Myeloperoxidase Myeloperoxidase Acute Myeloid Leukemia ( MPO MPO Acute Myeloid Leukemia) deficiency is an inherited or acquired disorder caused by mutations in the MPO MPO Acute Myeloid Leukemia gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics on chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 17, leading to a deficiency of MPO MPO Acute Myeloid Leukemia in neutrophils Neutrophils Granular leukocytes having a nucleus with three to five lobes connected by slender threads of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing fine inconspicuous granules and stainable by neutral dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation and monocytes Monocytes Large, phagocytic mononuclear leukocytes produced in the vertebrate bone marrow and released into the blood; contain a large, oval or somewhat indented nucleus surrounded by voluminous cytoplasm and numerous organelles. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation. This deficiency particularly impairs destruction of pathogens in phagolysosomes. While the majority of patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are asymptomatic and do not suffer from an increased frequency of infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease, a minority (particularly diabetic patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship) can develop serious fungal infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease. Histochemical staining of neutrophils Neutrophils Granular leukocytes having a nucleus with three to five lobes connected by slender threads of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing fine inconspicuous granules and stainable by neutral dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation for MPO MPO Acute Myeloid Leukemia can provide the diagnosis. There is no specific management for MPO MPO Acute Myeloid Leukemia deficiency, and prophylactic antibiotics are not indicated.
Last updated: Nov 10, 2024
Genetic mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations:
Primary MPO MPO Acute Myeloid Leukemia deficiency:
Acquired (secondary) MPO MPO Acute Myeloid Leukemia deficiency:
Neutrophils Neutrophils Granular leukocytes having a nucleus with three to five lobes connected by slender threads of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing fine inconspicuous granules and stainable by neutral dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation are the 1st line of defense against pathogens:
MPO-deficient neutrophils Neutrophils Granular leukocytes having a nucleus with three to five lobes connected by slender threads of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing fine inconspicuous granules and stainable by neutral dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation:
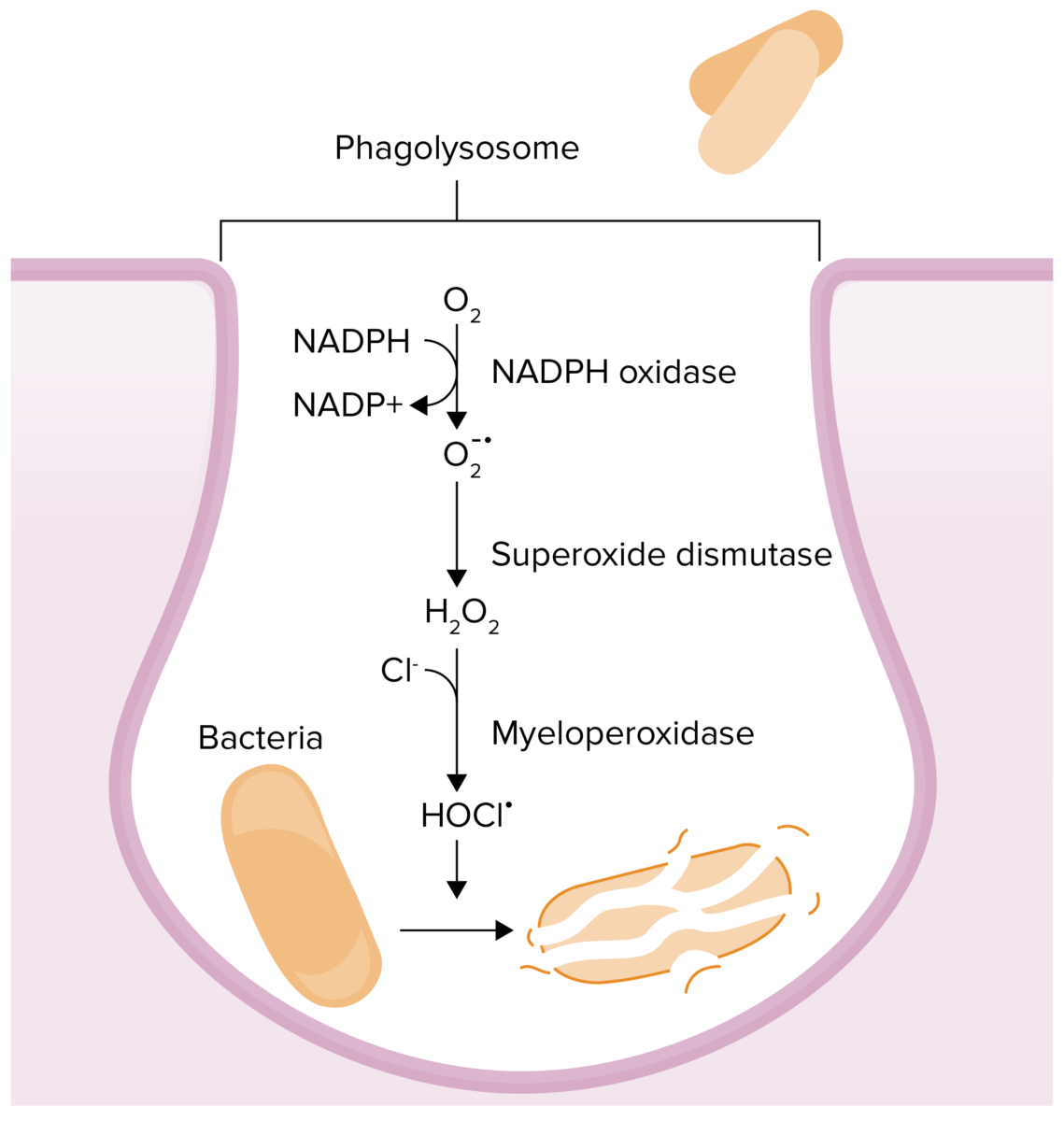
Chemical reactions that occur in phagolysosomes in an effort to kill a pathogen:
Myeloperoxidase deficiency results in an inability to convert hydrogen peroxide to hypochlorous acid.
Because most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are asymptomatic, no specific treatment for MPO MPO Acute Myeloid Leukemia deficiency is required.