Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome is a broad category of glomerular diseases characterized by glomerular hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension. These features are in contrast to those of nephrotic syndrome, which includes glomerular diseases characterized by severe proteinuria, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephritic Syndrome is a renal condition with signs and symptoms produced by inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body's defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation of the glomeruli (glomerulonephritis) and increased permeability of the glomerular barriers. Defining features include hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children (but below nephrotic range), RBC casts with dysmorphic RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology on urine microscopy, and increased serum creatinine. Causes can be genetic, autoimmune, idiopathic Idiopathic Dermatomyositis, or post-infectious. The most common cause is acute post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis. General clinical findings include edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema, hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, and oliguria Oliguria Decreased urine output that is below the normal range. Oliguria can be defined as urine output of less than or equal to 0. 5 or 1 ml/kg/hr depending on the age. Renal Potassium Regulation. Diagnosis is made based on history, physical exam, and laboratory data. A renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis is sometimes necessary to establish the underlying cause. There can be a combined nephritic-nephrotic picture, especially in the chronic presentation. Treatment and prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas depend on cause and severity.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome is a broad category of glomerular diseases characterized by glomerular hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension. These features are in contrast to those of nephrotic syndrome, which includes glomerular diseases characterized by severe proteinuria, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephritic Syndrome is defined as renal disease caused by immune-mediated inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation and injury of the glomeruli with classic features of:
Primary (renal) causes of nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome is a broad category of glomerular diseases characterized by glomerular hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension. These features are in contrast to those of nephrotic syndrome, which includes glomerular diseases characterized by severe proteinuria, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephritic Syndrome in children:
Secondary causes of nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome is a broad category of glomerular diseases characterized by glomerular hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension. These features are in contrast to those of nephrotic syndrome, which includes glomerular diseases characterized by severe proteinuria, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephritic Syndrome in children:

Urinary sample with hematuria: dark or tea-colored urine
Image: “hematuria” by omicsonline.org. License: CC BY 4.0
Severe case of IgA vasculitis or Henoch-Schönlein purpura:
Palpable purpura is noted on on the child’s foot, leg, and arm.
Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship can also present with manifestations of severe disease:
Clinical findings are specific to the underlying causes.
Laboratory data:
Imaging (renal ultrasound):
Disease-specific tests:
| Nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by severe proteinuria, hypoalbuminemia, and peripheral edema. In contrast, the nephritic syndromes present with hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephrotic Syndrome | Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome is a broad category of glomerular diseases characterized by glomerular hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension. These features are in contrast to those of nephrotic syndrome, which includes glomerular diseases characterized by severe proteinuria, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephritic Syndrome | |
|---|---|---|
| Edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema | ++++ | ++ |
| Blood pressure | Normal/raised | Raised |
| Proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children | ++++ | ++ |
| Hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma | – or microscopic | +++ |
| Other features |
|
|
| Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome Nephritic syndrome is a broad category of glomerular diseases characterized by glomerular hematuria, variable loss of renal function, and hypertension. These features are in contrast to those of nephrotic syndrome, which includes glomerular diseases characterized by severe proteinuria, although there is sometimes overlap of > 1 glomerular disease in the same individual. Nephritic Syndrome | Laboratory and additional tests | Renal biopsy Renal Biopsy Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-Associated Vasculitis results |
|---|---|---|
| Acute post-streptococcal GN |
|
|
| Membranoproliferative GN (a pattern of glomerular injury, not a specific disease; has types I-III) | ↓ C3 |
|
| Lupus GN |
|
|
| IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions nephropathy | Normal C3 |
|
| HSP HSP Henoch-Schönlein purpura (HSP), also known as immunoglobulin A vasculitis, is an autoimmune small-vessel vasculitis that typically presents as a tetrad of abdominal pain, arthralgia, hematuria, and purpuric rash. Henoch-Schönlein Purpura/ IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus |
|
|
| Alport syndrome Alport Syndrome Alport syndrome, also called hereditary nephritis, is a genetic disorder caused by a mutation in the genes encoding for the alpha chains of type IV collagen, resulting in the production of abnormal type IV collagen strands. Patients present with glomerulonephritis, hypertension, edema, hematuria, and proteinuria, as well as with ocular and auditory findings. Alport Syndrome (hereditary GN) | Skin biopsy Skin Biopsy Secondary Skin Lesions: monoclonal Ab against the alpha-5 (IV) chain (protein is absent) | EM: splitting Splitting Defense Mechanisms of the GBM, basketweave appearance |
| Rapidly progressive GN (denotes severe glomerular injury, but has different etiologies) | Depends on the underlying cause | Most common histology: crescent Crescent Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis formation in glomeruli |
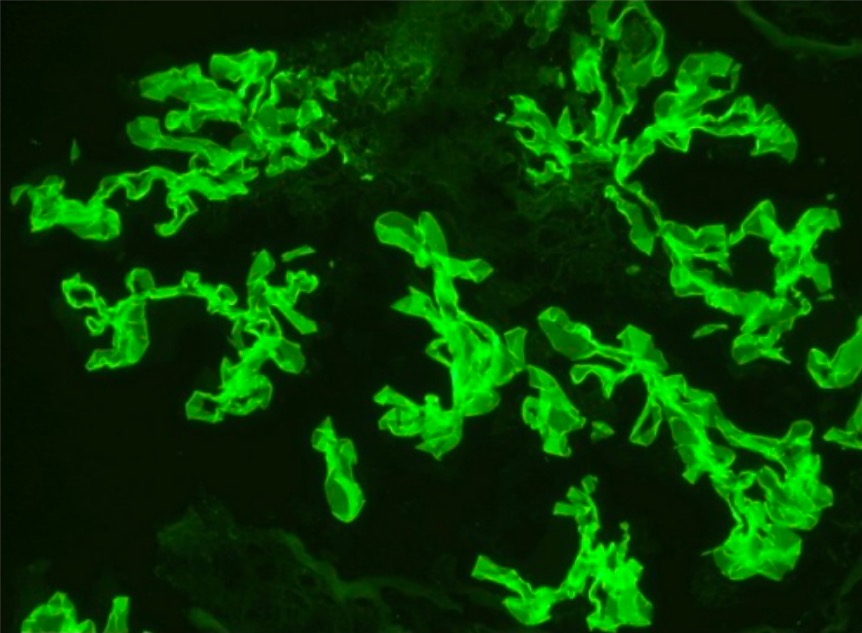
Immunofluorescence staining showing linear GBM staining for IgG consistent with Goodpasture’s disease membrane
Image: “Immunofluorescence staining” by Department of Internal Medicine, University of Oklahoma Health Sciences Center, Oklahoma City, OK 73117, USA. License: CC BY 3.0
IgA nephropathy: glomerulus with thickened mesangium and segmental mesangial hypercellularity
Image: “Glomerulus” by Section of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV 26506, USA. License: CC BY 4.0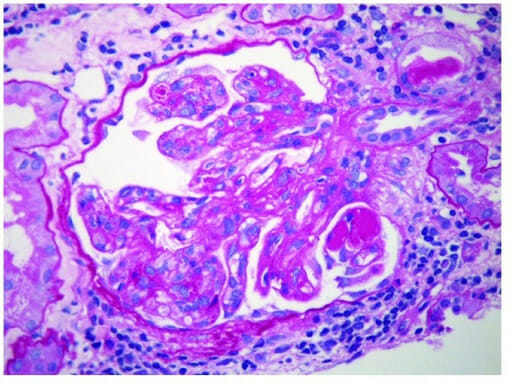
Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis:
Endocapillary proliferation with extensive subendothelial deposits along the glomerular capillary walls. Mesangial deposits are also present (electron microscopy).
Management depends on the cause and severity.