Nephrolithiasis is the formation of a stone, or calculus, anywhere along the urinary tract Urinary tract The urinary tract is located in the abdomen and pelvis and consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The structures permit the excretion of urine from the body. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and out through the urethra. Urinary Tract: Anatomy caused by the precipitation of solutes in the urine anywhere along the urinary tract Urinary tract The urinary tract is located in the abdomen and pelvis and consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The structures permit the excretion of urine from the body. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and out through the urethra. Urinary Tract: Anatomy. The most common type of kidney stone is the calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes oxalate, but other types include calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes phosphate Phosphate Inorganic salts of phosphoric acid. Electrolytes, struvite (ammonium magnesium Magnesium A metallic element that has the atomic symbol mg, atomic number 12, and atomic weight 24. 31. It is important for the activity of many enzymes, especially those involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Electrolytes phosphate Phosphate Inorganic salts of phosphoric acid. Electrolytes), uric acid, and cystine stones. Nephrolithiasis presents with severe, colicky flank pain Flank pain Pain emanating from below the ribs and above the ilium. Renal Cell Carcinoma, that often radiates to the groin Groin The external junctural region between the lower part of the abdomen and the thigh. Male Genitourinary Examination, and hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma due to ureteral damage. Diagnosis is made by noncontrast CT of the abdomen and pelvis Pelvis The pelvis consists of the bony pelvic girdle, the muscular and ligamentous pelvic floor, and the pelvic cavity, which contains viscera, vessels, and multiple nerves and muscles. The pelvic girdle, composed of 2 "hip" bones and the sacrum, is a ring-like bony structure of the axial skeleton that links the vertebral column with the lower extremities. Pelvis: Anatomy or by renal ultrasound, and urinalysis Urinalysis Examination of urine by chemical, physical, or microscopic means. Routine urinalysis usually includes performing chemical screening tests, determining specific gravity, observing any unusual color or odor, screening for bacteriuria, and examining the sediment microscopically. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) in Children is needed to exclude concomitant urinary tract Urinary tract The urinary tract is located in the abdomen and pelvis and consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The structures permit the excretion of urine from the body. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and out through the urethra. Urinary Tract: Anatomy infection ( UTI UTI Urinary tract infections (UTIs) represent a wide spectrum of diseases, from self-limiting simple cystitis to severe pyelonephritis that can result in sepsis and death. Urinary tract infections are most commonly caused by Escherichia coli, but may also be caused by other bacteria and fungi. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs)). Management depends on the size of the stone. Small stones (< 5 mm) are likely to pass on their own and are managed expectantly with hydration and analgesics. Large stones unlikely to pass spontaneously are treated with extracorporeal shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL), ureterorenoscopy, or percutaneous nephrolithotomy. Nephrolithiasis can be complicated by hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis is dilation of the renal collecting system as a result of the obstruction of urine outflow. Hydronephrosis can be unilateral or bilateral. Nephrolithiasis is the most common cause of hydronephrosis in young adults, while prostatic hyperplasia and neoplasm are seen in older patients. Hydronephrosis or acute pyelonephritis Acute pyelonephritis Inflammation of the kidney involving the renal parenchyma (the nephrons); kidney pelvis; and kidney calices. It is characterized by abdominal pain; fever; nausea; vomiting; and occasionally diarrhea. Imaging of the Urinary System. Adequate hydration is the best prophylactic intervention to prevent kidney stones.
Last updated: May 26, 2025
Nephrolithiasis (also known as kidney stones, urolithiasis, or urinary calculi) is the formation of stones anywhere along the urinary tract Urinary tract The urinary tract is located in the abdomen and pelvis and consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra. The structures permit the excretion of urine from the body. Urine flows from the kidneys through the ureters to the urinary bladder and out through the urethra. Urinary Tract: Anatomy.
There are 5 main types of kidney stones:
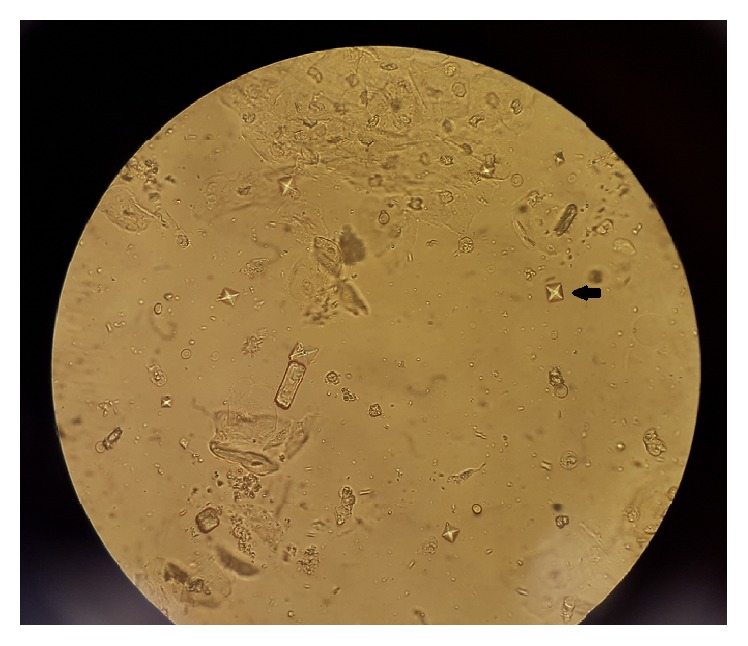
Black arrow showing an envelope, or dumbbell-shaped, calcium oxalate crystal under microscopy
Image: “Ethylene Glycol Poisoning: An Unusual Cause of Altered Mental Status and the Lessons Learned from Management of the Disease in the Acute Setting” by Case Reports in Critical Care. License: CC BY 4.0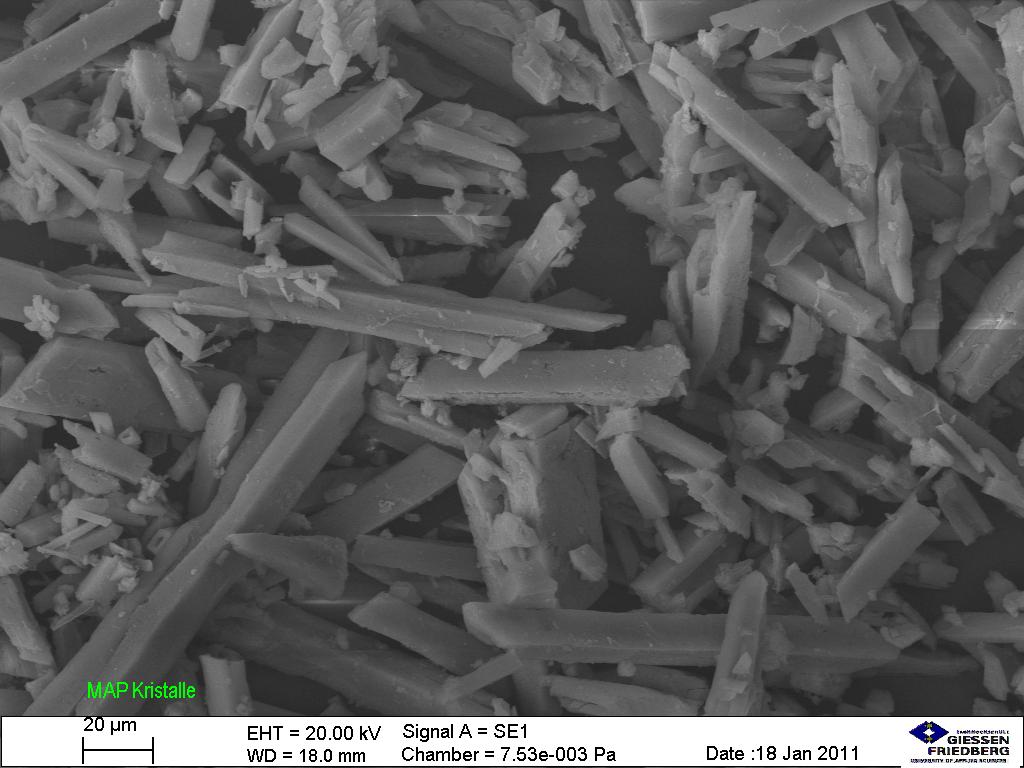
Struvite stone crystals under microscopy
Image: “Struvite under the microscope (5534899028)” by Sustainable Sanitation Alliance. License: CC BY 2.0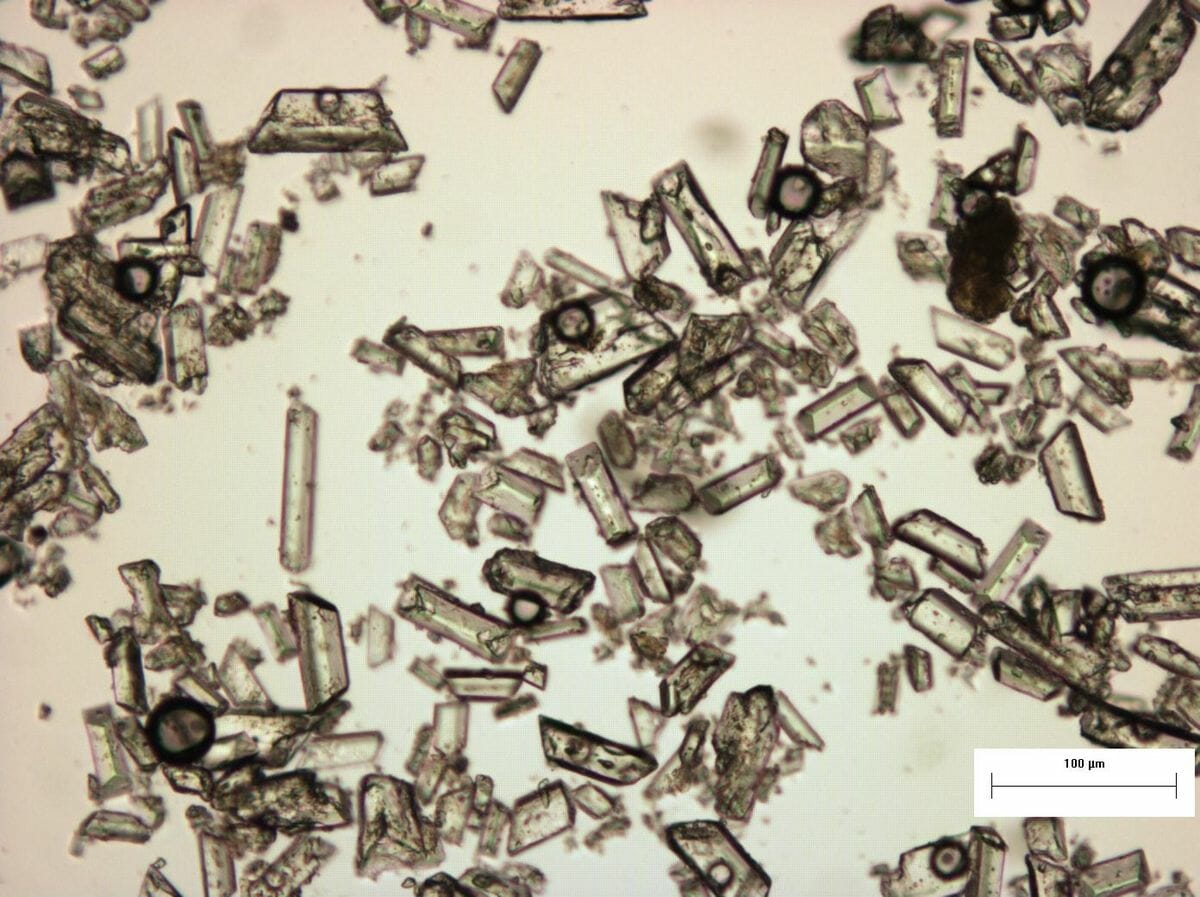
Struvite crystals and their specific structures under a microscope.
Image: “Struvite under the microscope (5267841405)” by SuSanA Secretariat. License: CC BY 2.0Normally soluble material supersaturates the urine and crystal formation begins.
Risk factors:
| Type of stone | % | Causes | Crystals | Urine pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes oxalate | 75% |
|
Envelope Envelope Bilayer lipid membrane acquired by viral particles during viral morphogenesis. Although the lipids of the viral envelope are host derived, various virus-encoded integral membrane proteins, i.e. Viral envelope proteins are incorporated there. Virology or dumbbell shaped | ↓ |
| Uric acid | 10% |
|
Rhomboid or rosette shaped | ↓ |
| Struvite (ammonium magnesium Magnesium A metallic element that has the atomic symbol mg, atomic number 12, and atomic weight 24. 31. It is important for the activity of many enzymes, especially those involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Electrolytes phosphate Phosphate Inorganic salts of phosphoric acid. Electrolytes) | 5%–10% | UTI UTI Urinary tract infections (UTIs) represent a wide spectrum of diseases, from self-limiting simple cystitis to severe pyelonephritis that can result in sepsis and death. Urinary tract infections are most commonly caused by Escherichia coli, but may also be caused by other bacteria and fungi. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) with urease-positive Urease-positive Helicobacter bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology | Coffin-lid shaped | ↑ |
| Calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes phosphate Phosphate Inorganic salts of phosphoric acid. Electrolytes | 5% | Increased urine pH pH The quantitative measurement of the acidity or basicity of a solution. Acid-Base Balance | Wedge-shaped prism | ↑ |
| Cystine | < 5% | Cystinuria | Hexagonal | ↓ |
Imaging:
Laboratory studies:
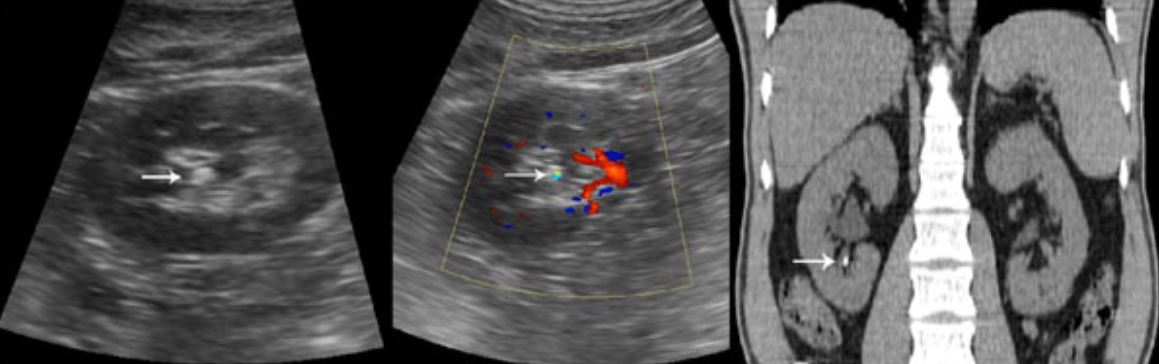
Left: White arrow shows renal calculus on ultrasound.
Right: White arrow shows renal calculus on CT scan.
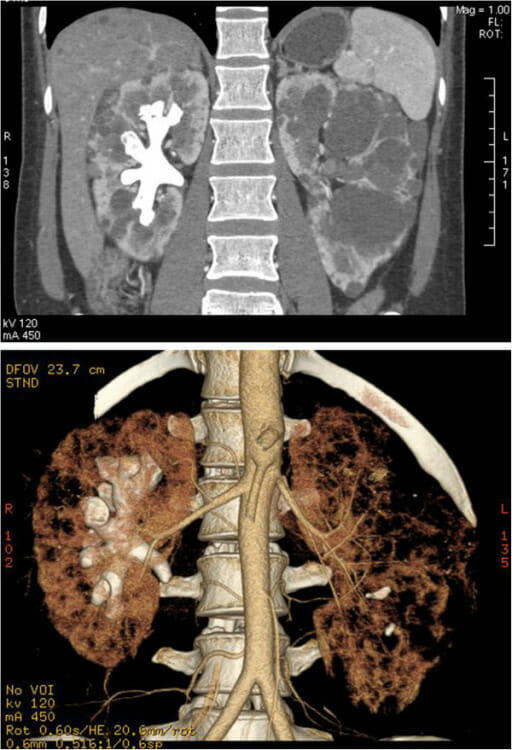
CT images of a complete staghorn calculus in the right kidney of a woman with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease:
Above: staghorn calculus and polycystic kidney in the coronal plane
Below: 3D image of the reconstructed calculus and kidney
General supportive care:
Stone-specific management: