Neurofibromatosis type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy (NF1), also known as phakomatosis, is a neurocutaneous disorder that is most commonly of autosomal dominant inheritance Autosomal dominant inheritance Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance due to mutations in the NF1 gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics. Neurofibromatosis type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy presents a range of clinical manifestations with the most prominent features being various pigmented skin Skin The skin, also referred to as the integumentary system, is the largest organ of the body. The skin is primarily composed of the epidermis (outer layer) and dermis (deep layer). The epidermis is primarily composed of keratinocytes that undergo rapid turnover, while the dermis contains dense layers of connective tissue. Skin: Structure and Functions lesions called café au lait macules (CALMs), benign Benign Fibroadenoma nerve-sheath tumors called neurofibromas, freckling of the inguinal and axillary regions, and iris hamartomas, referred to as Lisch nodules. At least half of the individuals with NF1 have learning disabilities Learning disabilities Conditions characterized by a significant discrepancy between an individual's perceived level of intellect and their ability to acquire new language and other cognitive skills. These may result from organic or psychological conditions. Relatively common subtypes include dyslexia, dyscalculia, and dysgraphia. DiGeorge Syndrome. Neurofibromatosis type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy may also cause osteodysplasia and malignant transformation Transformation Change brought about to an organism's genetic composition by unidirectional transfer (transfection; transduction, genetic; conjugation, genetic, etc.) and incorporation of foreign DNA into prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells by recombination of part or all of that DNA into the cell's genome. Bacteriology of tumors. The diagnosis is based on the typical clinical presentation and can be confirmed with genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies. Management depends on the clinical presentation and may vary from surgical removal to chemotherapy Chemotherapy Osteosarcoma/radiotherapy for tumors, occupational therapy Occupational Therapy Skilled treatment that helps individuals achieve independence in all facets of their lives. It assists in the development of skills needed for independent living. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder and PT for motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology impairments, treatment with growth hormone, and bracing in the case of bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types abnormalities.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
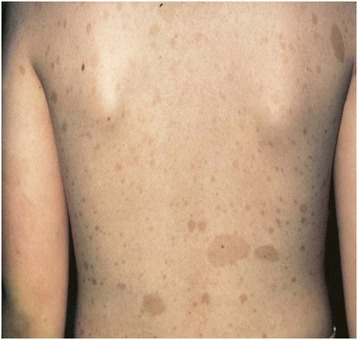
Café au lait macules (CALMs):
Image showing well-circumscribed, light-brown, pigmented CALMs that are commonly found in the general population. Macules can be few millimeters to several centimeters (> 20 cm) in size and may appear at birth or early life. The development of multiple CALMs may be associated with genetic syndromes such as neurofibroma type 1. Macules can be treated with laser therapy for cosmetic purposes.
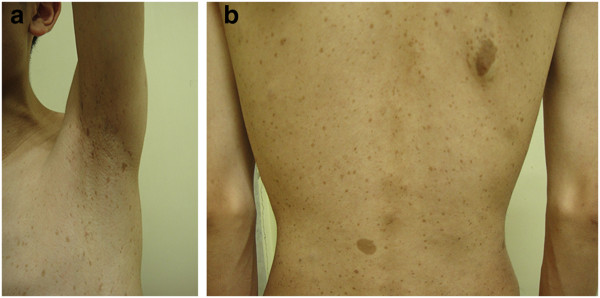
Axillary freckling and café au lait macules (CALMs):
Axillary freckling (a) and multiple CALMs (b) spreading over the skin of the trunk of an individual with neurofibroma type 1 (NF1)
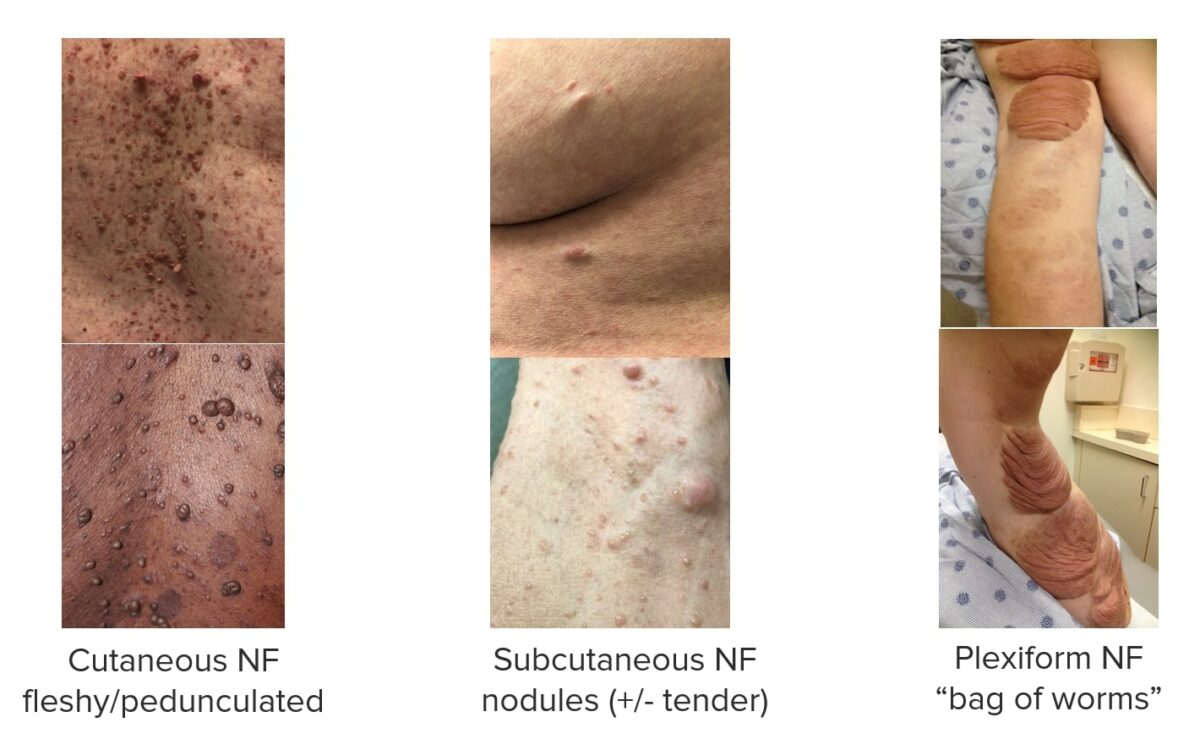
Neurofibromas (NF):
Images showing different types of neurofibromas associated with NF1.
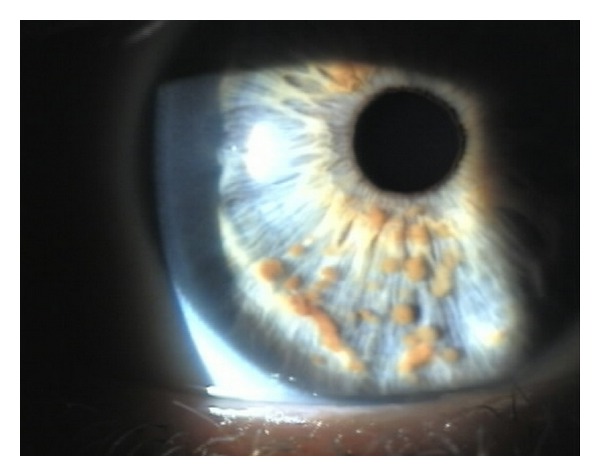
Lisch nodules in the iris:
Image showing pigmented hamartomas that derive from dendritic melanocytes
Image: “Multiple small, oval, yellow-brown papules (Lisch nodules) in the right iris” by Adams, E. G., et al. License: CC BY 3.0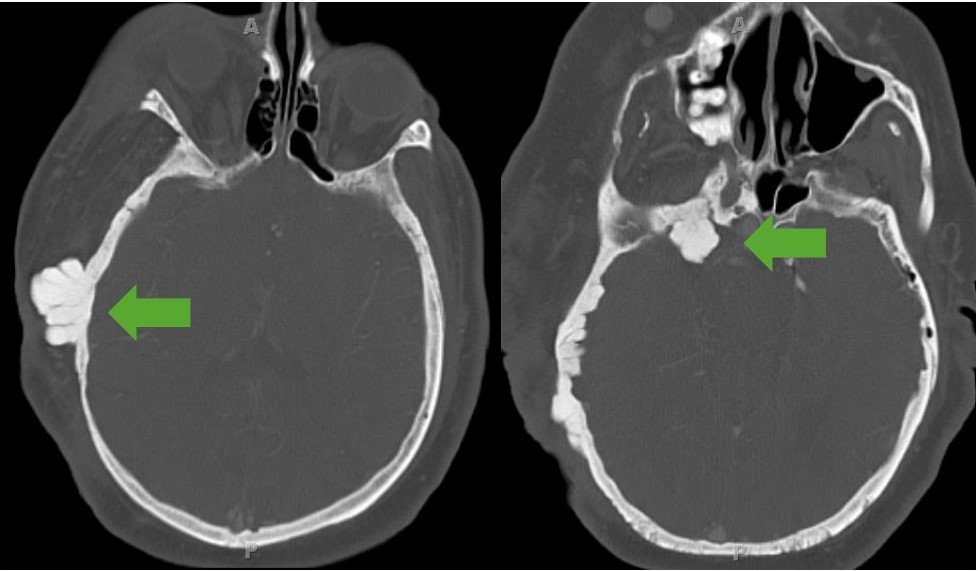
Sphenoid wing dysplasia:
CT image showing exophytic dysplasia of the sphenoid bone. Note the involvement of soft tissue seen as enlargement of the individual’s entire right side of the face.
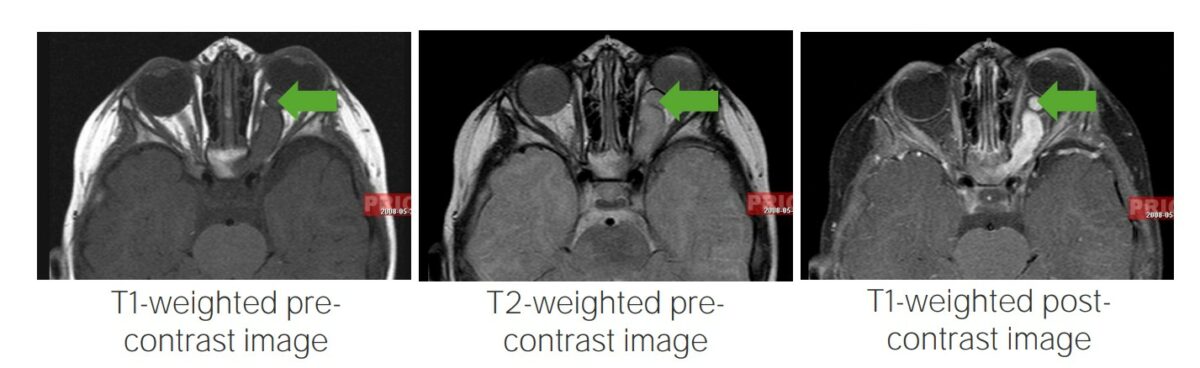
Optic pathway glioma:
MRI images showing optic pathway gliomas, a typical finding in individuals with neurofibroma type 1
The diagnosis of NF1 is usually made clinically based on the typical clinical presentation and confirmed by genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies.