Multiple pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care, or multifetal gestation, is a pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care with more than 1 fetus. Multiple pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care with more than 2 fetuses is referred to as a higher-order multiple pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care and the most common type of multiple pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care is a twin pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care. Due to advanced maternal age and evolving assisted reproductive technology Assisted Reproductive Technology Clinical and laboratory techniques used to enhance fertility in humans and animals. Reproductive Ethical Issues, the rates of multiple pregnancies have steadily increased over the past 3 decades. However, rates have slowly plateaued with the increase of the single embryo Embryo The entity of a developing mammal, generally from the cleavage of a zygote to the end of embryonic differentiation of basic structures. For the human embryo, this represents the first two months of intrauterine development preceding the stages of the fetus. Fertilization and First Week transfer. The perinatal mortality Mortality All deaths reported in a given population. Measures of Health Status and morbidity Morbidity The proportion of patients with a particular disease during a given year per given unit of population. Measures of Health Status rates of twin pregnancies are 3–7x higher than singleton pregnancies primarily because of higher rates of preterm delivery. Multiple pregnancies also carry a higher risk of obstetric complications such as congenital anomalies, preeclampsia Preeclampsia A complication of pregnancy, characterized by a complex of symptoms including maternal hypertension and proteinuria with or without pathological edema. Symptoms may range between mild and severe. Pre-eclampsia usually occurs after the 20th week of gestation, but may develop before this time in the presence of trophoblastic disease. Hypertensive Pregnancy Disorders, and gestational diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus. Multiple pregnancies are classified as high-risk and require astute obstetric care.
Last updated: Jan 5, 2026
Multiple pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care is a pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care with more than 1 fetus.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Zygosity | Refers to the genetic makeup of a twin pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care |
| Monozygotic twins |
|
| Dizygotic twins |
|
| Chorionicity | The number of chorions (equal to the number of placentas) |
| Amnionicity | The number of amnions surrounding the fetuses |
Statistics of the United States:
| Time of cleavage after fertilization Fertilization To undergo fertilization, the sperm enters the uterus, travels towards the ampulla of the fallopian tube, and encounters the oocyte. The zona pellucida (the outer layer of the oocyte) deteriorates along with the zygote, which travels towards the uterus and eventually forms a blastocyst, allowing for implantation to occur. Fertilization and First Week | Classification | Prevalence Prevalence The total number of cases of a given disease in a specified population at a designated time. It is differentiated from incidence, which refers to the number of new cases in the population at a given time. Measures of Disease Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| 1–3 days | Dichorionic-diamniotic | 20%–25% |
| 4–8 days | Monochorionic-diamniotic | 70%–75% |
| 9–12 days | Monochorionic-monoamniotic | 1%–5% |
| ≥ 13 days | Monochorionic-monoamniotic (conjoined twins) | Very rare |
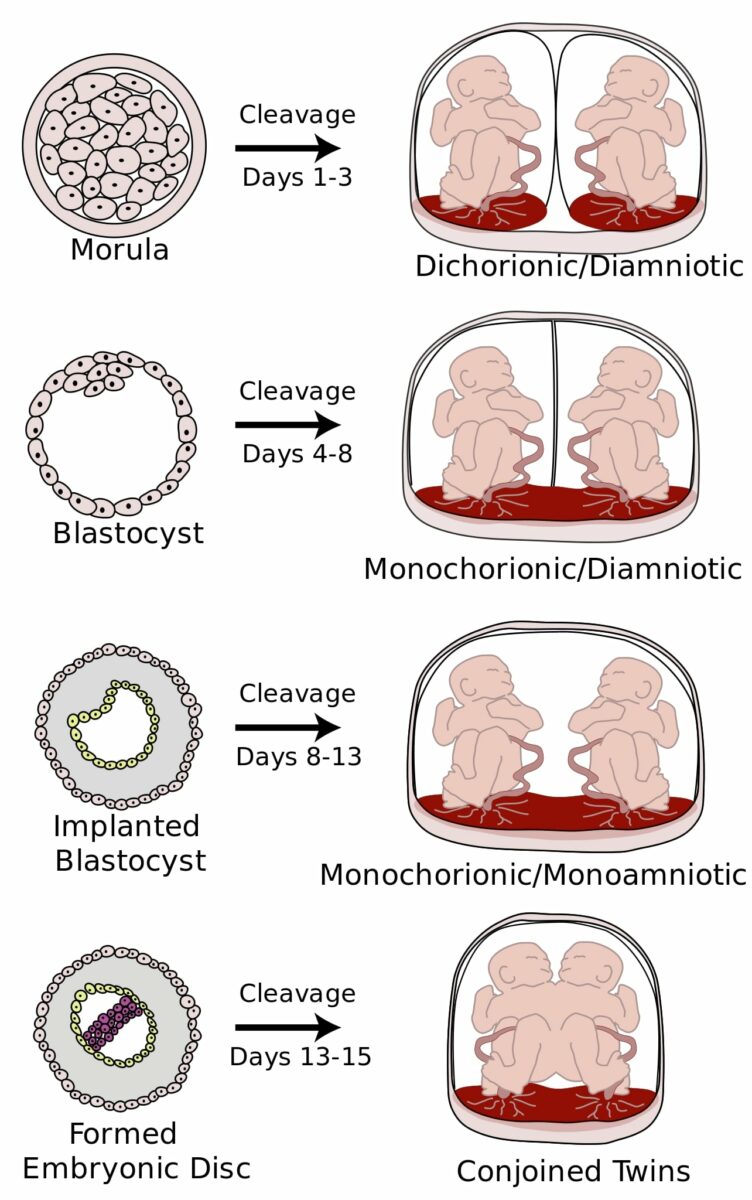
Types of monozygotic twins:
The image illustrates various types of monozygotic twins based on cleavage timing. Chorionicity and amnionicity are dependent on timing of cleavage after fertilization.
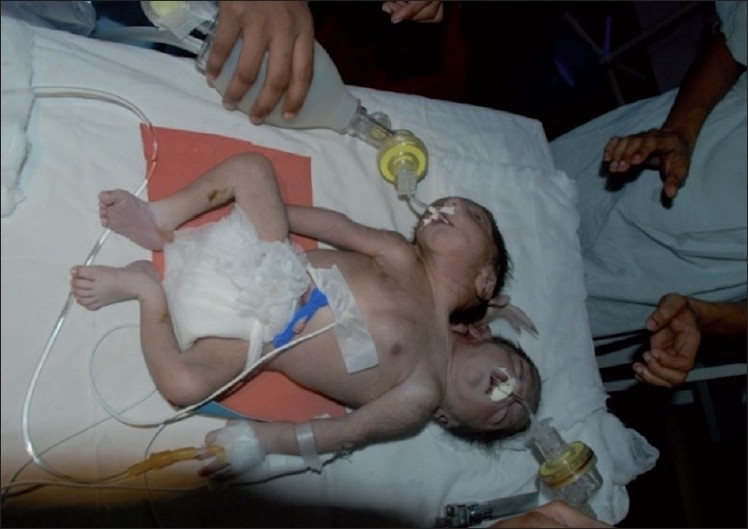
Conjoined twins: a result of cleavage timing ≥ 13 days
Image: “Conjoined twin” by Ambar S. S., Halkati P. C., Patted S. V., Yavagal S. License: CC BY 2.0Signs and symptoms:
Ultrasound findings:
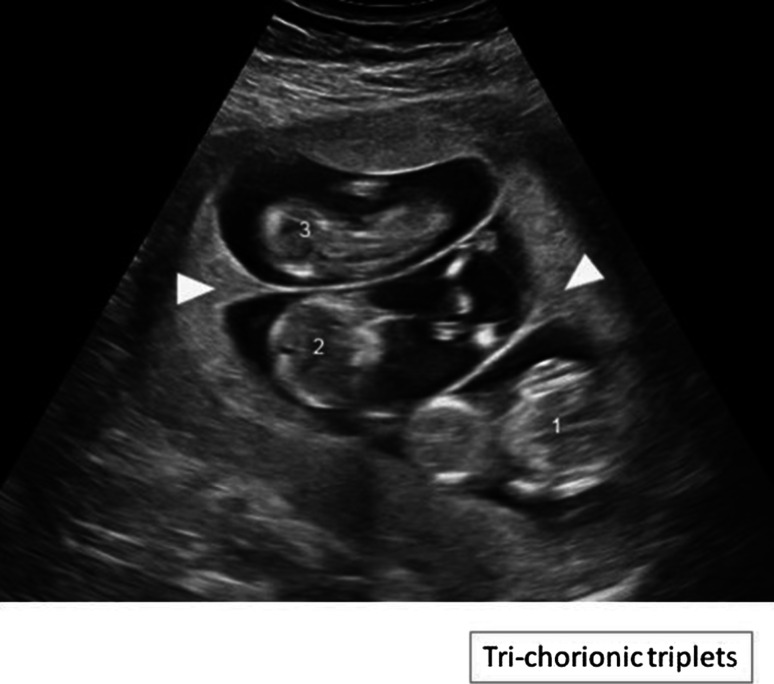
Ultrasound picture of trichorionic-triamniotic triplets:
Each fetus (1, 2, and 3) has a placenta and an amniotic sac. The arrowheads indicate the lambda sign.
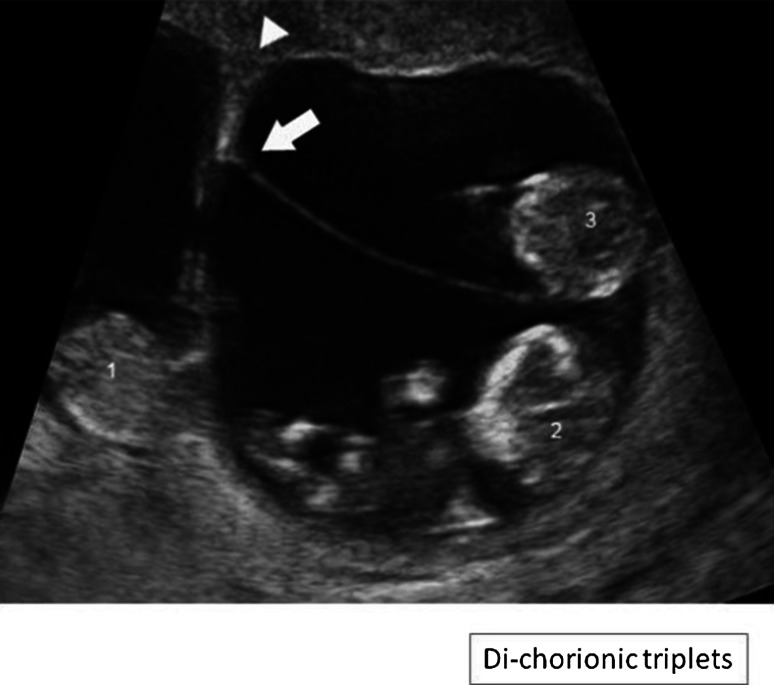
Ultrasound picture of a dichorionic-triamniotic triplet pregnancy:
The arrow indicates the amniotic membranes (T sign) of fetuses 2 and 3, which are a monochorionic-diamniotic pair. The lambda sign indicates the placenta for fetus 1.
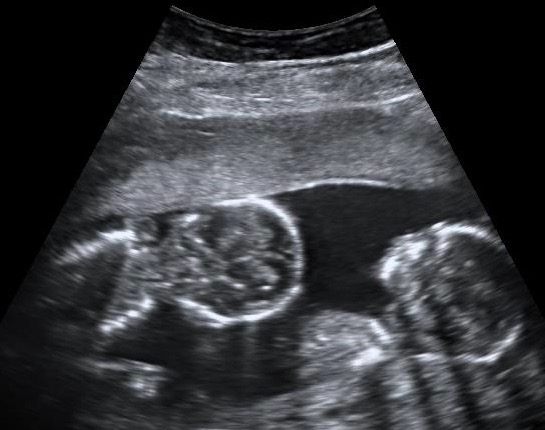
Ultrasound image of monochorionic-monoamniotic twins:
They share a single placenta and amniotic sac.
Multiple pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care is considered a high-risk pregnancy High-Risk Pregnancy Prenatal Care.
For twins the timing for delivery depends on chorionicity and amnioniticy:
Multiple pregnancy Pregnancy The status during which female mammals carry their developing young (embryos or fetuses) in utero before birth, beginning from fertilization to birth. Pregnancy: Diagnosis, Physiology, and Care presents higher risk to develop complications such as:
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome:
Twin anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types polycythemia Polycythemia An increase in the total red cell mass of the blood. Renal Cell Carcinoma sequence (TAPS):
Twin reversed arterial perfusion (TRAP):
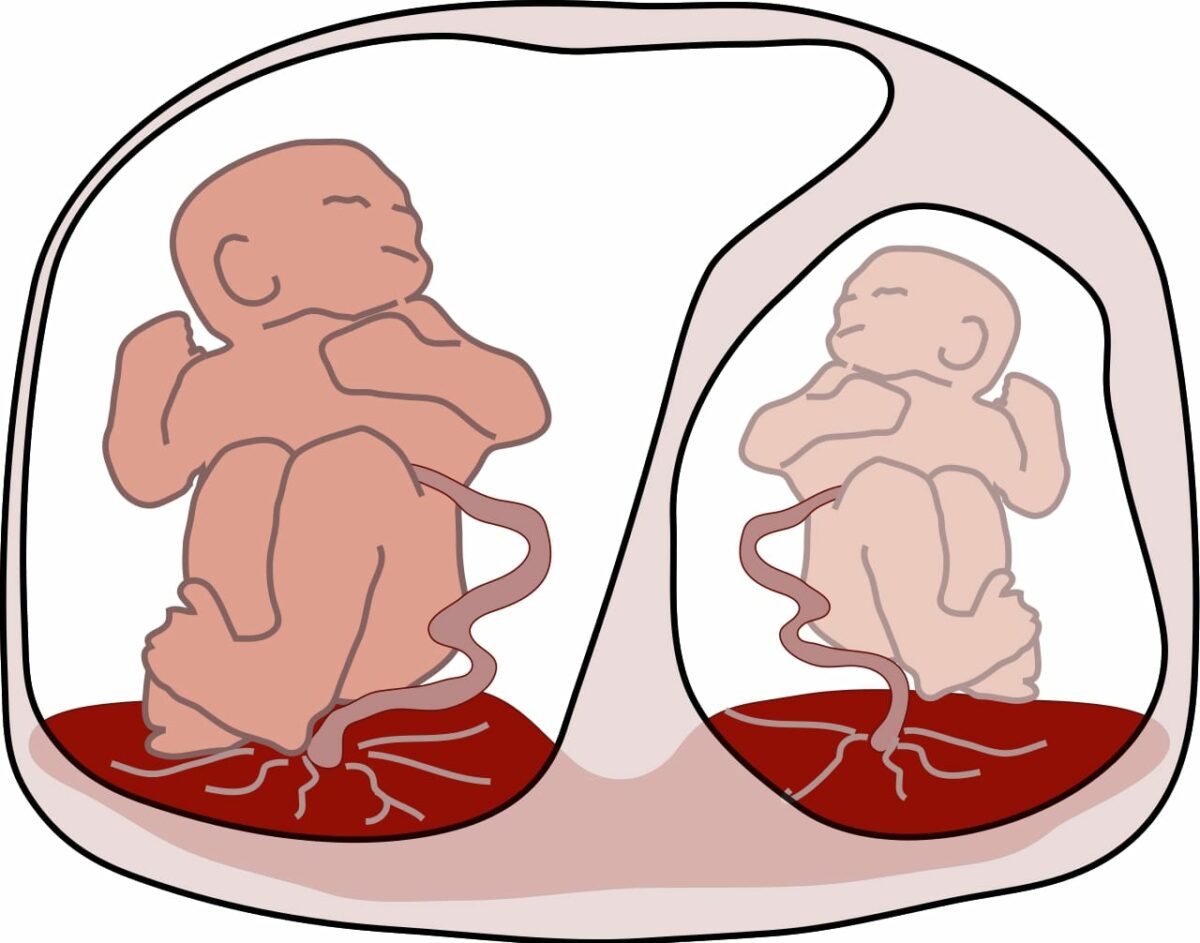
Twin-to-twin transfusion syndrome:
The image demonstrates a larger recipient twin on the left and a smaller, paler donor on the right.
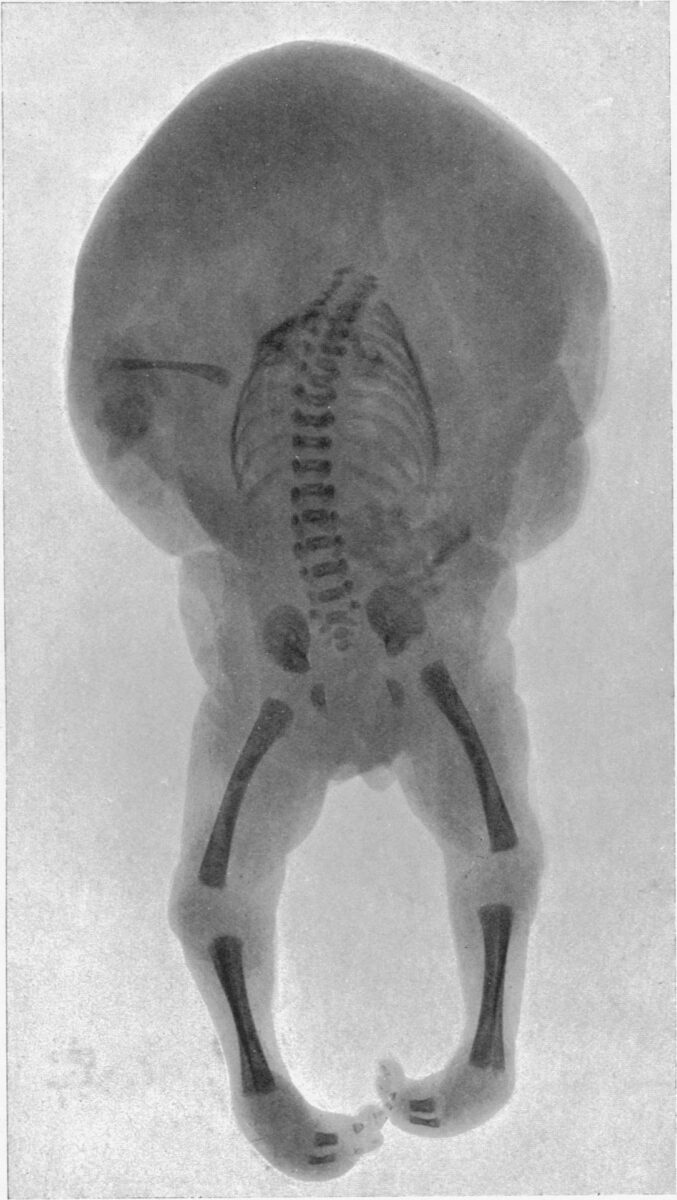
An acardiac fetus (similar to a twin reversed arterial perfusion (TRAP)) with a normally-developed lower body and an underdeveloped upper body
Image: “An acardiac foetus” by R. J. Gladstone. License: Public Domain