Neonatal abstinence syndrome (NAS), or neonatal withdrawal syndrome (NWS), occurs when in-utero addictive substances are suddenly discontinued due to birth. The most common substances include alcohol, nicotine Nicotine Nicotine is highly toxic alkaloid. It is the prototypical agonist at nicotinic cholinergic receptors where it dramatically stimulates neurons and ultimately blocks synaptic transmission. Nicotine is also important medically because of its presence in tobacco smoke. Stimulants, and rapidly increasing opioids Opioids Opiates are drugs that are derived from the sap of the opium poppy. Opiates have been used since antiquity for the relief of acute severe pain. Opioids are synthetic opiates with properties that are substantially similar to those of opiates. Opioid Analgesics. Some infants can also develop withdrawal symptoms from intrapartum or postnatal exposure to medication used for pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways control during labor. Clinical symptoms such as irritability, a high-pitched cry, tremor Tremor Cyclical movement of a body part that can represent either a physiologic process or a manifestation of disease. Intention or action tremor, a common manifestation of cerebellar diseases, is aggravated by movement. In contrast, resting tremor is maximal when there is no attempt at voluntary movement, and occurs as a relatively frequent manifestation of parkinson disease. Myotonic Dystrophies, fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, poor feeding, and hypertonia Hypertonia Abnormal increase in skeletal or smooth muscle tone. Skeletal muscle hypertonicity may be associated with pyramidal tract lesions or basal ganglia diseases. Neurological Examination can begin within hours of life and vary depending on the substance of exposure and, in some cases, multiple substances. Diagnosis is made by history, clinical presentation, and laboratory findings. Treatment is dependent on the substance(s) of exposure and severity of symptoms. The complications can be lifelong and include growth restrictions, decreased cognition, poor academic achievement, and fetal anomalies as seen in infants with fetal alcohol syndrome Fetal alcohol syndrome An umbrella term used to describe a pattern of disabilities and abnormalities that result from fetal exposure to ethanol during pregnancy. It encompasses a phenotypic range that can vary greatly between individuals, but reliably includes one or more of the following: characteristic facial dysmorphism, fetal growth retardation, central nervous system abnormalities, cognitive and/or behavioral dysfunction, birth defects. The level of maternal alcohol consumption does not necessarily correlate directly with disease severity. Alcohol Use Disorder.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
| Percentage of cases | Drug use |
|---|---|
| 20 | Marijuana |
| 16 | Cigarette smoking Smoking Willful or deliberate act of inhaling and exhaling smoke from burning substances or agents held by hand. Interstitial Lung Diseases |
| 8.5 | Alcohol use (any amount is considered unsafe) |
| 5.9 | Illicit drugs Illicit Drugs Drugs that are manufactured, obtained, or sold illegally. They include prescription drugs obtained or sold without prescription and non-prescription drugs. Illicit drugs are widely distributed, tend to be grossly impure and may cause unexpected toxicity. Delirium |
Different substances are associated with NAS.
The pathophysiology of NAS is complex and not clearly understood.
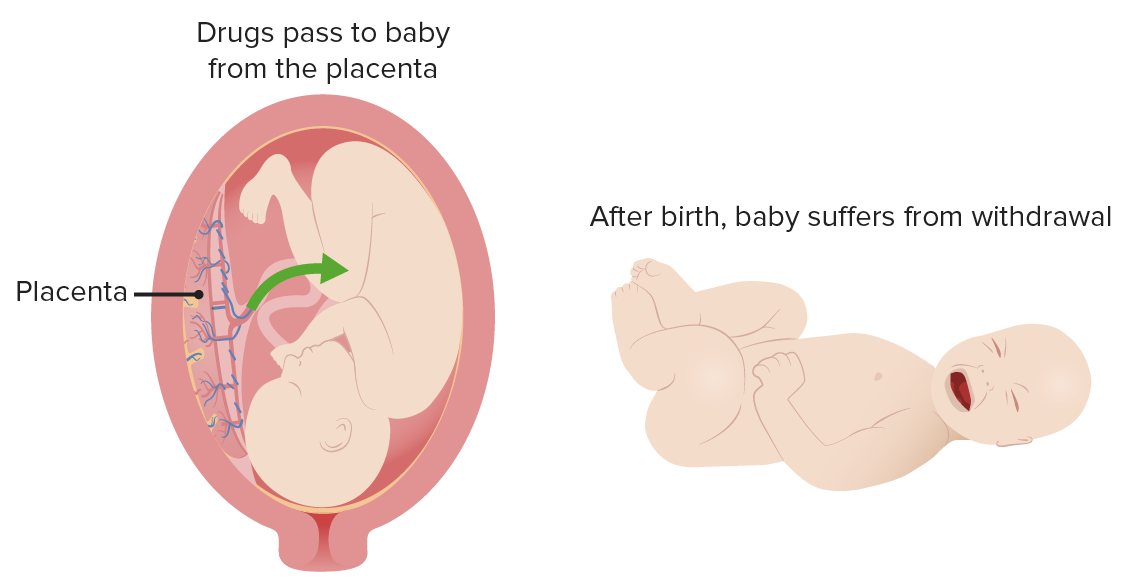
Neonatal abstinence syndrome
Image by Lecturio.Presentation can vary depending upon different factors, including:
| Gastrointestinal symptoms | Central nervous system Central nervous system The main information-processing organs of the nervous system, consisting of the brain, spinal cord, and meninges. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification symptoms | Autonomic symptoms Autonomic Symptoms Cluster Headaches |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
| Drug class | Examples | Onset after birth | Withdrawal duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Short-acting opioids Opioids Opiates are drugs that are derived from the sap of the opium poppy. Opiates have been used since antiquity for the relief of acute severe pain. Opioids are synthetic opiates with properties that are substantially similar to those of opiates. Opioid Analgesics | Heroin Heroin A narcotic analgesic that may be habit-forming. It is a controlled substance (opium derivative) listed in the U.S. Code of federal regulations, title 21 parts 329. 1, 1308. 11 (1987). Sale is forbidden in the United States by federal statute. Nephrotic Syndrome, hydrocodone Hydrocodone Opioid Analgesics, oxycodone Oxycodone A semisynthetic derivative of codeine. Opioid Analgesics, fentanyl Fentanyl A potent narcotic analgesic, abuse of which leads to habituation or addiction. It is primarily a mu-opioid agonist. Fentanyl is also used as an adjunct to general anesthetics, and as an anesthetic for induction and maintenance. Opioid Analgesics | 24–48 hours | 8–30 days |
| Long-acting opioids Opioids Opiates are drugs that are derived from the sap of the opium poppy. Opiates have been used since antiquity for the relief of acute severe pain. Opioids are synthetic opiates with properties that are substantially similar to those of opiates. Opioid Analgesics | Methadone Methadone A synthetic opioid that is used as the hydrochloride. It is an opioid analgesic that is primarily a mu-opioid agonist. Opioid Analgesics, buprenorphine Buprenorphine A derivative of the opioid alkaloid thebaine that is a more potent and longer lasting analgesic than morphine. It appears to act as a partial agonist at mu and kappa opioid receptors and as an antagonist at delta receptors. The lack of delta-agonist activity has been suggested to account for the observation that buprenorphine tolerance may not develop with chronic use. Opioid Analgesics | 24–72 hours, but can be delayed to up to 5 days | Up to 30 days |
| Benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines Benzodiazepines work on the gamma-aminobutyric acid type A (GABAA) receptor to produce inhibitory effects on the CNS. Benzodiazepines do not mimic GABA, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter in humans, but instead potentiate GABA activity. Benzodiazepines | Diazepam Diazepam A benzodiazepine with anticonvulsant, anxiolytic, sedative, muscle relaxant, and amnesic properties and a long duration of action. Its actions are mediated by enhancement of gamma-aminobutyric acid activity. Benzodiazepines, alprazolam Alprazolam A triazolobenzodiazepine compound with antianxiety and sedative-hypnotic actions, that is efficacious in the treatment of panic disorders, with or without agoraphobia, and in generalized anxiety disorders. Benzodiazepines, lorazepam Lorazepam A benzodiazepine used as an anti-anxiety agent with few side effects. It also has hypnotic, anticonvulsant, and considerable sedative properties and has been proposed as a preanesthetic agent. Benzodiazepines | 24–48 hours | Up to 14 days |
| Antidepressants | SSRIs SSRIs Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants, SNRIs SNRIs Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants, tricyclics | 24–48 hours | 2–8 days |
| Nicotine Nicotine Nicotine is highly toxic alkaloid. It is the prototypical agonist at nicotinic cholinergic receptors where it dramatically stimulates neurons and ultimately blocks synaptic transmission. Nicotine is also important medically because of its presence in tobacco smoke. Stimulants | Cigarettes | 24–48 hours | 7 days |
| Alcohol | Beer, wine, hard liquor | 2–12 hours | 3 days |
| Specimen | Detection | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Urine or blood (common method) | Detects exposure from a few days before birth | Noninvasive bag collection; best sample is the first urine |
| Cord blood | Detects exposure from few days to few hours before birth | Drug concentrations can be low. Thus, results can be falsely negative. |
| Meconium Meconium The thick green-to-black mucilaginous material found in the intestines of a full-term fetus. It consists of secretions of the intestinal glands; bile pigments; fatty acids; amniotic fluid; and intrauterine debris. It constitutes the first stools passed by a newborn. Prenatal and Postnatal Physiology of the Neonate stool (stool from the first bowel movement) | Detects exposure from the second trimester |
|
| Hair | Detects exposure from the third trimester to 3 months after birth | Must cut hair close to the scalp and therefore can be limited if there is insufficient hair at birth or growth |
The goal of management is to minimize the severity of NAS signs through supportive measures and, in severe cases, pharmacological measures.
| Opioids Opioids Opiates are drugs that are derived from the sap of the opium poppy. Opiates have been used since antiquity for the relief of acute severe pain. Opioids are synthetic opiates with properties that are substantially similar to those of opiates. Opioid Analgesics | Alcohol | Stimulants Stimulants Stimulants are used by the general public to increase alertness and energy, decrease fatigue, and promote mental focus. Stimulants have medical uses for individuals with ADHD and sleep disorders, and are also used in combination with analgesics in pain management. Stimulants | Antidepressants | Nicotine Nicotine Nicotine is highly toxic alkaloid. It is the prototypical agonist at nicotinic cholinergic receptors where it dramatically stimulates neurons and ultimately blocks synaptic transmission. Nicotine is also important medically because of its presence in tobacco smoke. Stimulants | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-term effects | |||||
| Fetal growth restriction Fetal growth restriction Fetal growth restriction (FGR), also known as intrauterine fetal growth restriction (IUGR), is an estimated fetal weight (EFW) or abdominal circumference < 10th percentile for gestational age. The term small for gestational age (SGA) is sometimes erroneously used interchangeably with FGR. Fetal Growth Restriction | + | + | + | + | + |
| Anomalies | – | + | – | + | – |
| Withdrawal | + | + | + | + | – |
| Neurobehavioral | + | + | + | + | + |
| Long-term effects | |||||
| Growth restriction | + | + | + | – | – |
| Behavioral difficulties | + | + | + | – | + |
| Cognition | + | + | + | – | + |
| Delayed language development | + | + | + | – | + |
| Lower academic achievements | + | + | + | – | + |
Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder Fetal alcohol spectrum disorder (FASD) is a group of neonatal pediatric disorders caused by maternal alcohol consumption during pregnancy. The term entails a range of physical and neurodevelopmental effects. Classification is based on severity and clinical presentation. Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder: a group of conditions that can occur in neonates whose mothers consume heavy amounts of alcohol during their pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. Problems may include characteristic craniofacial changes, short height, low body weight, small head size, low intelligence, behavior issues, and hearing impairments.