Fungi belong to the eukaryote domain and, like plants Plants Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic, have cell walls and vacuoles, exhibit cytoplasmic streaming, and are immobile. Almost all fungi, however, have cell walls composed of chitin Chitin A linear polysaccharide of beta-1->4 linked units of acetylglucosamine. It is the second most abundant biopolymer on earth, found especially in insects and fungi. When deacetylated it is called chitosan. Echinocandins and not cellulose. Fungi do not carry out photosynthesis but obtain their substrates for metabolism as saprophytes (obtain their food from dead matter). Mycosis is an infection caused by fungi.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Reproduction is either sexual or asexual.
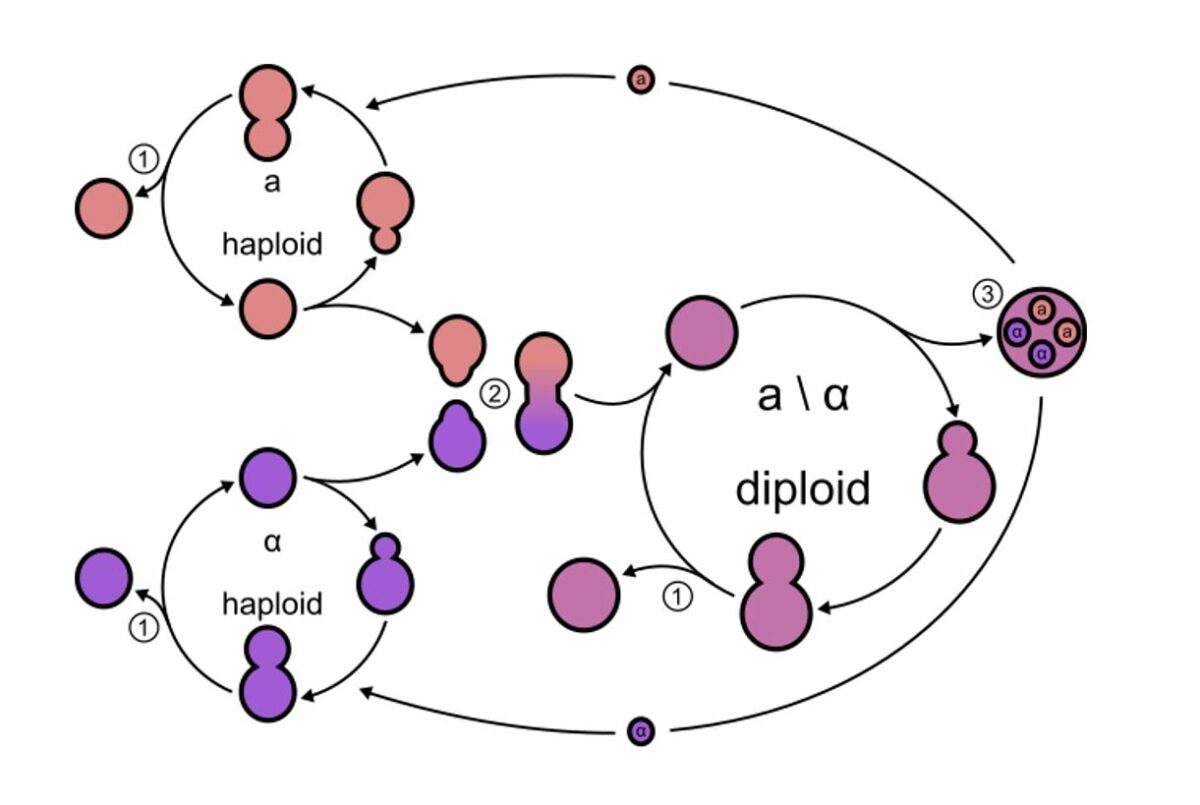
Budding in fungus:
Budding yeasts divide, asymmetrically. There are haploid and diploid states (2 mating types, a and α). Each mating type secretes its own type of pheromone.
1: Budding: Mitotic cell division can occur in the haploid and diploid states, resulting in genetically identical daughter cells.
2: Mating: Each mating type secretes its own type of pheromone, initiating the mating process. This results in a diploid cell.
3: Sporulation: Diploid cells can undergo meiosis, which results in spore formation. These spores can germinate into haploid cells.
| Toxin | Fungus | Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Aflatoxin Aflatoxin A potent hepatotoxic and hepatocarcinogenic mycotoxin produced by the aspergillus flavus group of fungi. It is also mutagenic, teratogenic, and causes immunosuppression in animals. It is found as a contaminant in peanuts, cottonseed meal, corn, and other grains. The mycotoxin requires epoxidation to aflatoxin b1 2, 3-oxide for activation. Microsomal monooxygenases biotransform the toxin to the less toxic metabolites aflatoxin m1 and q1. Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) and Liver Metastases |
|
Highly carcinogenic and often the cause of food poisoning Food poisoning Acute illnesses, usually affecting the gastrointestinal tract, brought on by consuming contaminated food or beverages. Most of these diseases are infectious, caused by a variety of bacteria, viruses, or parasites that can be foodborne. Sometimes the diseases are caused by harmful toxins from the microbes or other chemicals present in the food. Especially in the latter case, the condition is often called food poisoning. Clostridia (traces on nuts, grain, spices) |
| Amanitin Amanitin Cyclic peptides extracted from carpophores of various mushroom species. They are potent inhibitors of RNA polymerases in most eukaryotic species, blocking the production of mRNA and protein synthesis. These peptides are important in the study of transcription. Alpha-amanitin is the main toxin from the species amanita phalloides, poisonous if ingested by humans or animals. Toxicology of Plants | Amanita phalloides Amanita Phalloides Toxicology of Plants (death cap mushroom) | Inhibition of RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure polymerase II, lethal even in small doses |
| Muscarine Muscarine A toxic alkaloid found in amanita muscaria (fly fungus) and other fungi of the inocybe species. It is the first parasympathomimetic substance ever studied and causes profound parasympathetic activation that may end in convulsions and death. The specific antidote is atropine. Cholinomimetic Drugs | A. muscaria (toadstool or fly agaric mushroom) | Impacts the parasympathetic regulation of the nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification |
| Ergotamine Ergotamine A vasoconstrictor found in ergot of central europe. It is a serotonin agonist that has been used as an oxytocic agent and in the treatment of migraine disorders. Triptans and Ergot Alkaloids | Ergot fungus (Claviceps purpurea) | Impacts the autonomic nervous system Autonomic nervous system The ANS is a component of the peripheral nervous system that uses both afferent (sensory) and efferent (effector) neurons, which control the functioning of the internal organs and involuntary processes via connections with the CNS. The ANS consists of the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems. Autonomic Nervous System: Anatomy, causes hallucinations Hallucinations Subjectively experienced sensations in the absence of an appropriate stimulus, but which are regarded by the individual as real. They may be of organic origin or associated with mental disorders. Schizophrenia, and affects uterine contractions |
| Cyclosporine Cyclosporine A cyclic undecapeptide from an extract of soil fungi. It is a powerful immunosupressant with a specific action on T-lymphocytes. It is used for the prophylaxis of graft rejection in organ and tissue transplantation. Immunosuppressants A |
|
Immunosuppressant (clinical use: after organ transplantation Organ Transplantation Transplantation is a procedure that involves the removal of an organ or living tissue and placing it into a different part of the body or into a different person. Organ transplantations have become the therapeutic option of choice for many individuals with end-stage organ failure. Organ Transplantation) |
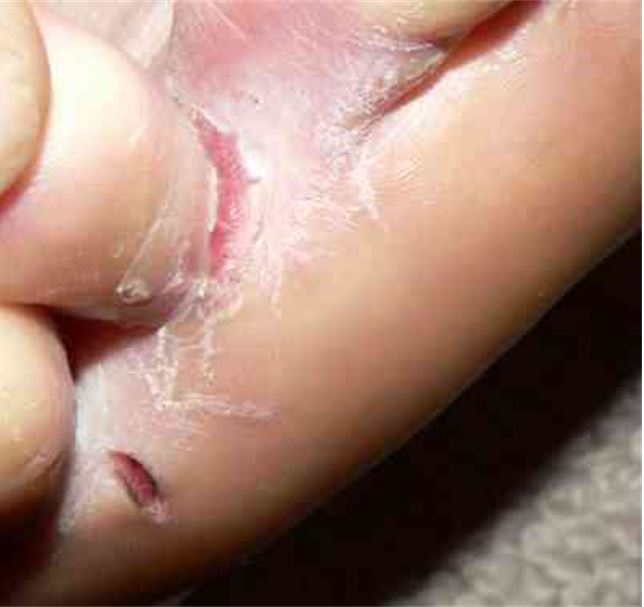
Tinea pedis is also known as athlete’s foot.
Image: “Tinea pedis interdigitalis” by Falloonb. License: Public DomainSome fungi are capable of producing substances that are effective as antimicrobials:
Many fungi are opportunists and are especially pathogenic in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship who are immunocompromised immunocompromised A human or animal whose immunologic mechanism is deficient because of an immunodeficiency disorder or other disease or as the result of the administration of immunosuppressive drugs or radiation. Gastroenteritis. Opportunistic systemic fungal infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease (mycoses) include candidiasis Candidiasis Candida is a genus of dimorphic, opportunistic fungi. Candida albicans is part of the normal human flora and is the most common cause of candidiasis. The clinical presentation varies and can include localized mucocutaneous infections (e.g., oropharyngeal, esophageal, intertriginous, and vulvovaginal candidiasis) and invasive disease (e.g., candidemia, intraabdominal abscess, pericarditis, and meningitis). Candida/Candidiasis, aspergillosis Aspergillosis Aspergillosis is an opportunistic fungal infection caused by Aspergillus species, which are common spore-forming molds found in our environment. As Aspergillus species are opportunistic, they cause disease primarily in patients who are immunocompromised. The organs that are most commonly involved are the lungs and sinuses. Aspergillus/Aspergillosis, mucormycosis Mucormycosis Mucormycosis is an angioinvasive fungal infection caused by multiple fungi within the order, Mucorales. The fungi are ubiquitous in the environment, but mucormycosis is very rare and almost always occurs in patients who are immunocompromised. Inhalation of fungal spores can cause rhinocerebral or pulmonary mucormycosis, direct inoculation can cause cutaneous mucormycosis, and ingestion can cause gastrointestinal mucormycosis. Mucorales/Mucormycosis, and fusariosis, and typically manifest with rapidly progressive pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia or fungemia Fungemia The presence of fungi circulating in the blood. Opportunistic fungal sepsis is seen most often in immunosuppressed patients with severe neutropenia or in postoperative patients with intravenous catheters and usually follows prolonged antibiotic therapy. Chronic Granulomatous Disease.
Caused by inhalation of fungal spores Spores The reproductive elements of lower organisms, such as bacteria; fungi; and cryptogamic plants. Anthrax, which results in pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia. Different infections Infections Invasion of the host organism by microorganisms or their toxins or by parasites that can cause pathological conditions or diseases. Chronic Granulomatous Disease have specific geographic distribution: