Neurofibromatosis type 2 is a neurocutaneous disorder that can arise from mutations in the NF2 gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics located in chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 22 and may be inherited in an autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance fashion or occur from de novo mutations. The main clinical features are bilateral vestibular schwannomas, intracranial/ spinal meningioma Spinal Meningioma Meningioma, and intramedullary and extramedullary spinal tumors. Other features can include eye lesions such as cataracts, skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions lesions, and peripheral neuropathy Neuropathy Leprosy. Diagnosis is made clinically from history and examination and confirmed with MRI, molecular testing, and histopathology. Tumor Tumor Inflammation surveillance Surveillance Developmental Milestones and Normal Growth and follow-up with screening Screening Preoperative Care of at-risk family members is recommended. Management includes surgical interventions, radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma therapy, and/or monoclonal antibody therapy with bevacizumab Bevacizumab An anti-vegf humanized murine monoclonal antibody. It inhibits vegf receptors and helps to prevent pathologic angiogenesis. Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The clinical presentation of NF2 may vary widely between individuals with de novo mutations and families carrying genetic mutations Genetic Mutations Carcinogenesis. Younger ages at onset are often associated with an atypical presentation with more severe symptoms.
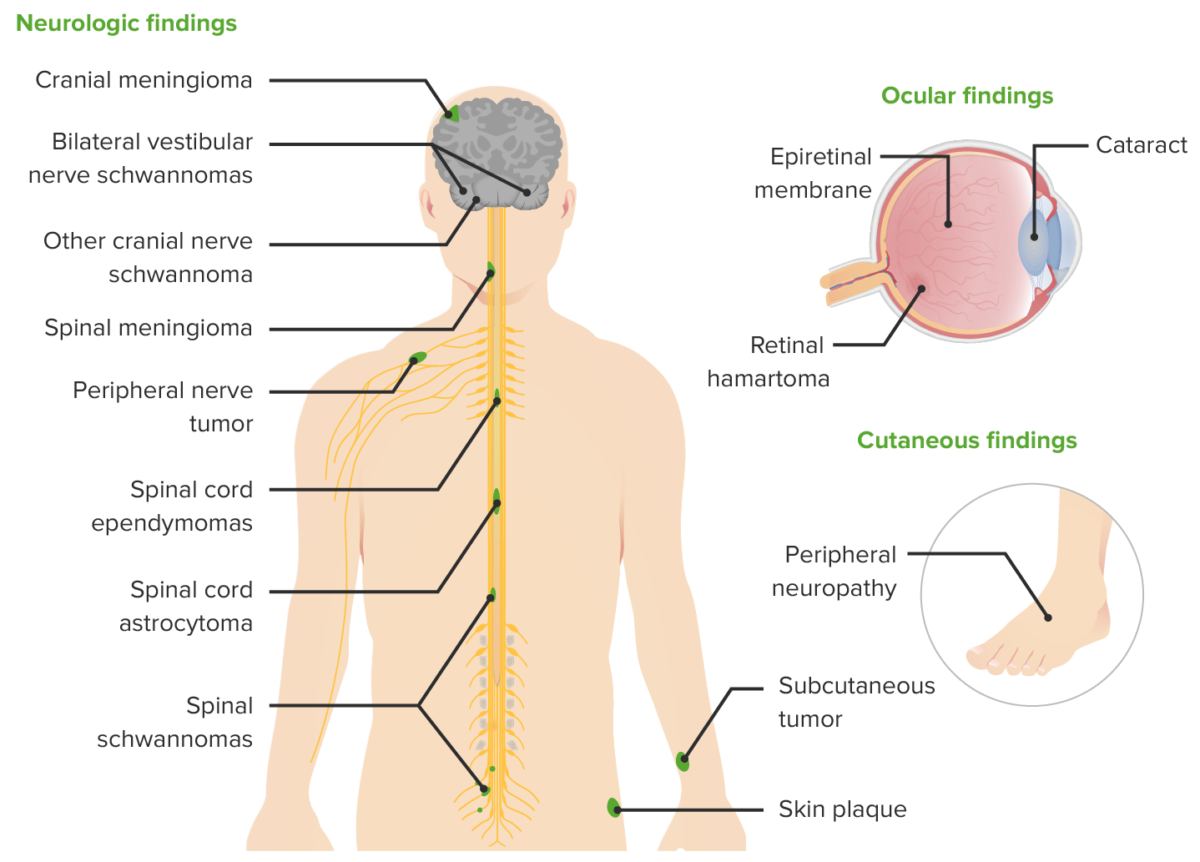
Clinical manifestations of NF2
Image by Lecturio.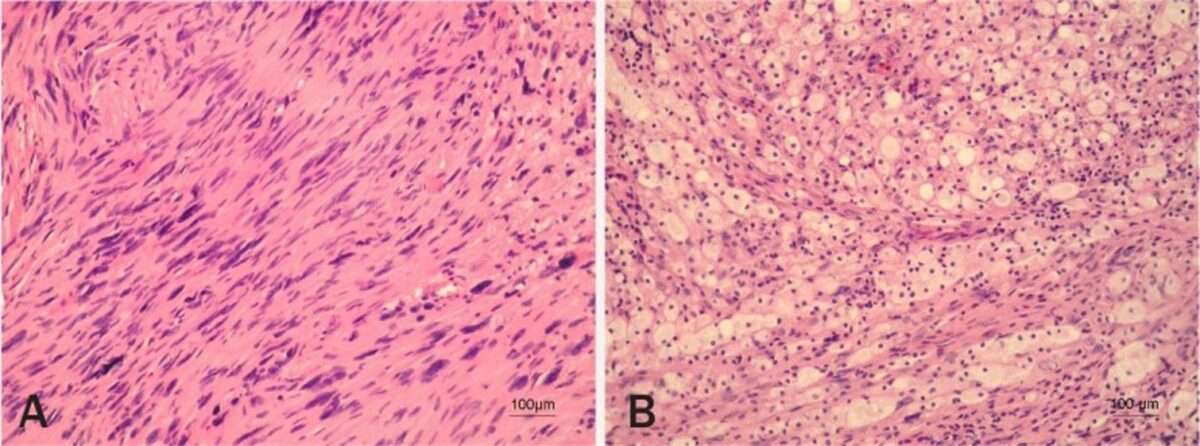
Vestibular schwannoma histopathology
Image: “Vestibular schwannoma” by Pećina-Slaus N, Zeljko M, Pećina HI, Nikuseva Martić T, Bacić N, Tomas D, Hrasćan R. License: CC BY 2.5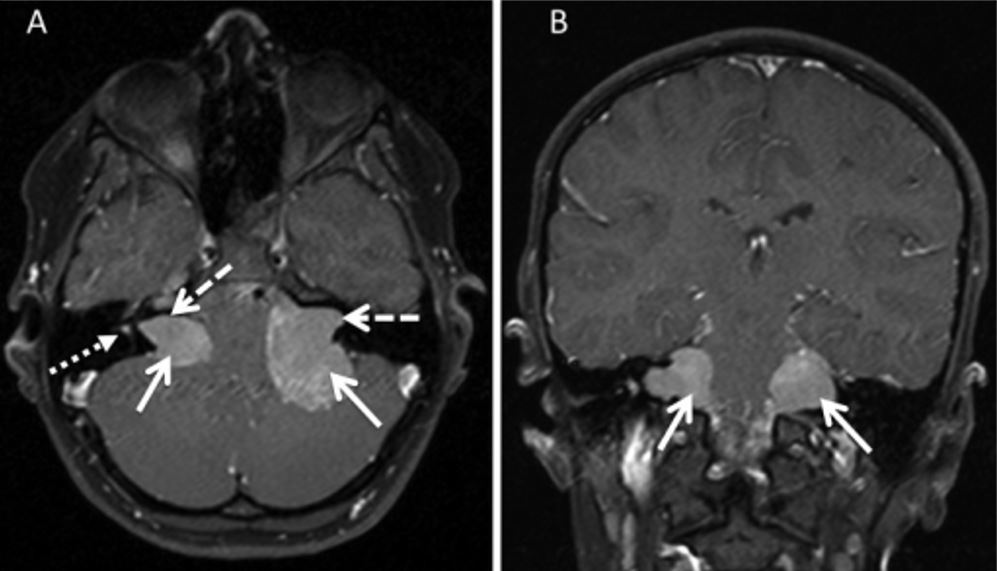
Bilateral vestibular schwannoma on MRI
Image: “T1 spin echo sequences” by Stivaros SM, et al. License: CC BY 4.0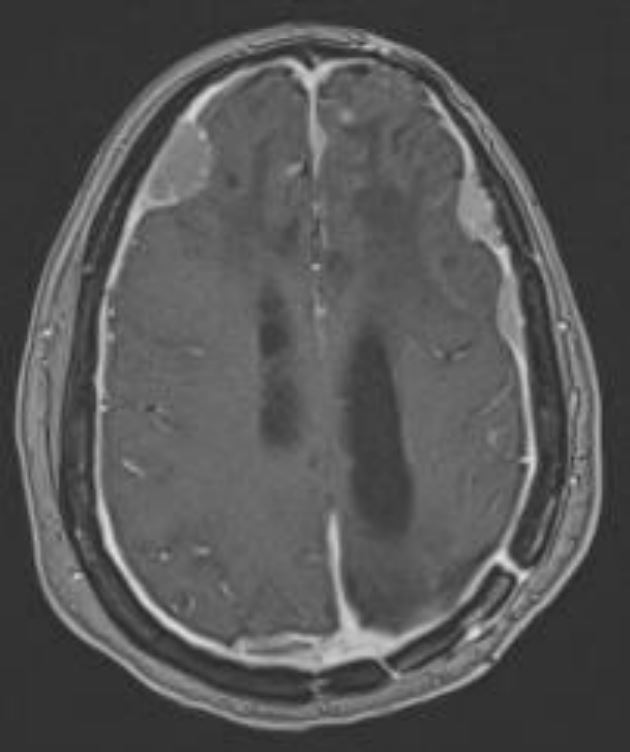
Intracranial meningioma
Image by Roy Strowd, MD.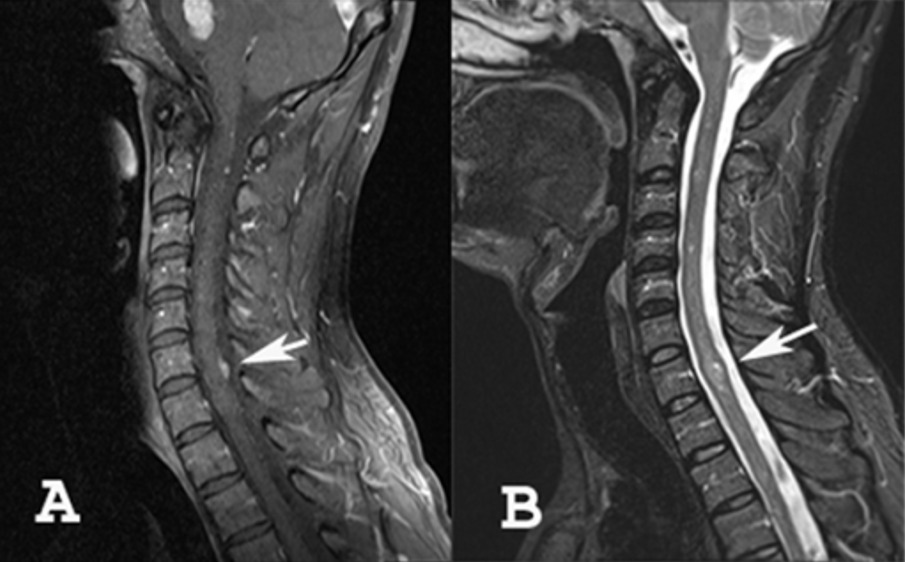
A: MRI showing meningioma of the cervical spine
B: MRI showing an intramedullary tumor (ependymoma or astrocytoma)
Management of NF2 is multidisciplinary and often involves contributions from multiple specialists.