than increasing insulin Insulin Insulin is a peptide hormone that is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas. Insulin plays a role in metabolic functions such as glucose uptake, glycolysis, glycogenesis, lipogenesis, and protein synthesis. Exogenous insulin may be needed for individuals with diabetes mellitus, in whom there is a deficiency in endogenous insulin or increased insulin resistance. Insulin secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies. This group of medications includes the biguanides, thiazolidinediones, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals. It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Hyponatremia– glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance transport protein 2 inhibitors, and amylin analogs. Mechanisms of action vary, but they can include increasing peripheral insulin Insulin Insulin is a peptide hormone that is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas. Insulin plays a role in metabolic functions such as glucose uptake, glycolysis, glycogenesis, lipogenesis, and protein synthesis. Exogenous insulin may be needed for individuals with diabetes mellitus, in whom there is a deficiency in endogenous insulin or increased insulin resistance. Insulin sensitivity, reducing glucagon Glucagon A 29-amino acid pancreatic peptide derived from proglucagon which is also the precursor of intestinal glucagon-like peptides. Glucagon is secreted by pancreatic alpha cells and plays an important role in regulation of blood glucose concentration, ketone metabolism, and several other biochemical and physiological processes. Gastrointestinal Secretions release, inhibiting gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis Gluconeogenesis is the process of making glucose from noncarbohydrate precursors. This metabolic pathway is more than just a reversal of glycolysis. Gluconeogenesis provides the body with glucose not obtained from food, such as during a fasting period. The production of glucose is critical for organs and cells that cannot use fat for fuel. Gluconeogenesis, slowing glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption, and increasing satiety. Metformin is the initial medication of choice; others may be used as an alternative monotherapy or as adjunctive therapy. Most of these medications are not associated with severe hypoglycemia Severe Hypoglycemia Hypoglycemia, except for amylin analogs or when medications are used in conjunction with other hypoglycemic agents.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Hyperglycemic medications can be classified on the basis of their mechanism of action:
Insulinotropic drugs: ↑ insulin Insulin Insulin is a peptide hormone that is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas. Insulin plays a role in metabolic functions such as glucose uptake, glycolysis, glycogenesis, lipogenesis, and protein synthesis. Exogenous insulin may be needed for individuals with diabetes mellitus, in whom there is a deficiency in endogenous insulin or increased insulin resistance. Insulin secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies
Non-insulinotropic drugs: do not affect insulin Insulin Insulin is a peptide hormone that is produced by the beta cells of the pancreas. Insulin plays a role in metabolic functions such as glucose uptake, glycolysis, glycogenesis, lipogenesis, and protein synthesis. Exogenous insulin may be needed for individuals with diabetes mellitus, in whom there is a deficiency in endogenous insulin or increased insulin resistance. Insulin release
Metformin is the only available medication in the biguanide drug class.
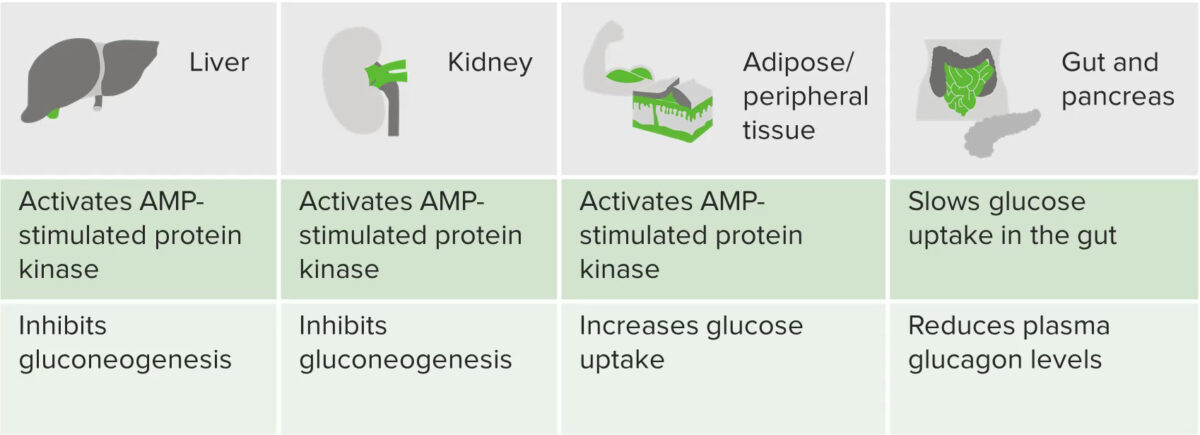
Graphic summarizing the actions of metformin
Image by Lecturio.Drugs associated with increased metformin toxicity Toxicity Dosage Calculation:
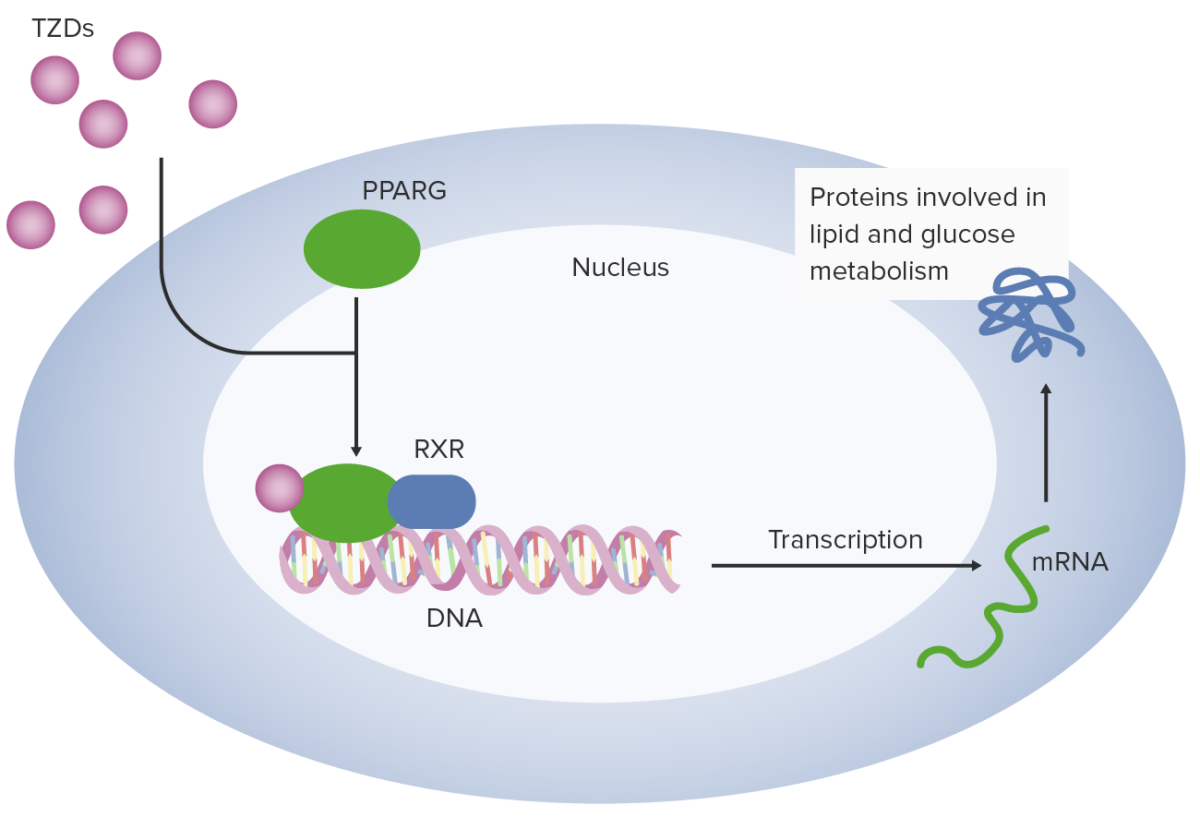
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) work in adipocytes by binding peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma (PPARG). Peroxisome proliferator–activated receptor gamma combines with retinoid X receptor (RXR) to facilitate transcription of multiple genes related to glucose utilization and metabolism.
Image by Lecturio.TZDs are used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus:
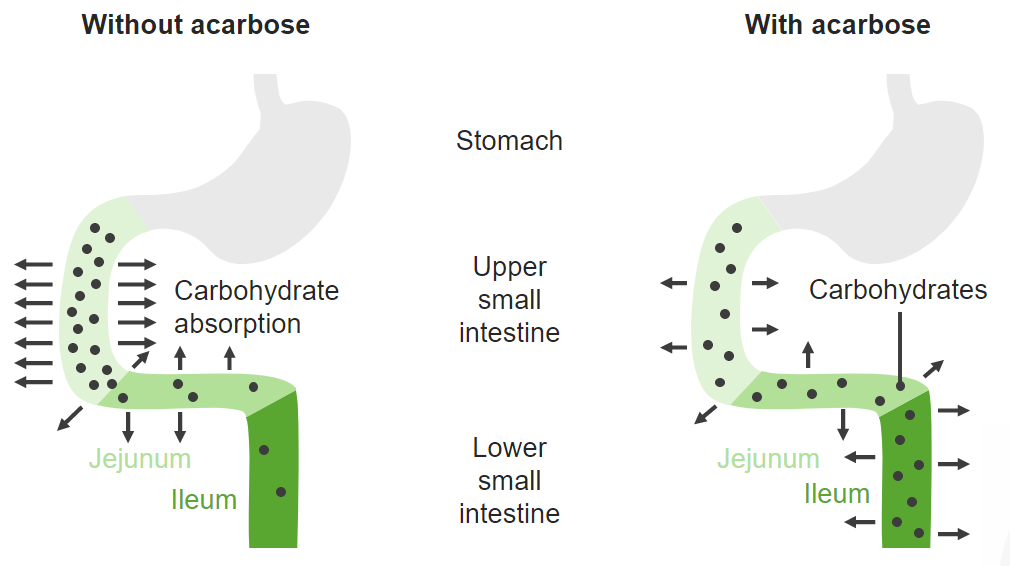
Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors competitively inhibit enzymes used to convert carbohydrates to monosaccharides (such as glucose) in the proximal small intestine. This process defers digestion to the distal small intestine, slowing glucose absorption and blunting postprandial blood glucose spikes.
Image by Lecturio.Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors are used to treat type 2 diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus as either:
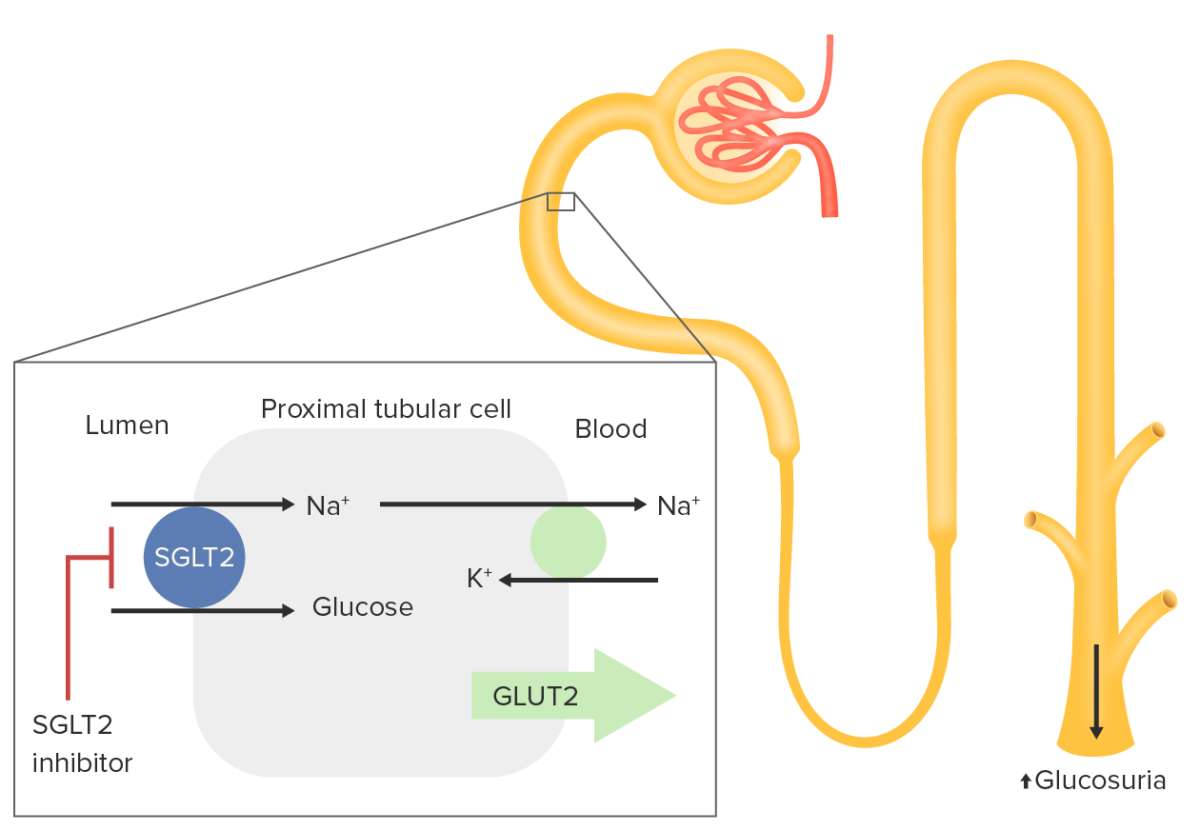
Sodium–glucose transport protein 2 (SGLT2) is expressed in the proximal tubule:
Sodium–glucose transport protein 2 is responsible for reabsorption of approximately 90% of filtered glucose. Glucose is normally imported into the proximal renal tubular cell with a sodium ion. This ion is driven by Na efflux out of the cell by the Na
Inhibition of SGLT2 results in increased renal excretion of glucose, thus lowering blood glucose levels.
Sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals. It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Hyponatremia– glucose Glucose A primary source of energy for living organisms. It is naturally occurring and is found in fruits and other parts of plants in its free state. It is used therapeutically in fluid and nutrient replacement. Lactose Intolerance transport protein 2 inhibitors are used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus:
Additional indications:
Pramlintide is the only medication in the amylin analog class.
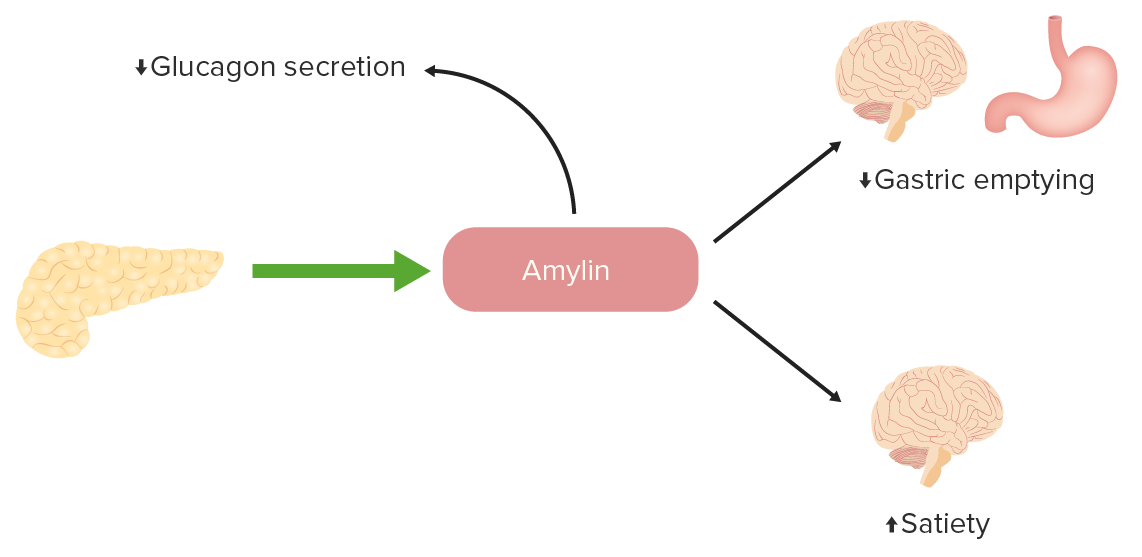
The function of amylin in glucose regulation:
Amylin is a peptide that is normally released by pancreatic beta cells in conjunction with insulin. There is a deficiency of amylin in diabetes, so analogs can be given to promote satiety, slow gastric emptying, and decrease inappropriate glucagon secretion.
The following table compares the different (noninsulin) type 2 diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus medications:
| Drug | Mechanism | Indications | Adverse effects |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sulfonylureas Sulfonylureas Sulfonamides and Trimethoprim |
|
|
|
| Meglitinides |
|
|
|
| GLP-1 GLP-1 A peptide of 36 or 37 amino acids that is derived from proglucagon and mainly produced by the intestinal l cells. Glp-1(1-37 or 1-36) is further n-terminally truncated resulting in glp-1(7-37) or glp-1-(7-36) which can be amidated. These glp-1 peptides are known to enhance glucose-dependent insulin release, suppress glucagon release and gastric emptying, lower blood glucose, and reduce food intake. Insulinomas agonists |
|
|
|
| DPP-4 inhibitors |
|
Adjunctive therapy |
|
| Biguanides |
|
|
|
| Thiazolidinediones |
|
|
|
| Alpha-glucosidase inhibitors |
|
|
|
| SGLT2 inhibitors |
|
|
|
| Amylin analogs |
|
|
|
The effects of diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus medications on weight may be a factor in choosing therapy: