Multiple sclerosis Sclerosis A pathological process consisting of hardening or fibrosis of an anatomical structure, often a vessel or a nerve. Wilms Tumor (MS) is a chronic inflammatory autoimmune disease that leads to demyelination of the nerves in the CNS. Young women are more predominantly affected by this most common demyelinating condition. The etiology of MS is unclear; however, both genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role. The clinical presentation varies widely depending on the site of lesions, but typically includes neurological symptoms that affect vision Vision Ophthalmic Exam, motor Motor Neurons which send impulses peripherally to activate muscles or secretory cells. Nervous System: Histology functions, sensation, and autonomic function. The diagnosis is made via MRI of the entire CNS ( brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification and spine Spine The human spine, or vertebral column, is the most important anatomical and functional axis of the human body. It consists of 7 cervical vertebrae, 12 thoracic vertebrae, and 5 lumbar vertebrae and is limited cranially by the skull and caudally by the sacrum. Vertebral Column: Anatomy) as well as CSF examination. Management involves corticosteroids Corticosteroids Chorioretinitis for acute exacerbations and disease-modifying agents to reduce these exacerbations and slow disease progression. The average life expectancy Life expectancy Based on known statistical data, the number of years which any person of a given age may reasonably expected to live. Population Pyramids of individuals with MS is decreased by 5–10 years.
Last updated: Nov 15, 2025
Multiple sclerosis Sclerosis A pathological process consisting of hardening or fibrosis of an anatomical structure, often a vessel or a nerve. Wilms Tumor (MS) is an immune-mediated disease resulting in demyelination of the nerves of the CNS.
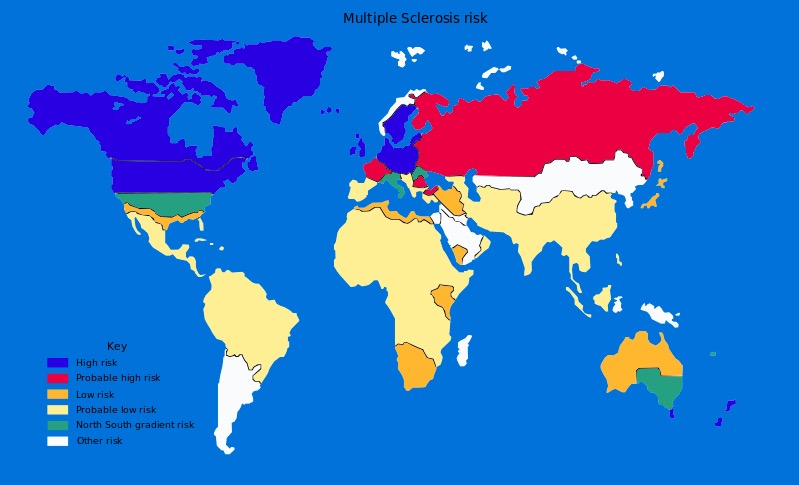
Global prevalence of multiple sclerosis
Image: “Multiple sclerosis risk” by Dekoder. License: Public DomainThe exact etiology of MS is unknown. The disease is thought to be multifactorial with genetic predisposition and environmental factors playing contributive roles.
Genetic factors:
Environmental factors:
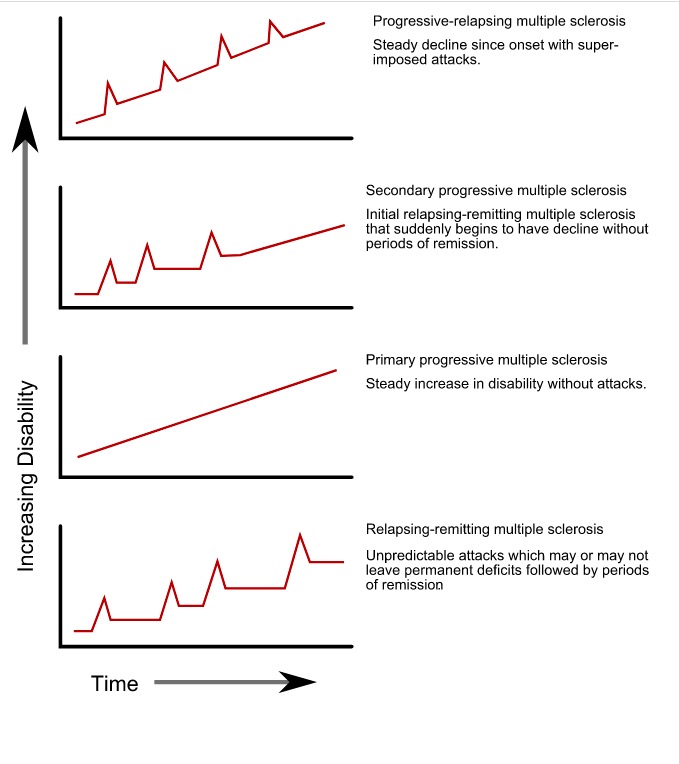
Progression types of multiple sclerosis
Image: “Progression types of multiple sclerosis” by GetThePapersGetThePapers. License: Public Domain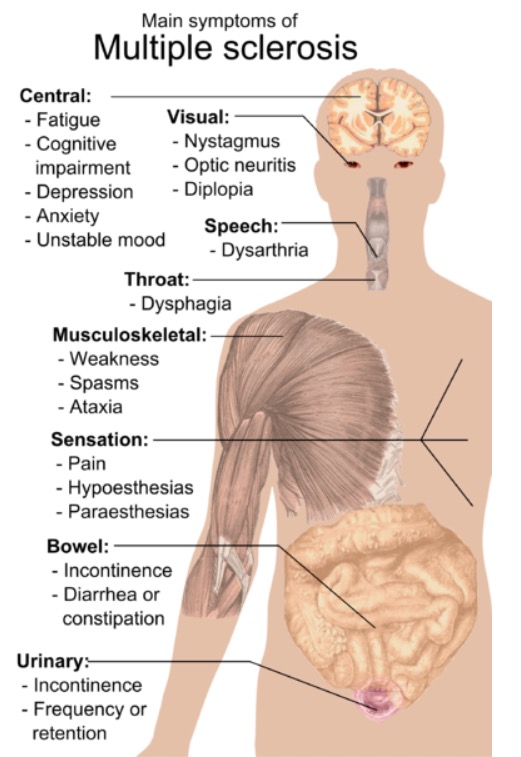
Symptoms of multiple sclerosis
Image: “Main symptoms of multiple sclerosis” by Mikael Häggström. License: Public DomainThe diagnosis of MS is that of exclusion, meaning that neurological symptoms that cannot be better explained by a condition other than MS are excluded. The diagnosis is obtained with the following:
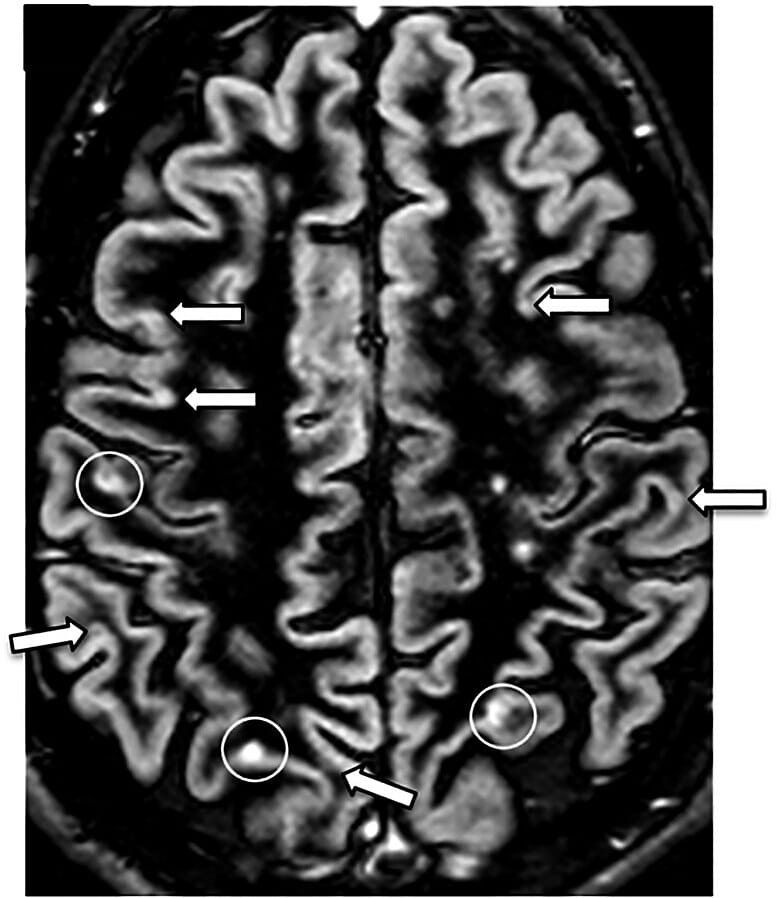
Double inversion recovery (DIR):
MRI showing multiple sclerosis lesions (white circles surround 1 juxtacortical lesion and 2 cortical lesions)
Currently, there is no cure for MS. The goals of management are to improve symptoms, slow disease progression, and maintain the quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement of life.