Nitrates are a class of medications that cause systemic vasodilation Vasodilation The physiological widening of blood vessels by relaxing the underlying vascular smooth muscle. Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs ( veins Veins Veins are tubular collections of cells, which transport deoxygenated blood and waste from the capillary beds back to the heart. Veins are classified into 3 types: small veins/venules, medium veins, and large veins. Each type contains 3 primary layers: tunica intima, tunica media, and tunica adventitia. Veins: Histology > arteries Arteries Arteries are tubular collections of cells that transport oxygenated blood and nutrients from the heart to the tissues of the body. The blood passes through the arteries in order of decreasing luminal diameter, starting in the largest artery (the aorta) and ending in the small arterioles. Arteries are classified into 3 types: large elastic arteries, medium muscular arteries, and small arteries and arterioles. Arteries: Histology) by smooth muscle relaxation. Nitrates are primarily indicated for the treatment of angina, where preferential venodilation Venodilation Venous Function causes pooling of blood, decreased preload Preload Cardiac Mechanics, and ultimately decreased myocardial O2 demand. At high doses, nitrates can decrease afterload Afterload Afterload is the resistance in the aorta that prevents blood from leaving the heart. Afterload represents the pressure the LV needs to overcome to eject blood into the aorta. Cardiac Mechanics and may be used in hypertensive crises. The main adverse effects include headache Headache The symptom of pain in the cranial region. It may be an isolated benign occurrence or manifestation of a wide variety of headache disorders. Brain Abscess, hypotension Hypotension Hypotension is defined as low blood pressure, specifically < 90/60 mm Hg, and is most commonly a physiologic response. Hypotension may be mild, serious, or life threatening, depending on the cause. Hypotension, and reflex tachycardia Tachycardia Abnormally rapid heartbeat, usually with a heart rate above 100 beats per minute for adults. Tachycardia accompanied by disturbance in the cardiac depolarization (cardiac arrhythmia) is called tachyarrhythmia. Sepsis in Children. Repeated use of nitrates leads to tolerance Tolerance Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics. Contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation include concomitant therapy with PDE5 inhibitors, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is the most commonly inherited cardiomyopathy, which is characterized by an asymmetric increase in thickness (hypertrophy) of the left ventricular wall, diastolic dysfunction, and often left ventricular outflow tract obstruction. Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy, and suspected right ventricular infarction.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
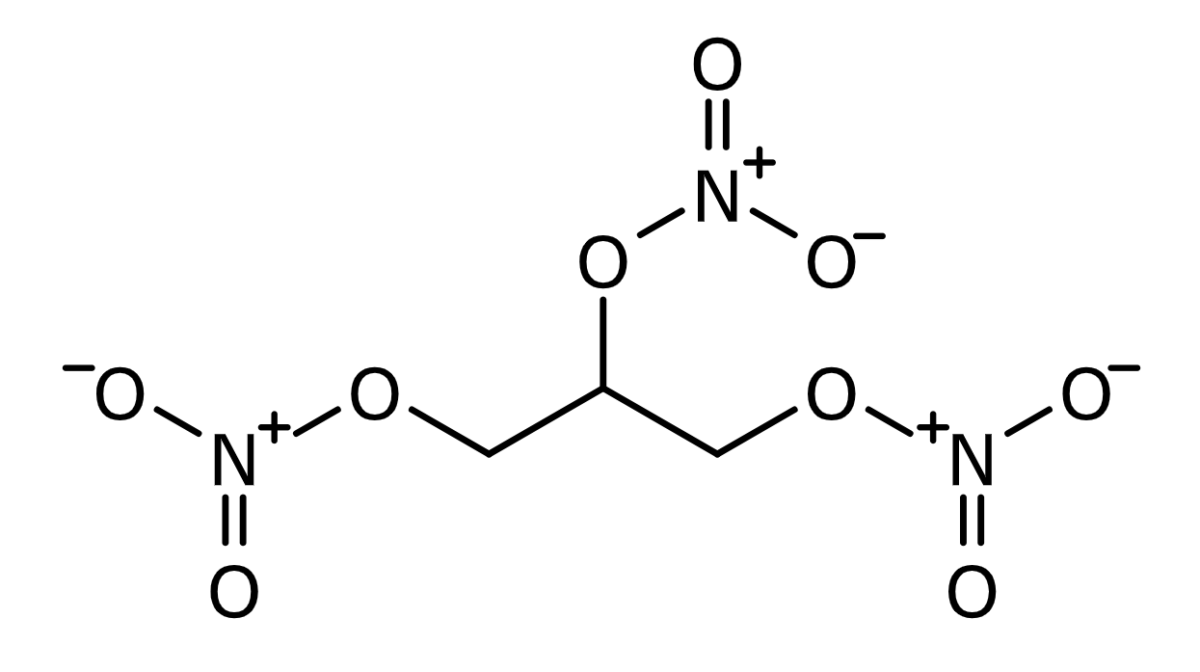
Nitroglycerine chemical structure
Image: “Skeletal formula of zwitterionic nitroglycerin” by BartVL71. License: Public DomainExogenously administered nitrates are converted to NO after entering the cell:
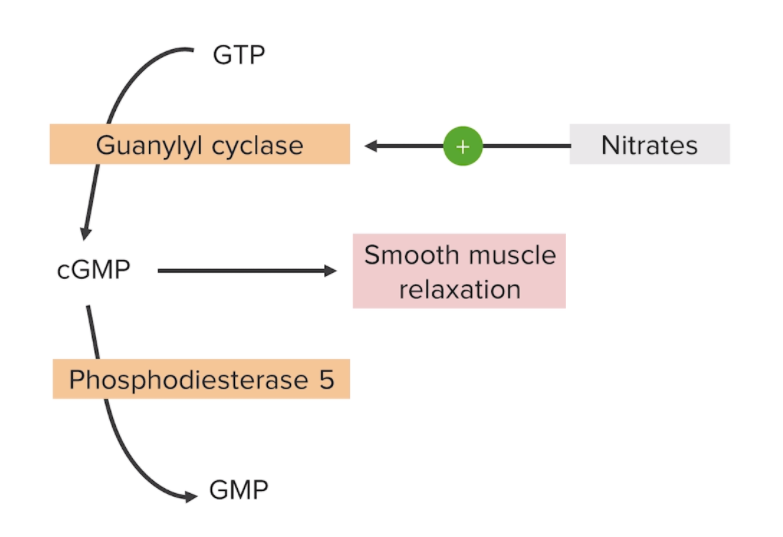
Mechanism of action for nitrates:
Stimulation of guanylyl cyclase induces the conversion of guanosine-5′-triphosphate (GTP) to cGMP, resulting in vascular smooth muscle relaxation and vasodilation.
GMP: guanosine monophosphate
| Medications | Common formulations | Indications | Clinical pearls |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitroglycerin |
|
|
|
| Isosorbide dinitrate | Oral |
|
|
| Isosorbide mononitrate | Oral |
|
Active metabolite of isosorbide dinitrate (better bioavailability Bioavailability Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics) |
| Sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals. It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Hyponatremia nitroprusside | IV |
|
Combines with hemoglobin to produce cyanide Cyanide Inorganic salts of hydrogen cyanide containing the -cn radical. The concept also includes isocyanides. It is distinguished from nitriles, which denotes organic compounds containing the -cn radical. Cyanide Poisoning and cyanmethemoglobin |
| Amyl nitrite Nitrite Salts of nitrous acid or compounds containing the group NO2-. The inorganic nitrates of the type mno2 (where m=metal) are all insoluble, except the alkali nitrites. The organic nitrites may be isomeric, but not identical with the corresponding nitro compounds. Kidney Function Tests | Inhalation |
|
|
| Sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals. It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Hyponatremia nitrite Nitrite Salts of nitrous acid or compounds containing the group NO2-. The inorganic nitrates of the type mno2 (where m=metal) are all insoluble, except the alkali nitrites. The organic nitrites may be isomeric, but not identical with the corresponding nitro compounds. Kidney Function Tests | IV | Cyanide Cyanide Inorganic salts of hydrogen cyanide containing the -cn radical. The concept also includes isocyanides. It is distinguished from nitriles, which denotes organic compounds containing the -cn radical. Cyanide Poisoning poisoning | Similar mechanism as that of amyl nitrite Nitrite Salts of nitrous acid or compounds containing the group NO2-. The inorganic nitrates of the type mno2 (where m=metal) are all insoluble, except the alkali nitrites. The organic nitrites may be isomeric, but not identical with the corresponding nitro compounds. Kidney Function Tests |
PDE5 inhibitors