Neuromuscular blockers are skeletal muscle relaxant medications that block muscle contraction through a couple of mechanisms. Depolarizing neuromuscular blockers bind BIND Hyperbilirubinemia of the Newborn to nicotinic cholinergic receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors (nAChRs), locking the ion channel open. This results in an initial, persistent depolarization Depolarization Membrane Potential, followed by receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors desensitization to result in muscle relaxation and paralysis. Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers also bind BIND Hyperbilirubinemia of the Newborn to these same receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors; however, they act by keeping the channel closed to prevent depolarization Depolarization Membrane Potential. These agents are often used as an adjunct to general anesthesia General anesthesia Procedure in which patients are induced into an unconscious state through use of various medications so that they do not feel pain during surgery. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts during surgery, and to facilitate endotracheal intubation Intubation Peritonsillar Abscess. Since these medications also work on muscles associated with breathing, respiratory support should be employed. It is also important that adequate sedation is also given, since these agents do not have a sedative effect. Common adverse effects include anaphylaxis Anaphylaxis An acute hypersensitivity reaction due to exposure to a previously encountered antigen. The reaction may include rapidly progressing urticaria, respiratory distress, vascular collapse, systemic shock, and death. Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction, bradycardia Bradycardia Bradyarrhythmia is a rhythm in which the heart rate is less than 60/min. Bradyarrhythmia can be physiologic, without symptoms or hemodynamic change. Pathologic bradyarrhythmia results in reduced cardiac output and hemodynamic instability causing syncope, dizziness, or dyspnea. Bradyarrhythmias, hypotension Hypotension Hypotension is defined as low blood pressure, specifically < 90/60 mm Hg, and is most commonly a physiologic response. Hypotension may be mild, serious, or life threatening, depending on the cause. Hypotension, and prolonged paralysis. Physicians Physicians Individuals licensed to practice medicine. Clinician–Patient Relationship should also be aware of the potential for muscle fasciculations Fasciculations Involuntary contraction of the muscle fibers innervated by a motor unit. Fasciculations may be visualized as a muscle twitch or dimpling under the skin, but usually do not generate sufficient force to move a limb. They may represent a benign condition or occur as a manifestation of motor neuron disease or peripheral nervous system diseases. Polyneuropathy and hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia Hyperkalemia is defined as a serum potassium (K+) concentration >5.2 mEq/L. Homeostatic mechanisms maintain the serum K+ concentration between 3.5 and 5.2 mEq/L, despite marked variation in dietary intake. Hyperkalemia can be due to a variety of causes, which include transcellular shifts, tissue breakdown, inadequate renal excretion, and drugs. Hyperkalemia with succinylcholine Succinylcholine A quaternary skeletal muscle relaxant usually used in the form of its bromide, chloride, or iodide. It is a depolarizing relaxant, acting in about 30 seconds and with a duration of effect averaging three to five minutes. Succinylcholine is used in surgical, anesthetic, and other procedures in which a brief period of muscle relaxation is called for. Cholinomimetic Drugs.
Last updated: Feb 13, 2025
Neuromuscular blockers can be classified based on their mechanism of action.
Normal physiology:
Depolarizing neuromuscular blockers:
Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers:
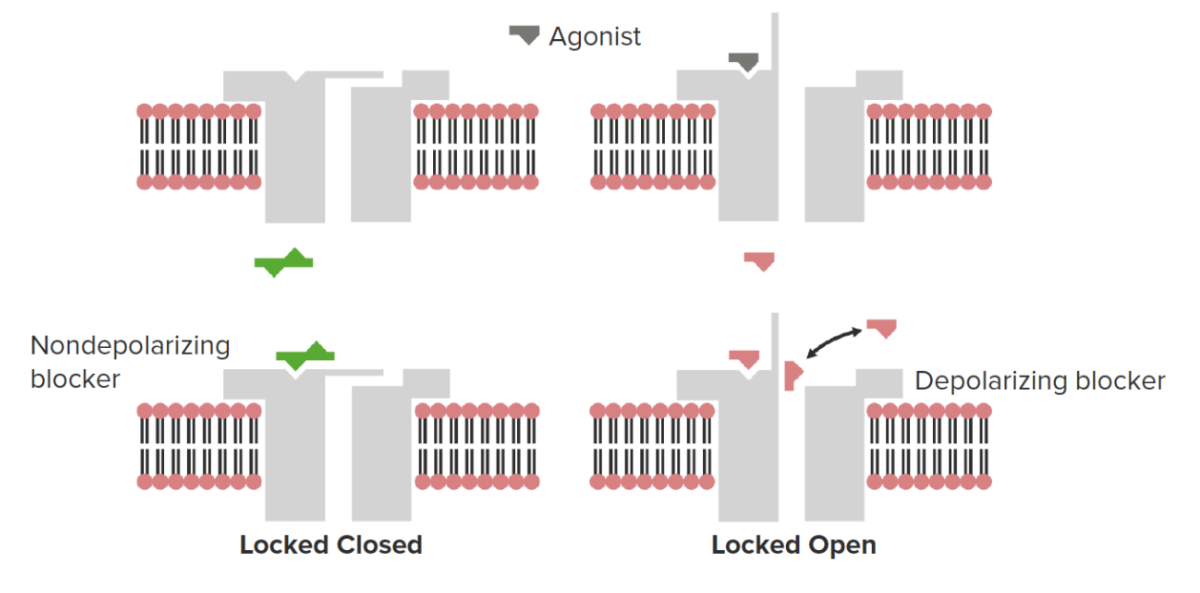
Neuromuscular blockers bind to ionotropic N1 nicotinic cholinergic receptors (nAChRs) and can either close the ion channel (nondepolarizing blocker) or lock the ion channel in the open position (depolarizing blocker). The latter will result in a short period of transient muscle contraction before the channel becomes desensitized, resulting in muscle relaxation.
Image by Lecturio.| Medication | Onset of action (min) | Duration of action (min) | Metabolism | Excretion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Succinylcholine Succinylcholine A quaternary skeletal muscle relaxant usually used in the form of its bromide, chloride, or iodide. It is a depolarizing relaxant, acting in about 30 seconds and with a duration of effect averaging three to five minutes. Succinylcholine is used in surgical, anesthetic, and other procedures in which a brief period of muscle relaxation is called for. Cholinomimetic Drugs | < 1 | 4–6 | Plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products pseudocholinesterase | Urine |
| Atracurium | 2–3 | 20–35 |
|
Urine (minimal) |
| Cisatracurium | 2–3 | 20–35 | Hofmann elimination Elimination The initial damage and destruction of tumor cells by innate and adaptive immunity. Completion of the phase means no cancer growth. Cancer Immunotherapy* | Urine and bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy |
| Pancuronium | 2–3 | 60–100 |
|
Urine and bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy |
| Rocuronium | 1–2 | 30 |
|
Bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy and urine |
| Vecuronium | 3–5 | 45–65 |
|
Bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy and urine |
| Medication | Adverse effects | Precautions | Contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation | Drug interactions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Succinylcholine Succinylcholine A quaternary skeletal muscle relaxant usually used in the form of its bromide, chloride, or iodide. It is a depolarizing relaxant, acting in about 30 seconds and with a duration of effect averaging three to five minutes. Succinylcholine is used in surgical, anesthetic, and other procedures in which a brief period of muscle relaxation is called for. Cholinomimetic Drugs |
|
Atypical plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products cholinesterase Cholinesterase Liver Function Tests gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics → altered metabolism |
|
|
| Atracurium |
|
Resistance Resistance Physiologically, the opposition to flow of air caused by the forces of friction. As a part of pulmonary function testing, it is the ratio of driving pressure to the rate of air flow. Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing in burn or immobilized patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship | Hypersensitivity | |
| Cisatracurium |
|
|||
| Pancuronium |
|
Renal and hepatic impairment → reduced clearance | ||
| Rocuronium |
|
|
||
| Vecuronium |
|
Renal and hepatic impairment |