Myotonic dystrophies are genetic disorders due to autosomal-dominant genetic mutations Genetic Mutations Carcinogenesis and have 2 major clinical forms: myotonic dystrophy type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy (DM1) and myotonic dystrophy type 2 (DM2). Myotonic dystrophies are heterogeneous diseases primarily affecting the muscles, but, unlike other muscular dystrophies, also have multisystem effects. Both DM1 and DM2 present with myotonia Myotonia Prolonged failure of muscle relaxation after contraction. This may occur after voluntary contractions, muscle percussion, or electrical stimulation of the muscle. Myotonia is a characteristic feature of myotonic disorders. Ion Channel Myopathy, muscle weakness, and myalgias Myalgias Painful sensation in the muscles. Tick-borne Encephalitis Virus; however, DM1 is severe and carries a reduced life expectancy Life expectancy Based on known statistical data, the number of years which any person of a given age may reasonably expected to live. Population Pyramids, whereas DM2 is mild with a normal life expectancy Life expectancy Based on known statistical data, the number of years which any person of a given age may reasonably expected to live. Population Pyramids. Diagnosis is made clinically, with genetic testing, and by electromyography Electromyography Recording of the changes in electric potential of muscle by means of surface or needle electrodes. Becker Muscular Dystrophy (EMG). Management is primarily supportive.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Myotonic dystrophy is an inherited, autosomal-dominant muscular disease, which causes muscle relaxation incompetence, resulting in progressive muscle wasting Muscle Wasting Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and weakness.
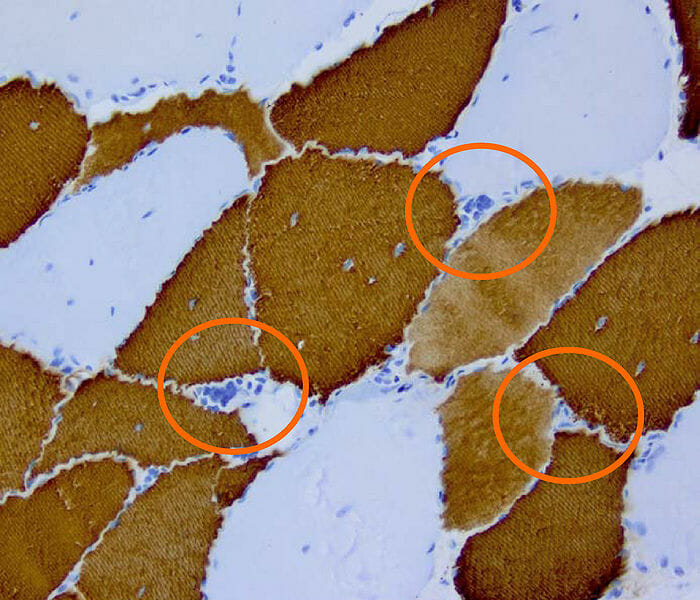
Histopathology of myotonic dystrophy type 2
Image: “DM2 Histopathology” by Marvin 101. License: CC BY 3.0Both types of myotonic dystrophy cause myotonia Myotonia Prolonged failure of muscle relaxation after contraction. This may occur after voluntary contractions, muscle percussion, or electrical stimulation of the muscle. Myotonia is a characteristic feature of myotonic disorders. Ion Channel Myopathy (sustained muscle contraction) with difficulty or delay in relaxation after use.
Symptoms:
Associated manifestations:
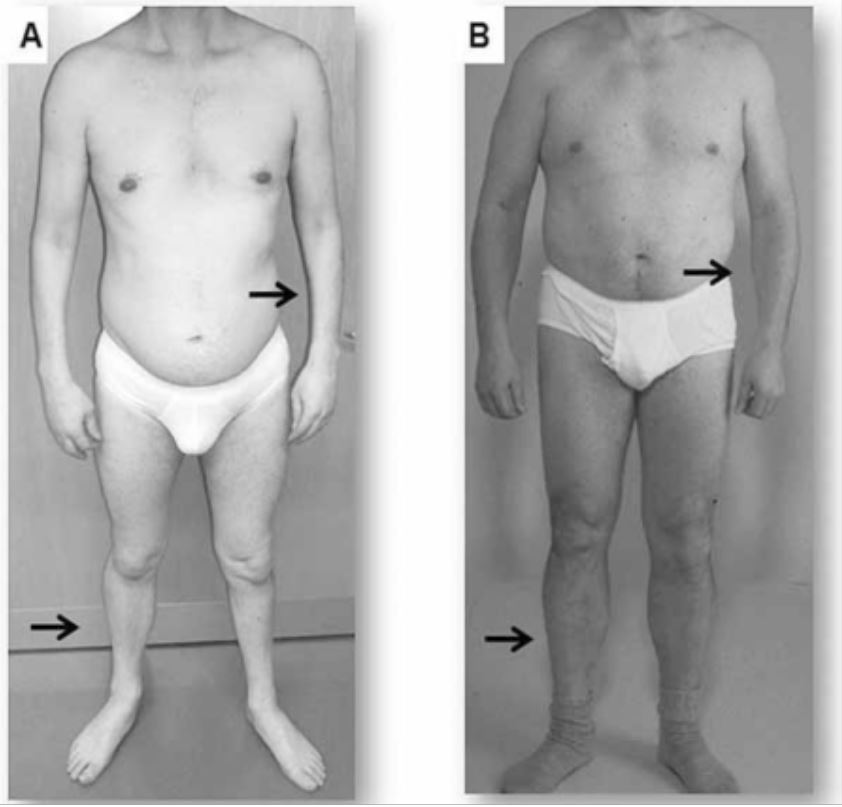
Clinical presentation of 2 adults with myotonic dystrophy
A: Atrophy of the forearm and lower leg in a patient with DM1
B: Atrophy is not seen in this patient with DM2, in which symptoms tend to be milder and more proximal.