Neuroblastoma is a malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax that arises from the neural crest Neural crest The two longitudinal ridges along the primitive streak appearing near the end of gastrulation during development of nervous system (neurulation). The ridges are formed by folding of neural plate. Between the ridges is a neural groove which deepens as the fold become elevated. When the folds meet at midline, the groove becomes a closed tube, the neural tube. Hirschsprung Disease cell derivatives along the sympathetic chain (neuroblasts) and is most commonly located in the adrenal medulla Adrenal Medulla The inner portion of the adrenal gland. Derived from ectoderm, adrenal medulla consists mainly of chromaffin cells that produces and stores a number of neurotransmitters, mainly adrenaline (epinephrine) and norepinephrine. The activity of the adrenal medulla is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy. The tumor Tumor Inflammation often presents in childhood with a flank mass Mass Three-dimensional lesion that occupies a space within the breast Imaging of the Breast that crosses the midline. Neuroblastoma can also manifest as opsoclonus-myoclonus paraneoplastic syndrome. The tumor Tumor Inflammation is diagnosed through biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma, and supporting data include measuring the catecholamine breakdown products such as vanilmandelic acid (VMA) and homovanillic acid (HVA) in urine. Imaging studies are needed to localize the tumor Tumor Inflammation. Management depends on several factors such as the stage of malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax and the patient’s age at the time of diagnosis. Prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is favorable in the early stages of neuroblastoma.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Neuroblastoma, an extracranial malignant solid tumor Tumor Inflammation, is a neuroendocrine malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax originating from sympathetic nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification stem cells (neuroblasts).
| Categories | Specific tumors |
|---|---|
| Neuroepithelial tumors in the CNS |
|
| Meningeal tumors |
|
| Sellar region tumors |
|
| Primary CNS lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum | Primary CNS lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum |
| Metastasis Metastasis The transfer of a neoplasm from one organ or part of the body to another remote from the primary site. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis to the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification (5x more common than primary brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification tumors) | Most commonly arising from: |
| Peripheral tumors |
|
Neuroblastomas arise from mutations in primitive cells of the sympathetic ganglion (which includes the adrenal medulla Adrenal Medulla The inner portion of the adrenal gland. Derived from ectoderm, adrenal medulla consists mainly of chromaffin cells that produces and stores a number of neurotransmitters, mainly adrenaline (epinephrine) and norepinephrine. The activity of the adrenal medulla is regulated by the sympathetic nervous system. Adrenal Glands: Anatomy). The cells are known as neuroblasts and are derived from neural crest cells Neural crest cells Gastrulation and Neurulation.
The diagnosis is suspected based on history and exam findings. The key lab tests for neuroblastomas show evidence of elevated catecholamines Catecholamines A general class of ortho-dihydroxyphenylalkylamines derived from tyrosine. Adrenal Hormones. Imaging is used to identify the tumor Tumor Inflammation, and a biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma is required for definitive diagnosis.
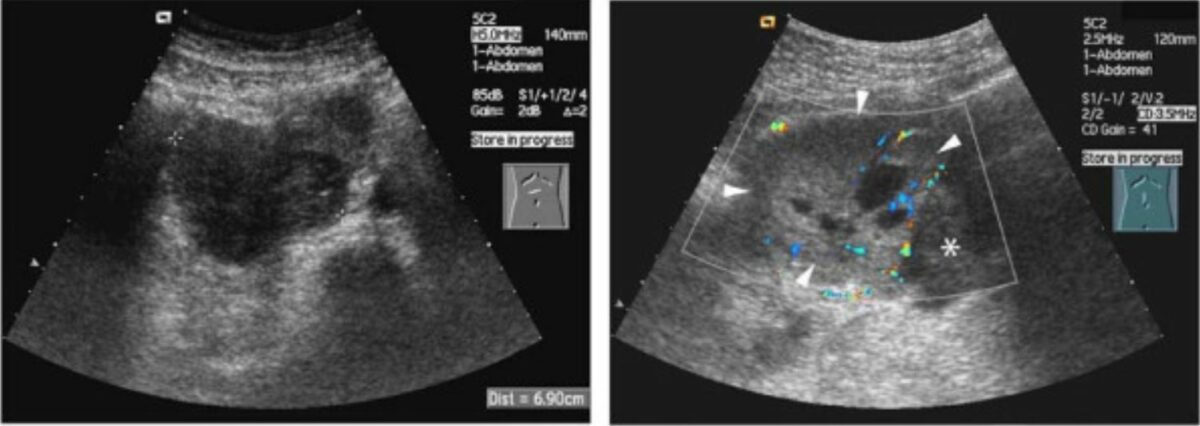
Ultrasound of neuroblastoma:
The classic appearance is a heterogenous mass with internal vascularity.
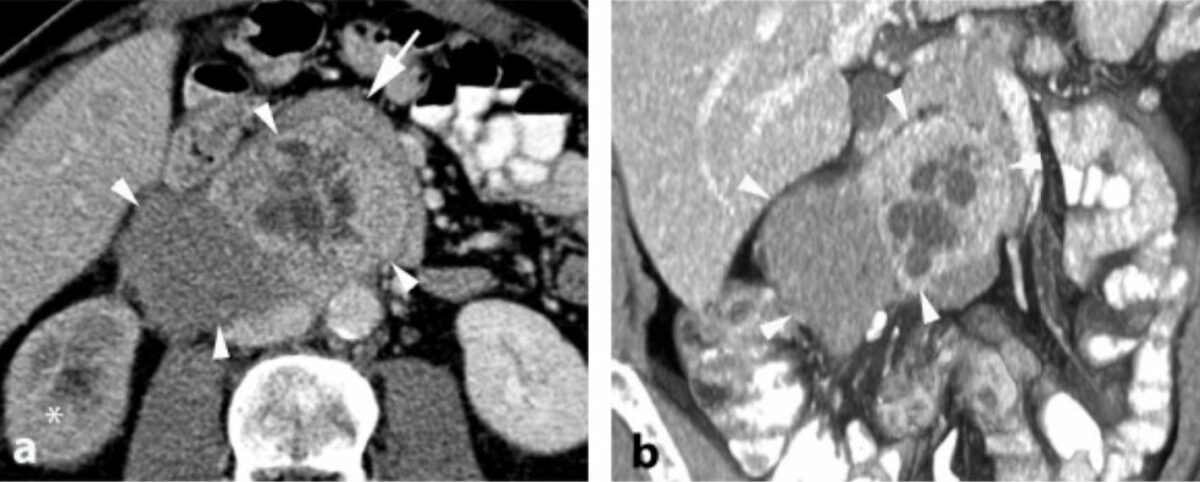
CT of neuroblastoma:
The tumor commonly appears heterogenous with calcifications.
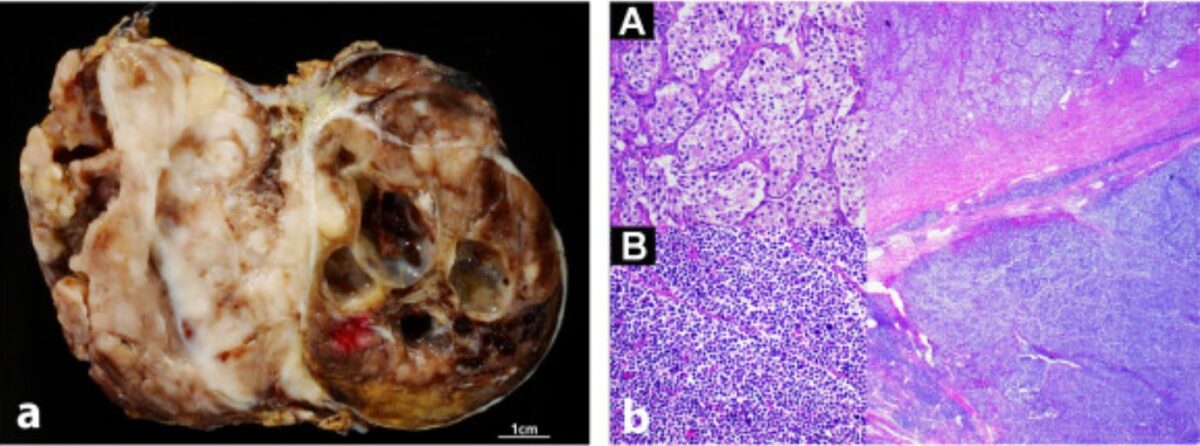
Neuroblastoma in gross and histologic appearance: macroscopic (left) and microscopic (right) images of neuroblastoma
Image: “Radiological and pathological findings of a metastatic composite paraganglioma with neuroblastoma in a man: a case report” by Fritzsche FR, Bode PK, Koch S, Frauenfelder T. License: CC BY 2.0Multiple staging Staging Methods which attempt to express in replicable terms the extent of the neoplasm in the patient. Grading, Staging, and Metastasis systems exist, but the INSS is one of the most common. Body imaging, a biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma of the primary tumor Tumor Inflammation, bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma, and a bone scan Bone Scan Osteosarcoma are required:
Management of neuroblastoma depends on whether the patient is considered to have a low-, intermediate-, or high-risk neuroblastoma. Localized disease is often curable.
Risk stratification depends on the stage of the malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax at the time of the diagnosis, MYCN amplification, chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 1p deletion, and age at the time of the diagnosis (later age of diagnosis = worse prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual’s condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas).