Nephrotic syndrome is a renal disorder caused by conditions that increase the permeability of the glomerular filtration barriers. Nephrotic syndrome affects all age groups but has a higher pediatric prevalence. This disorder can be due to both primary (renal) and secondary (systemic) causes. Minimal change disease (MCD), is the most common presentation in children. Hallmark features include proteinuria of >40 mg/m²/hour, hypoalbuminemia, hypercholesterolemia Hypercholesterolemia A condition with abnormally high levels of cholesterol in the blood. It is defined as a cholesterol value exceeding the 95th percentile for the population. Lipid Disorders, and edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema. Diagnosis is based on history, physical exam, laboratory tests confirming nephrotic-range proteinuria and workup for systemic disease. Genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies is recommended in some cases. Steroids Steroids A group of polycyclic compounds closely related biochemically to terpenes. They include cholesterol, numerous hormones, precursors of certain vitamins, bile acids, alcohols (sterols), and certain natural drugs and poisons. Steroids have a common nucleus, a fused, reduced 17-carbon atom ring system, cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene. Most steroids also have two methyl groups and an aliphatic side-chain attached to the nucleus. Benign Liver Tumors are the initial treatment in a classic presentation of the typically steroid-responsive MCD. In other cases, renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis is indicated. Management and prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas vary depending on the underlying cause and response to steroids Steroids A group of polycyclic compounds closely related biochemically to terpenes. They include cholesterol, numerous hormones, precursors of certain vitamins, bile acids, alcohols (sterols), and certain natural drugs and poisons. Steroids have a common nucleus, a fused, reduced 17-carbon atom ring system, cyclopentanoperhydrophenanthrene. Most steroids also have two methyl groups and an aliphatic side-chain attached to the nucleus. Benign Liver Tumors.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by severe proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and peripheral edema. In contrast, the nephritic syndromes present with hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephrotic Syndrome is a renal disorder characterized by increased permeability of the glomerular filtration Glomerular filtration The kidneys are primarily in charge of the maintenance of water and solute homeostasis through the processes of filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion. Glomerular filtration is the process of converting the systemic blood supply into a filtrate, which will ultimately become the urine. Glomerular Filtration barriers significantly leading to severe proteinuria.
Classic features include:
Different general classification systems can overlap:
Idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by severe proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and peripheral edema. In contrast, the nephritic syndromes present with hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephrotic Syndrome is further classified on the basis of steroid responsiveness:
Congenital/infantile:
Primary (90% idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis):
Secondary:
The structure of the glomerulus creates a filtration system, the glomerular filtration Glomerular filtration The kidneys are primarily in charge of the maintenance of water and solute homeostasis through the processes of filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion. Glomerular filtration is the process of converting the systemic blood supply into a filtrate, which will ultimately become the urine. Glomerular Filtration barrier, composed of:
Under normal circumstances, the passage of proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis across the glomerular filtration Glomerular filtration The kidneys are primarily in charge of the maintenance of water and solute homeostasis through the processes of filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion. Glomerular filtration is the process of converting the systemic blood supply into a filtrate, which will ultimately become the urine. Glomerular Filtration barrier is controlled by their size or charge.
Genetic or immune-mediated factors lead to:
Effects:
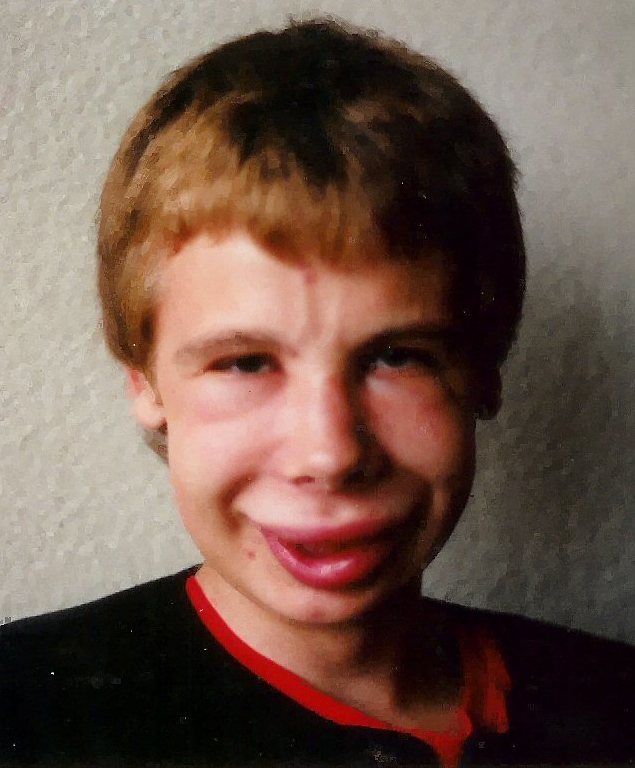
Nephrotic syndrome:
Condition is accompanied by retention of water and sodium. The image shows facial swelling/edema. The degree to which edema occurs can vary between slight edema in the eyelids that decreases during the day, to swelling affecting the lower limbs, to generalized swelling or full-blown anasarca.
| Nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by severe proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and peripheral edema. In contrast, the nephritic syndromes present with hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephrotic Syndrome | Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome is a broad category of glomerular diseases characterized by glomerular hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension. These features are in contrast to those of nephrotic syndrome, which includes glomerular diseases characterized by severe proteinuria, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephritic Syndrome | |
|---|---|---|
| Edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema | ++++ | ++ |
| Blood pressure | Normal/raised | Raised |
| Proteinuria | ++++ | ++ |
| Hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma | – or microscopic | +++ |
| Other features |
|
|
| Nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by severe proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and peripheral edema. In contrast, the nephritic syndromes present with hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephrotic Syndrome | Laboratory and additional tests | Renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis results |
|---|---|---|
| MCD | Renal function generally remains good; no hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma |
|
| FSGS | May have hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma in urine |
|
| Mesangial proliferation | May have hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma in urine |
|
| MPGN MPGN Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) is also known as mesangiocapillary glomerulonephritis. Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis is a pattern of glomerular injury characterized by mesangial hypercellularity, endocapillary proliferation, and thickening of the glomerular basement membrane (double contour formation). Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis (a pattern of glomerular injury with types I–III) | ↓ C3 |
|
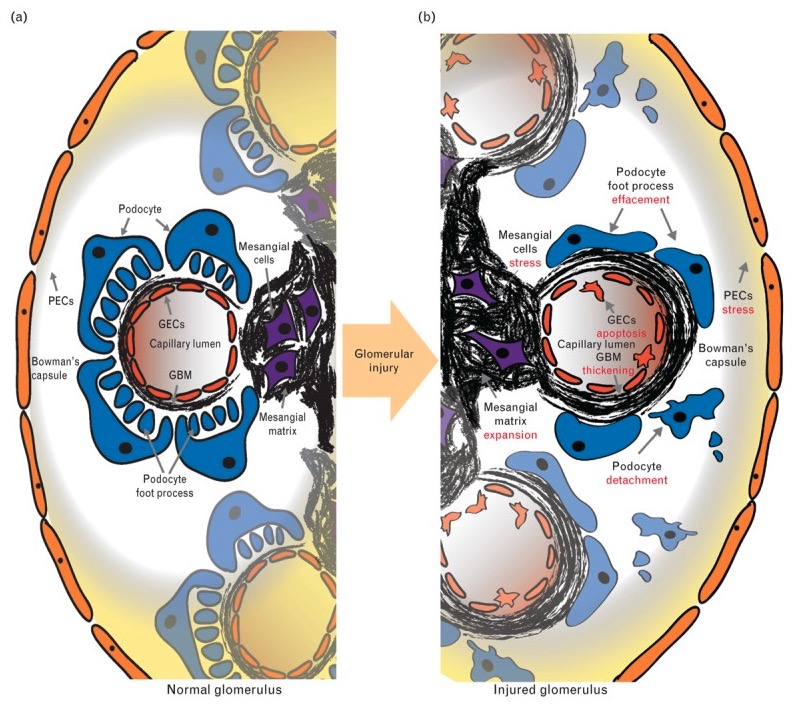
Normal glomerulus versus glomerular disease:
The normal structure (a): PECs (parietal epithelial cells) line Bowman’s capsule; podocytes, GECs (glomerular endothelial cells) form the capillary wall; and mesangial cells are centrally located within the glomerular tuft. The two main extracellular matrix compartments are the GBM and the mesangial matrix.
In glomerular injury (b): Morphologic change is observed across the spectrum of glomerular disease and includes mesangial cell proliferation, mesangial matrix expansion (seen in mesangial proliferative nephropathy and MPGN, GBM thickening (seen in MPGN), podocyte foot process effacement, and podocyte detachment (seen in FSGS and MCD).
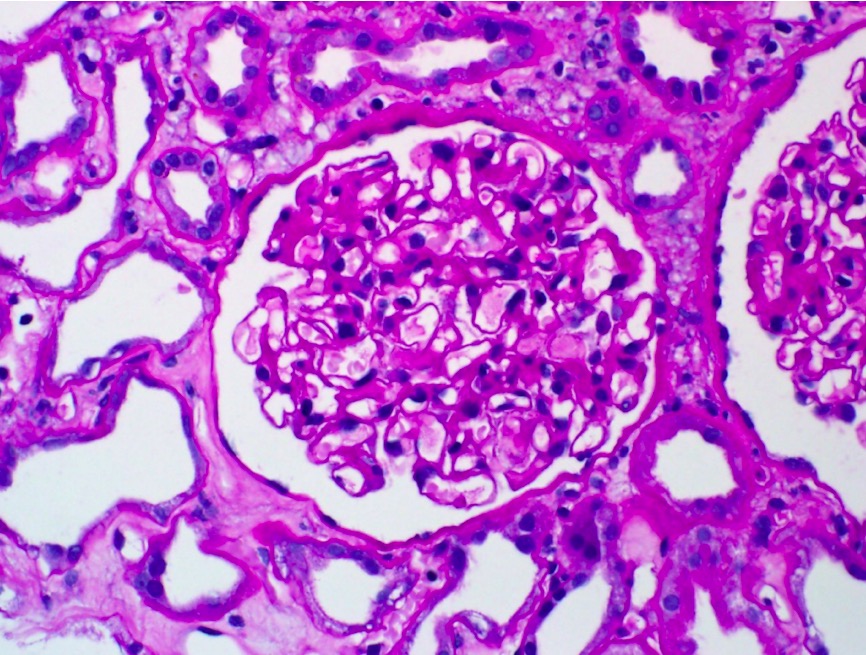
Minimal change disease:
Light microscopy shows no evidence of cellular crescents, fibrinoid necrosis, or endocapillary hypercellularity.
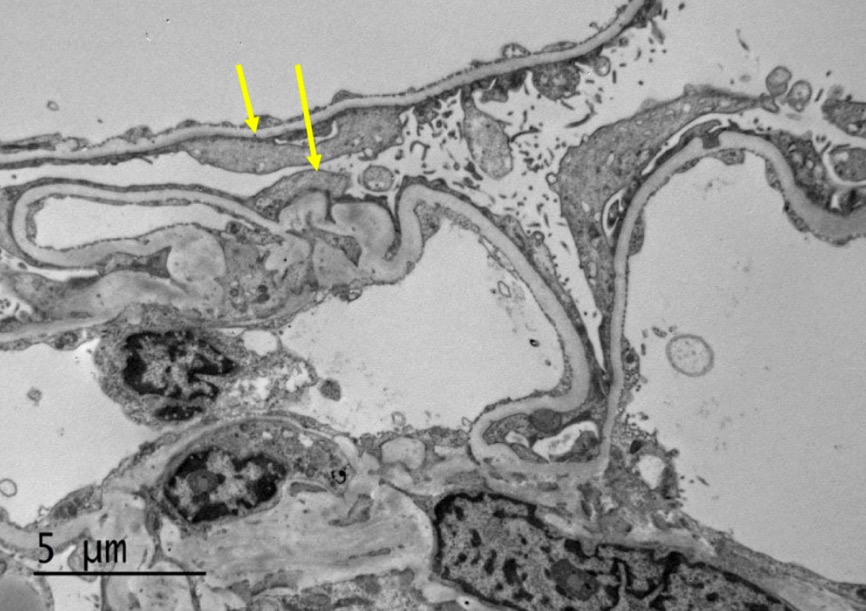
Electron microscopy of MCD:
The image shows diffuse effacement of podocyte foot processes (arrows). The capillary loop basement membranes are uniform and of normal thickness. No capillary loop hypercellularity or sclerosis or electron-dense deposits are identified. The mesangial matrix is not expanded and has no hypercellularity or electron-dense deposits. The tubular basement membranes do not show evidence of immune-type deposits.
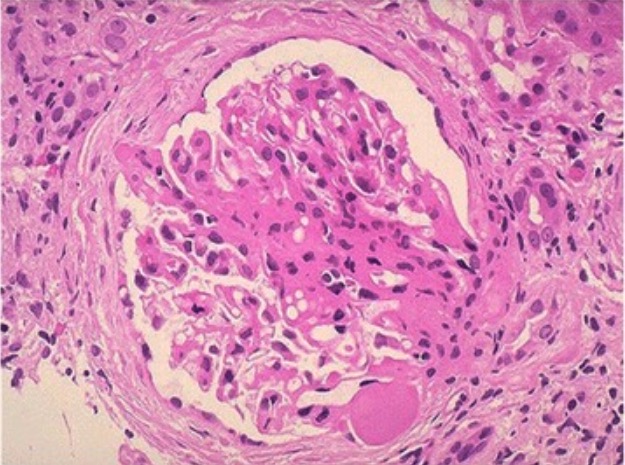
Photomicrograph of FSGS:
An area of collagenous sclerosis runs across the middle of the glomerulus.