Neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways is one of the most common complaints in the general population. Depending on symptom duration, it can be acute, subacute, or chronic. There are many causes of neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, including degenerative disease, trauma, rheumatologic disease, and infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Musculoskeletal conditions can range in severity from simple strain to radiculopathy Radiculopathy Disease involving a spinal nerve root which may result from compression related to intervertebral disk displacement; spinal cord injuries; spinal diseases; and other conditions. Clinical manifestations include radicular pain, weakness, and sensory loss referable to structures innervated by the involved nerve root. Rheumatoid Arthritis and myelopathy. A careful history and physical examination is essential in discovering the etiology and guiding therapy. Treatment of the majority of cases of neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways is conservative and activity-based.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways is a common symptom presenting to medical providers.
Musculoskeletal conditions:
Nonmusculoskeletal conditions:
Neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways may be classified on the basis of the duration of symptoms:
Important open-ended questions to ask when evaluating a patient with pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways can be remembered with:
Basic examination:
Special tests and signs:
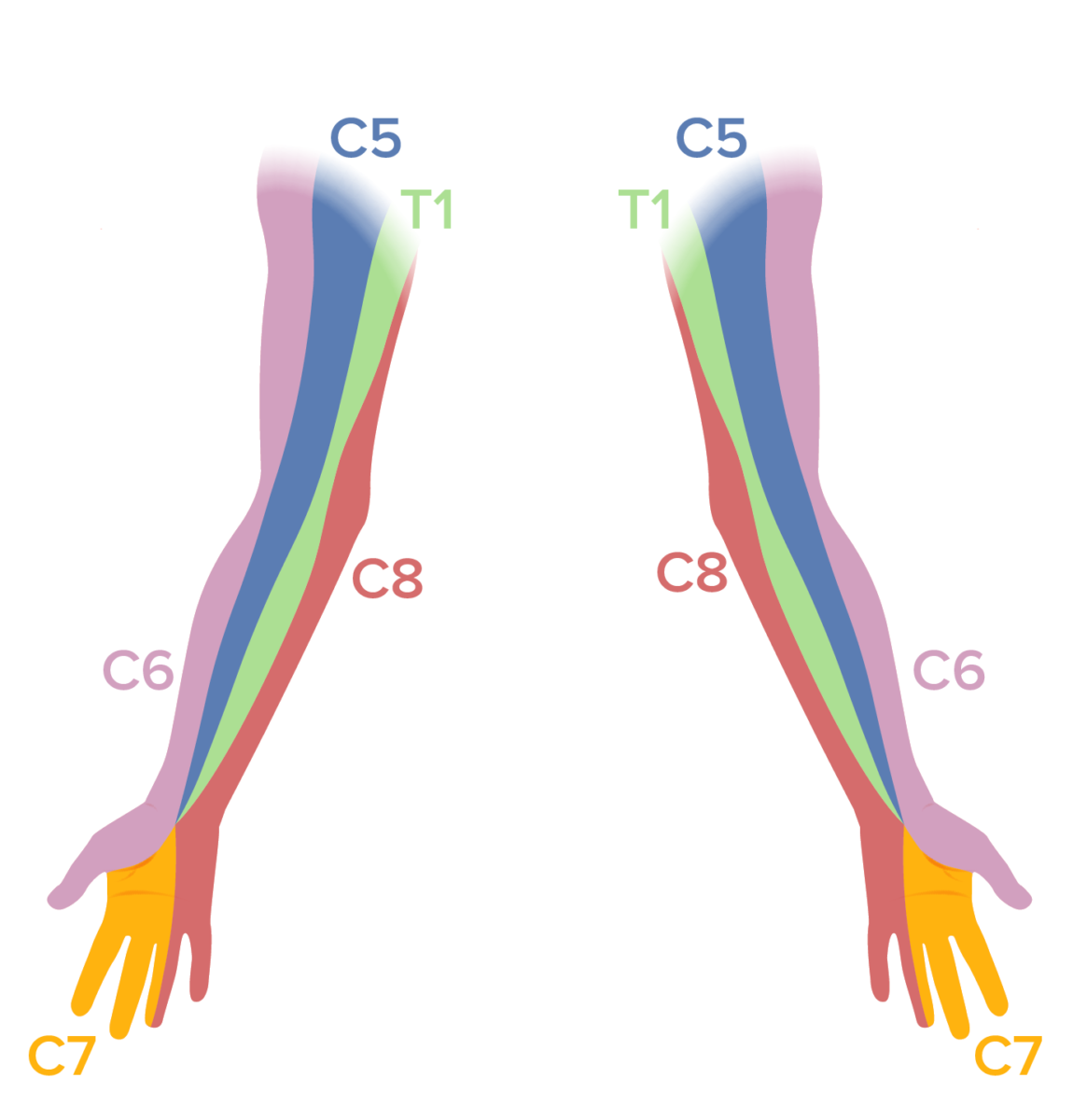
Dermatomal map of the upper extremities:
A sensory examination should be performed in patients with neck pain. Sensory deficits in a dermatomal distribution can be noted in patients with cervical radiculopathy.
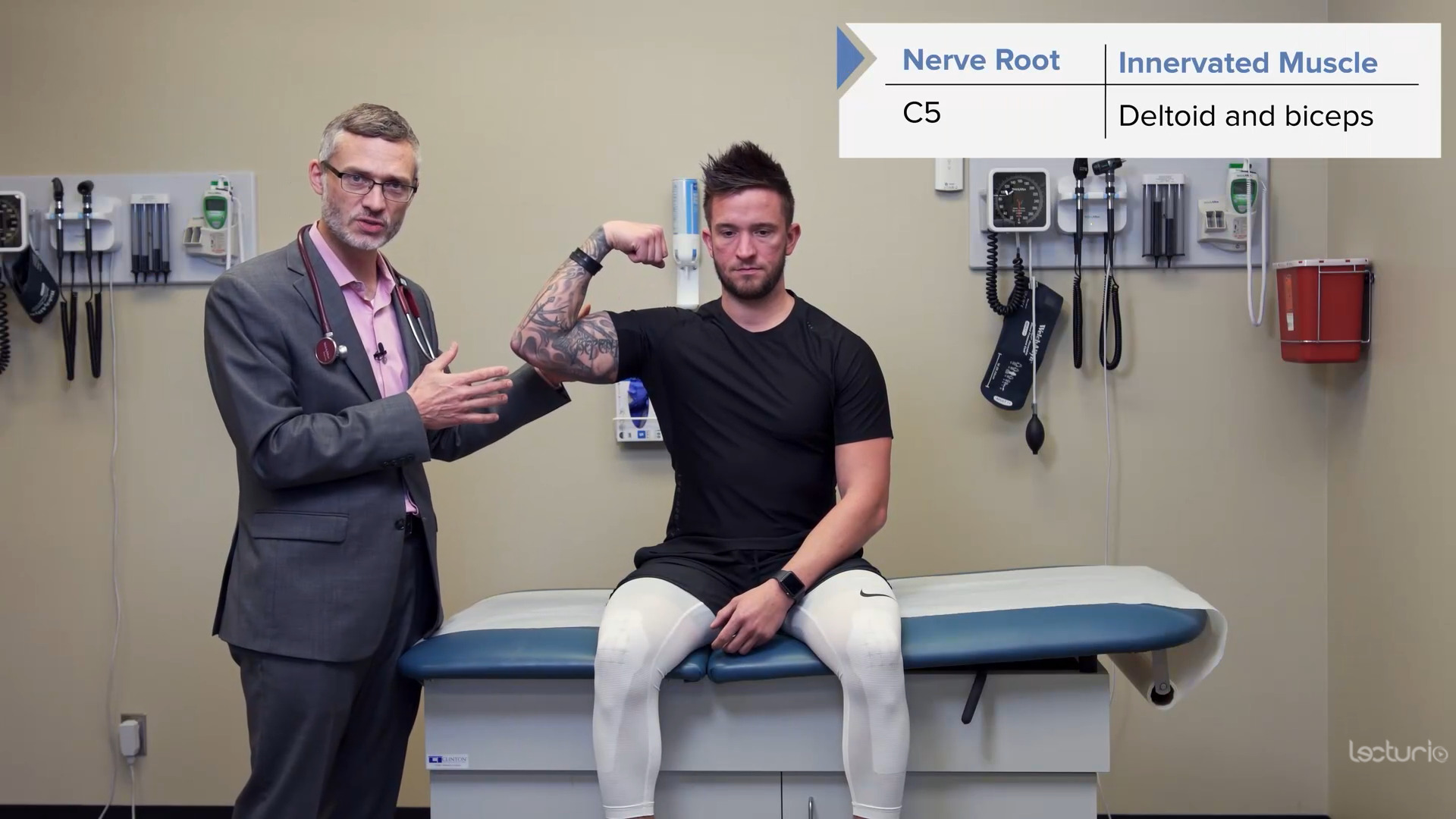
Strength testing the C5 myotome, the deltoids, and the biceps
Image by Lecturio.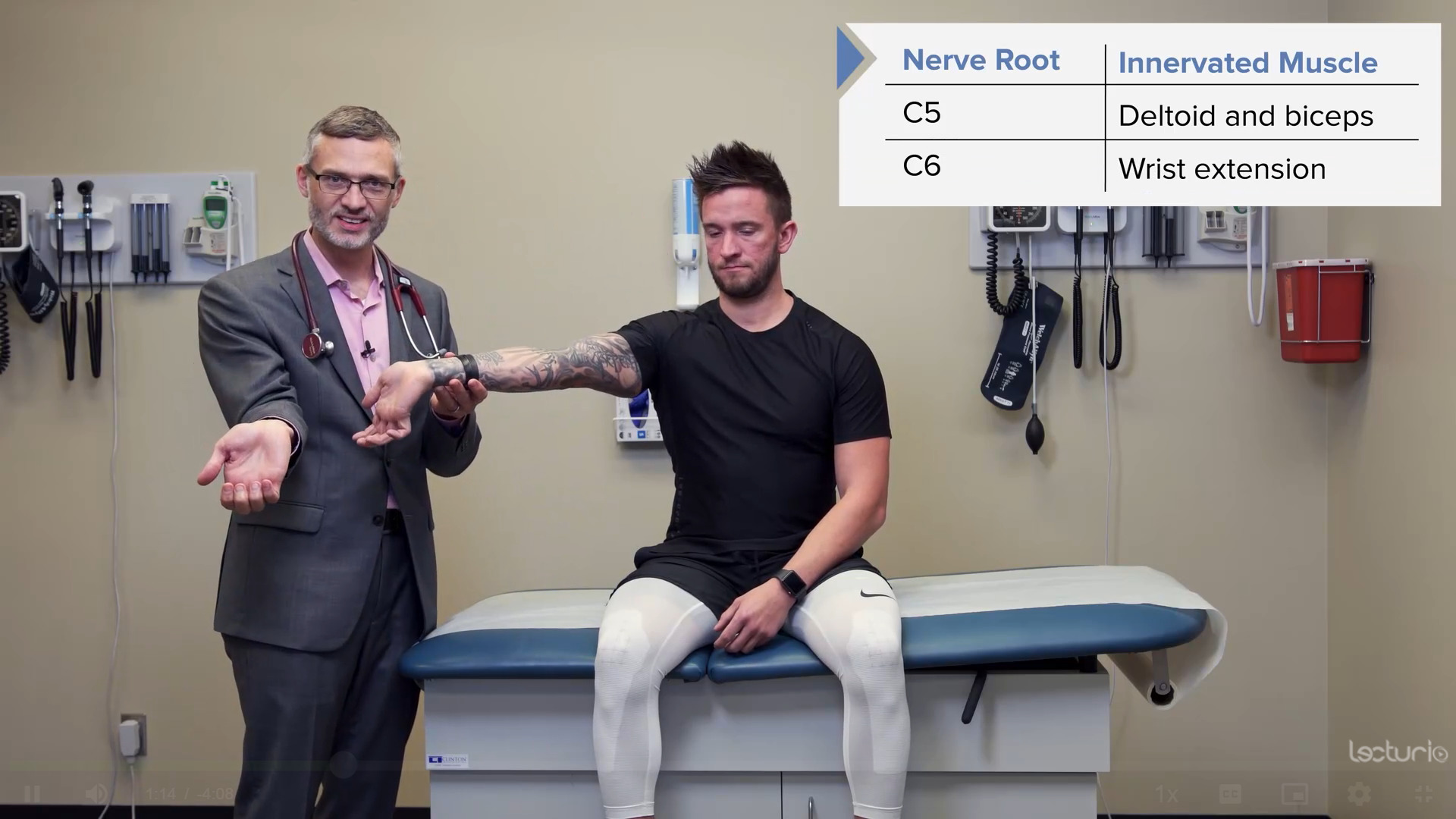
Strength testing the C6 myotome, the triceps, and the wrist extensors
Image by Lecturio.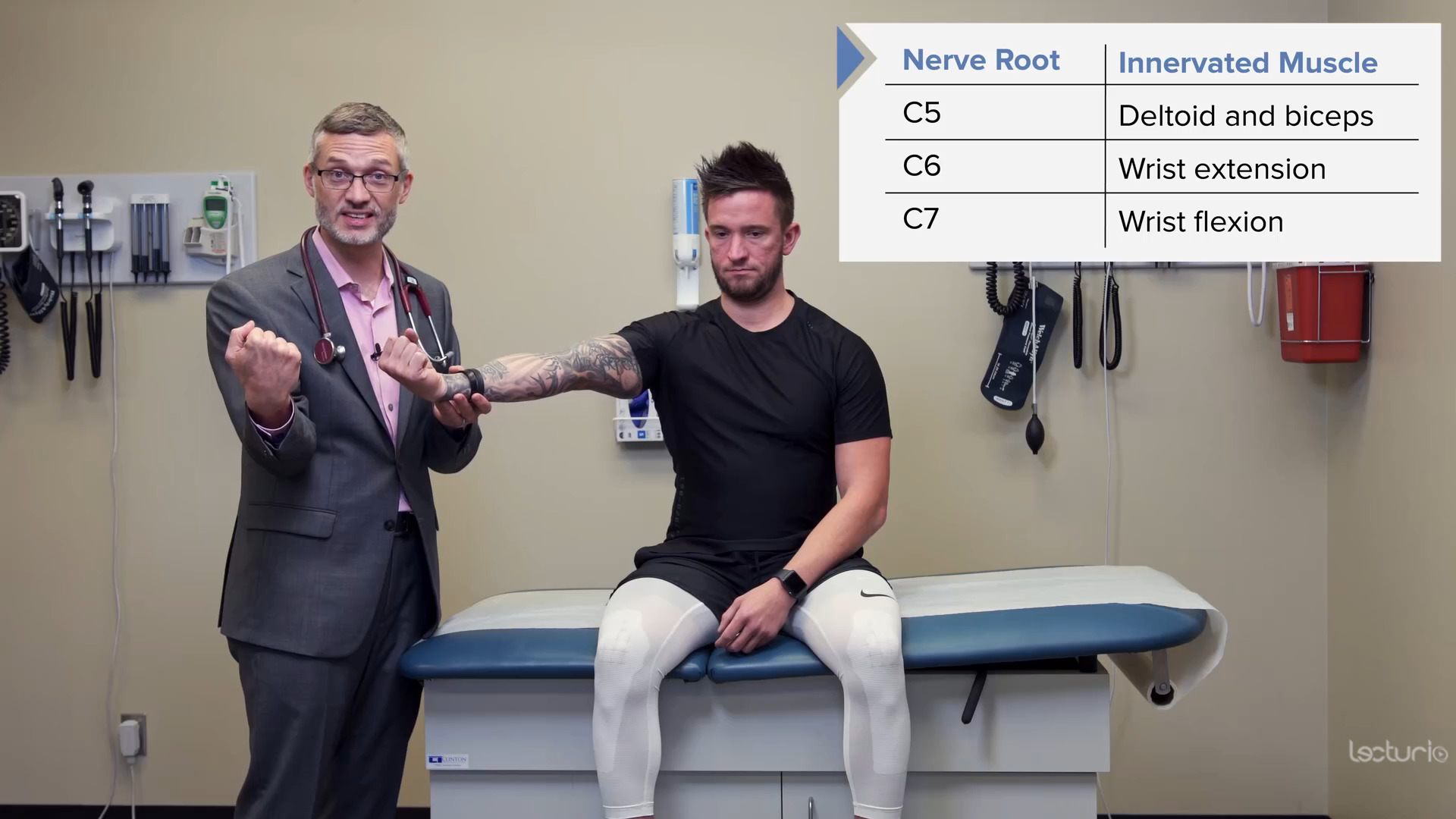
Strength testing the C7 myotome and the wrist flexors
Image by Lecturio.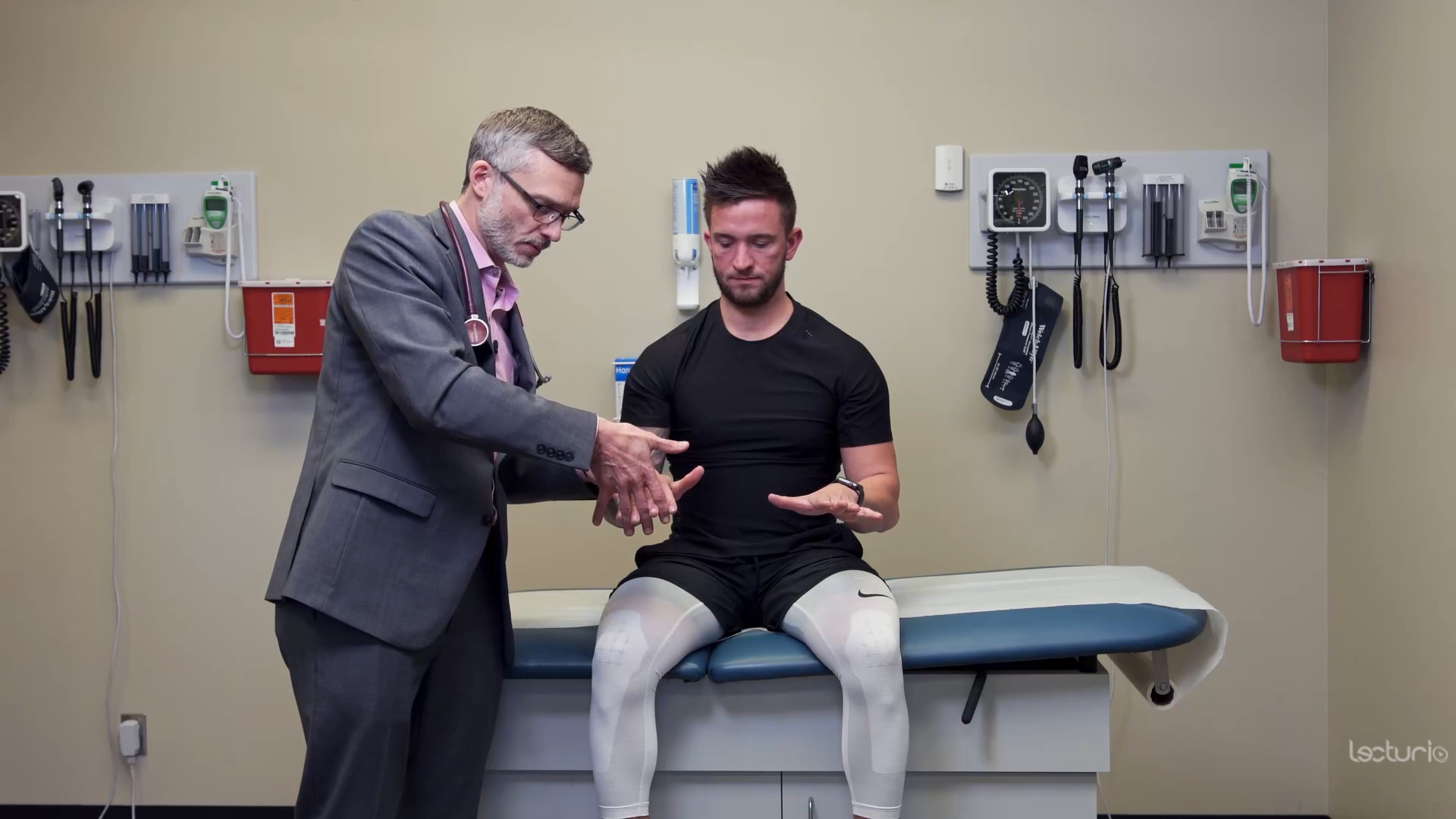
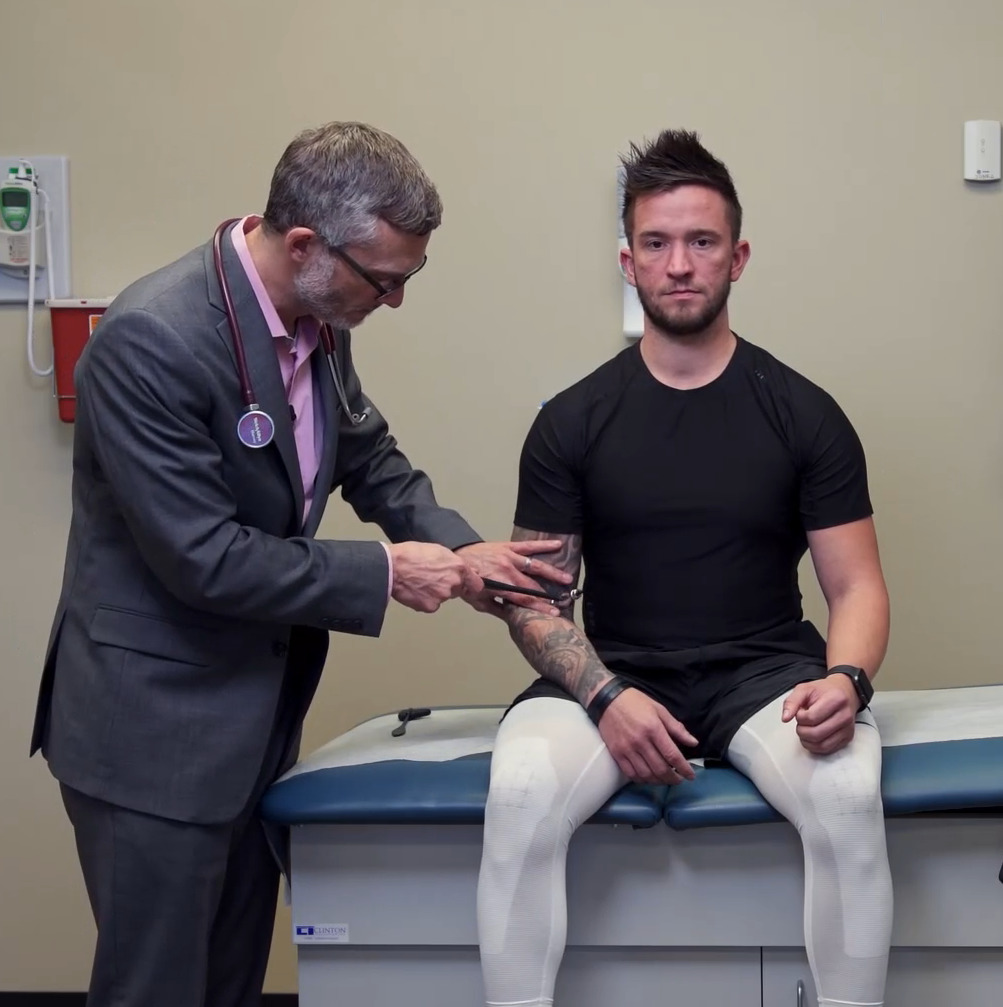
Strength testing the C8 and T1 myotomes and the interosseous muscles:
Note the individual squeezes the examiner’s fingers.
Reflex testing of the C5 nerve root and the biceps tendon reflex
Image by Lecturio.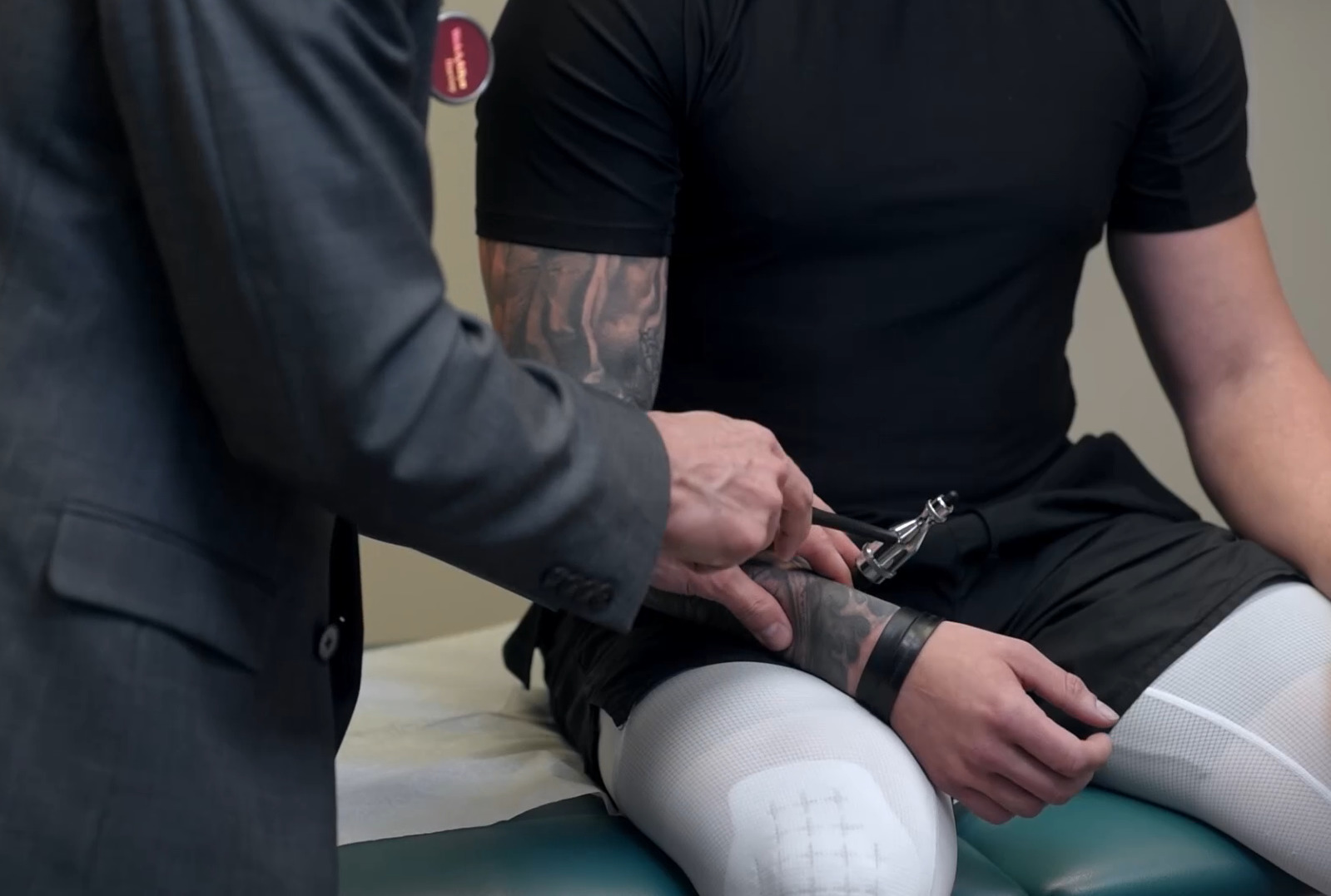
Reflex testing of the C6 nerve root and the brachioradialis tendon reflex
Image by Lecturio.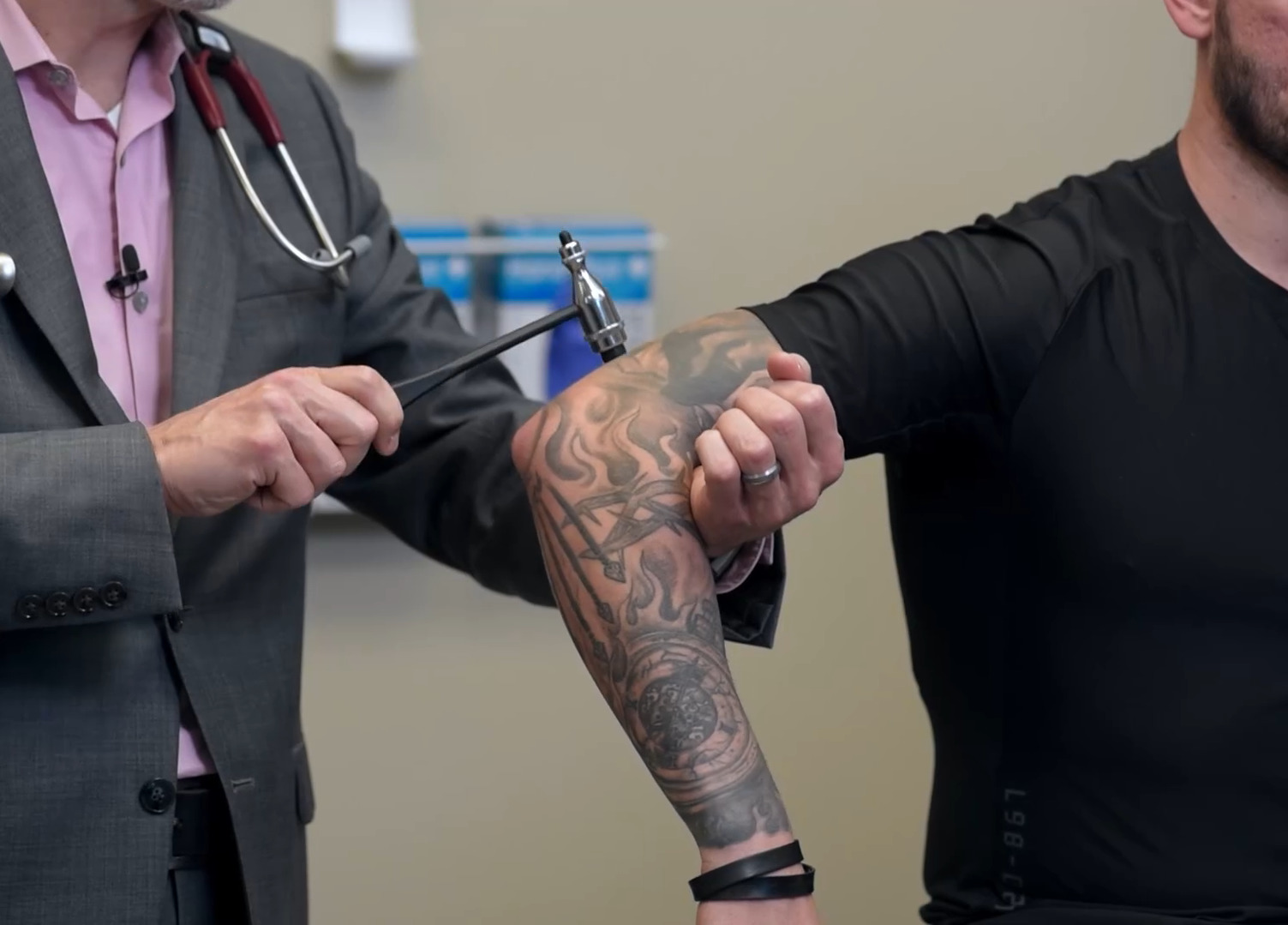
Reflex testing of the C7 nerve root and the triceps tendon reflex
Image by Lecturio.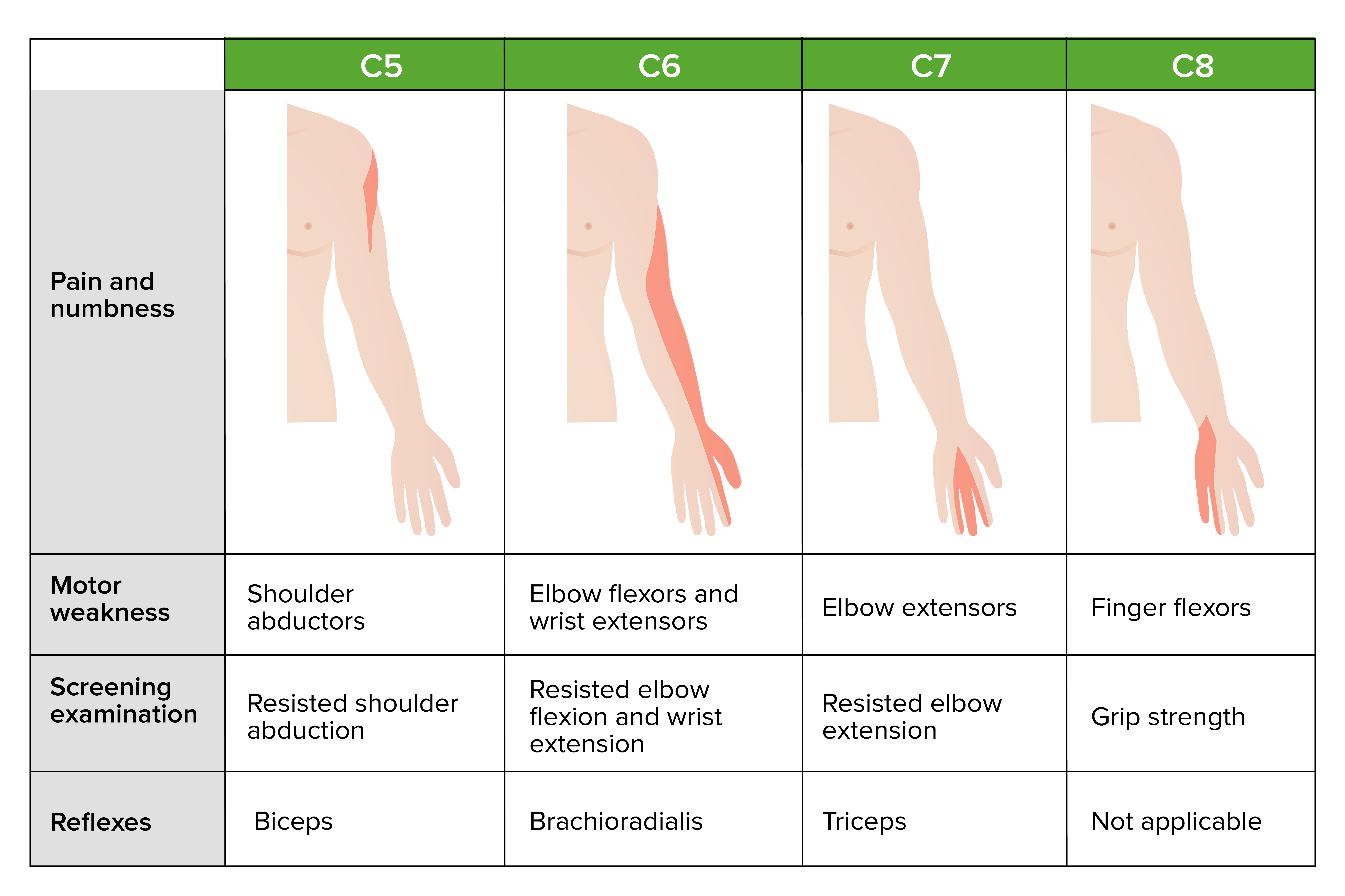
Symptoms and findings due to common cervical radicular syndromes
Image by Lecturio.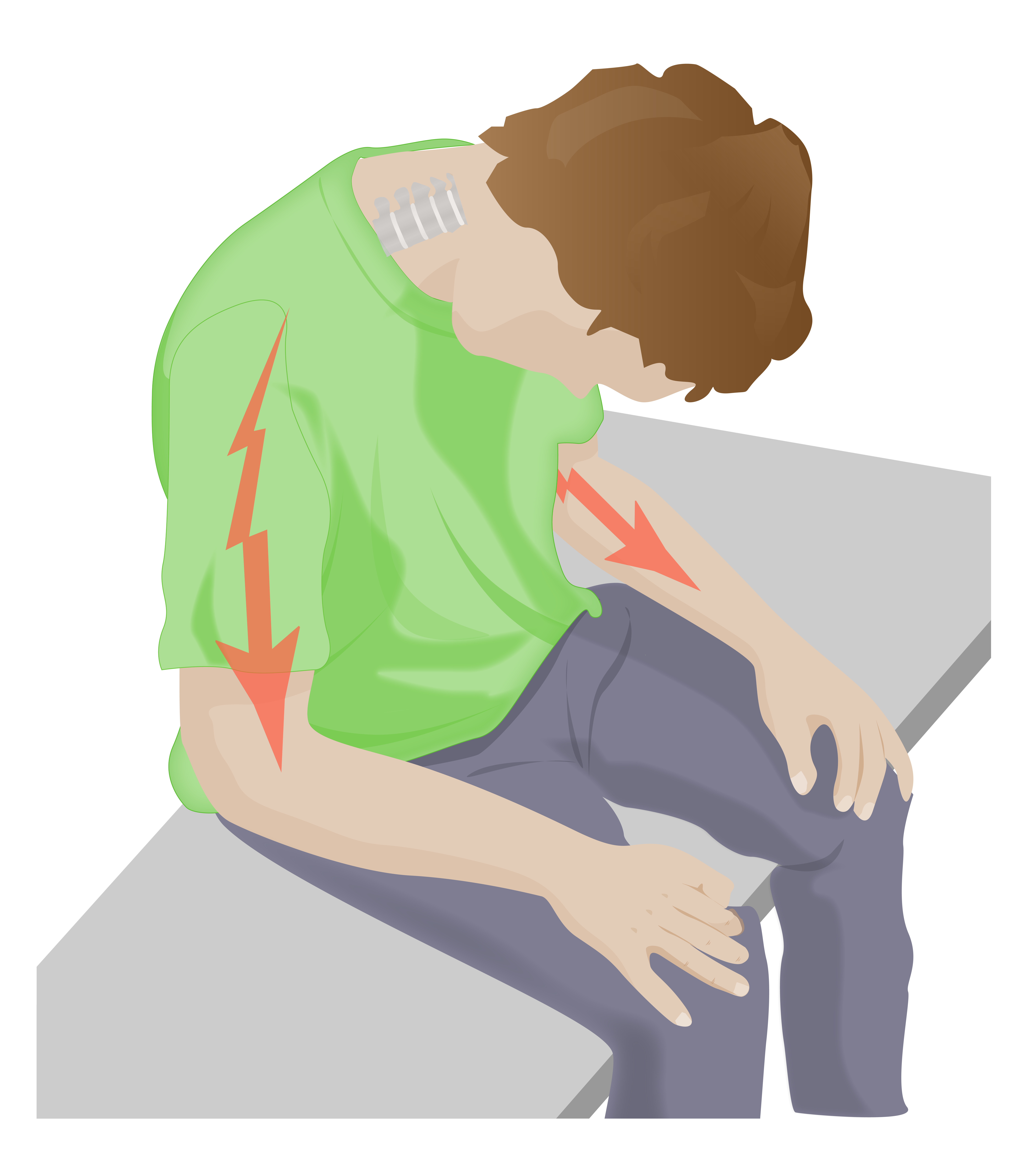
Lhermitte’s sign:
Forward flexion of the neck results in radiation of pain down the spine or arms.
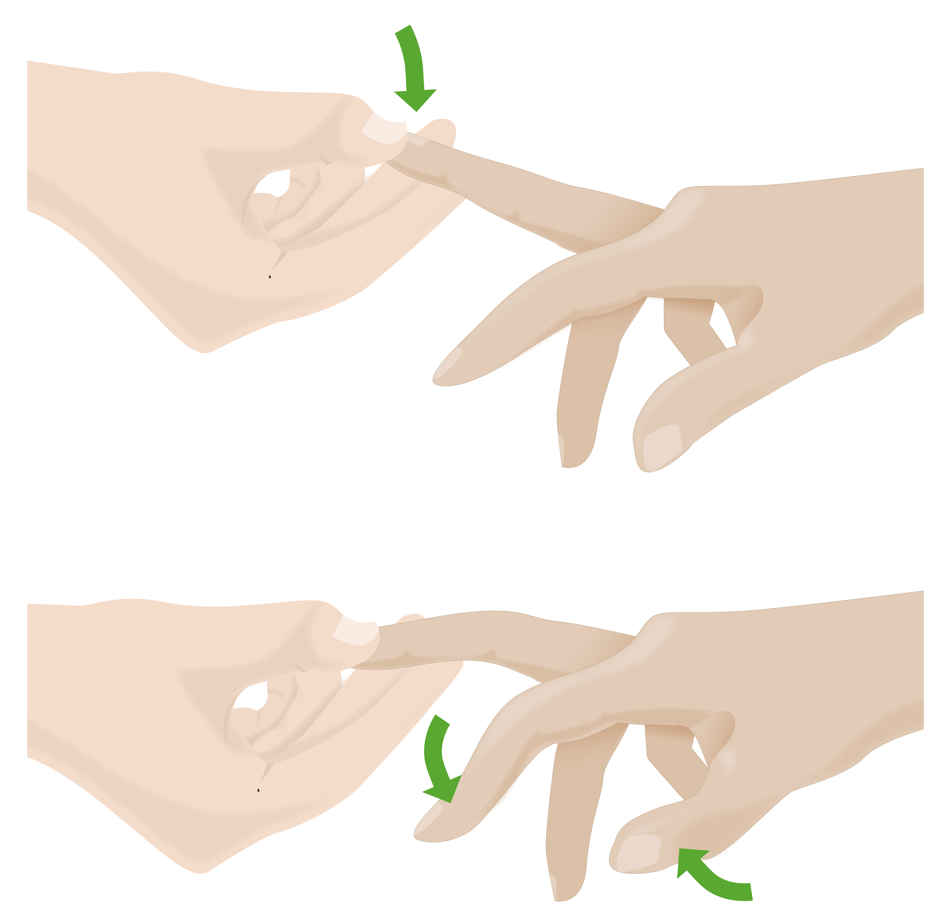
Hoffmann sign:
Flicking down on the middle fingernail results in flexion of the thumb and index finger, which can indicate cervical myelopathy.
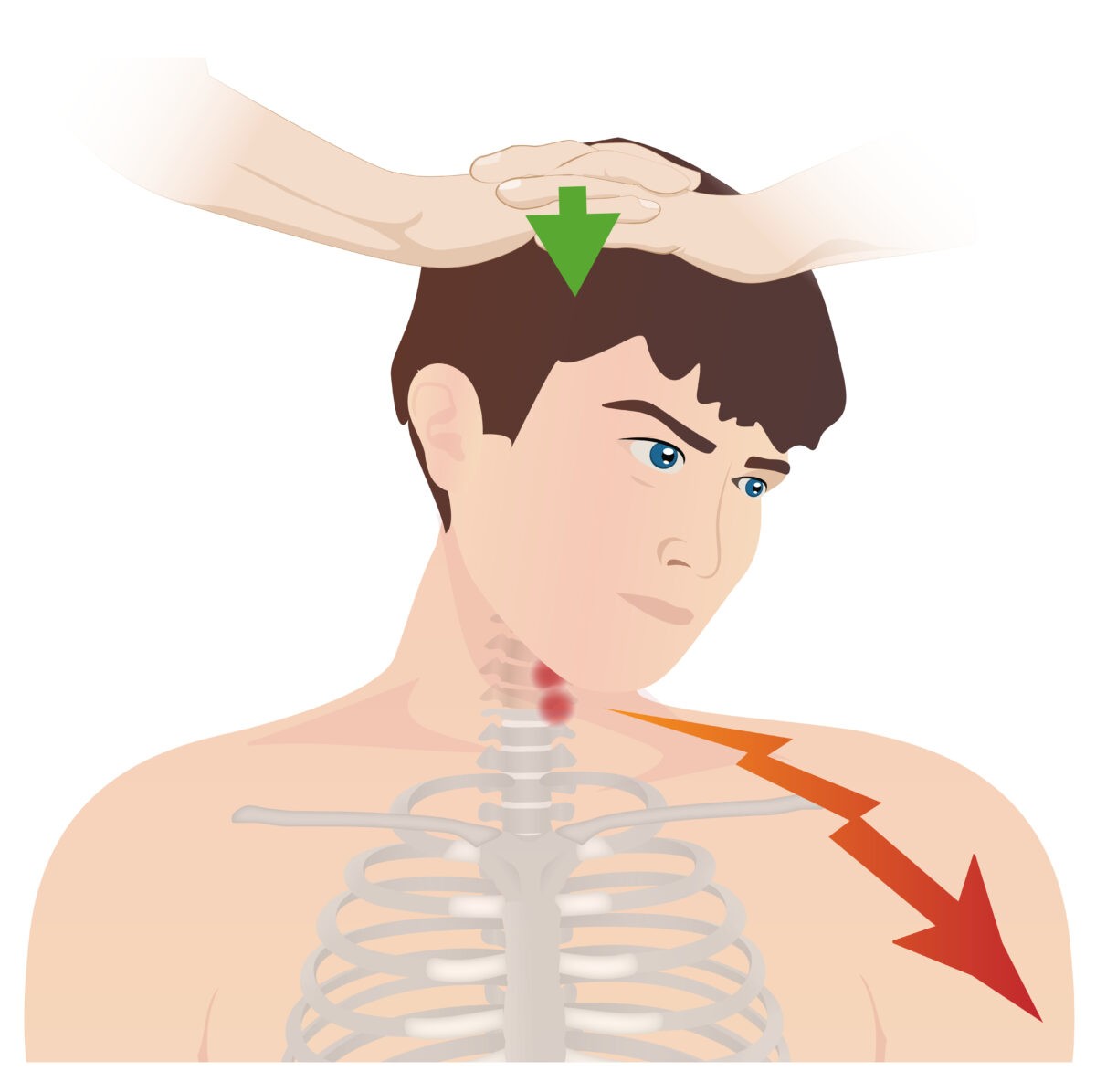
Spurling test:
This test is used in the evaluation of cervical radiculopathy in patients presenting with neck pain. The patient’s head is turned to the affected side while extended. A downward force is applied to the top of the head. A positive test is indicated by radiation of pain down the corresponding dermatome.
The following symptoms suggest serious pathology and should elicit an urgent evaluation:
The differential diagnoses related to neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways is vast and can be narrowed on the basis of the history and physical examination.
The following table compares the clinical and diagnostic clues for some common musculoskeletal conditions manifesting with neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways.
| Condition | Clinical features | Diagnosis |
|---|---|---|
| Cervical strain |
|
Clinical |
| Cervical spondylosis Spondylosis A degenerative spinal disease that can involve any part of the vertebra, the intervertebral disk, and the surrounding soft tissue. Central Cord Syndrome |
|
|
| Whiplash injury |
|
|
| Cervical radiculopathy Cervical Radiculopathy Spinal Disk Herniation |
|
|
| Cervical myelopathy |
|
MRI showing:
|
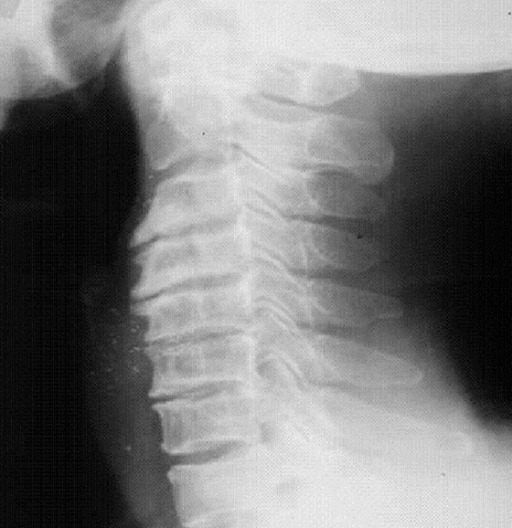
Radiographic representation of cervical spondylosis
Image: “fig1: Radiographic representation of cervical spondylosis.” by Lisa A Ferrara. License: CC BY 3.0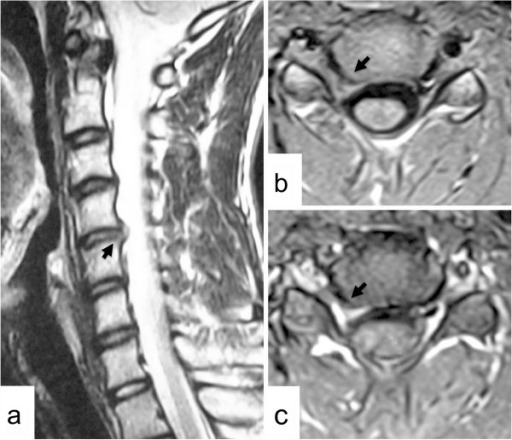
a: Right parasagittal T2-weighted MRI scan of the cervical spine
b: Axial T1-weighted MRI scan at the C4–C5 level showing a herniated intervertebral disk in the right C4–C5 intervertebral foramen (arrows)
c: Partially enhanced herniated disk (arrow) after contrast medium
Early management of neck Neck The part of a human or animal body connecting the head to the rest of the body. Peritonsillar Abscess pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways focuses on proper initial evaluation, early return of motion, pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways management, and judicious use of physical therapy Physical Therapy Becker Muscular Dystrophy.
Conservative measures are usually used in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship without major trauma or red flag findings.
General treatment:
Physical and movement therapy:
The following may be considered in association with pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways management and/or physical medicine and rehabilitation: