Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products cells (activated B lymphocytes B lymphocytes Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies of IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions. Osteoclastic activity results in bone resorption Bone resorption Bone loss due to osteoclastic activity. Bones: Remodeling and Healing, bone Bone Bone is a compact type of hardened connective tissue composed of bone cells, membranes, an extracellular mineralized matrix, and central bone marrow. The 2 primary types of bone are compact and spongy. Bones: Structure and Types pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, pathologic fractures, and metabolic disturbances. Excessive secretion Secretion Coagulation Studies of antibodies Antibodies Immunoglobulins (Igs), also known as antibodies, are glycoprotein molecules produced by plasma cells that act in immune responses by recognizing and binding particular antigens. The various Ig classes are IgG (the most abundant), IgM, IgE, IgD, and IgA, which differ in their biologic features, structure, target specificity, and distribution. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions results in proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children and associated kidney damage as well as production and tissue deposition of amyloid fibrils. Metabolic disturbances combined with tissue amyloid deposition cause end-organ damage. Diagnosis is established by plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products electrophoresis Electrophoresis An electrochemical process in which macromolecules or colloidal particles with a net electric charge migrate in a solution under the influence of an electric current. Blotting Techniques and bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma. Treatments to slow down the disease progression are available; however, there is no cure for MM. The median survival is approximately 3 years.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Multiple myeloma (MM) is a bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis malignancy Malignancy Hemothorax arising from monoclonal plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products cells.
Features of MM: “CRAB“
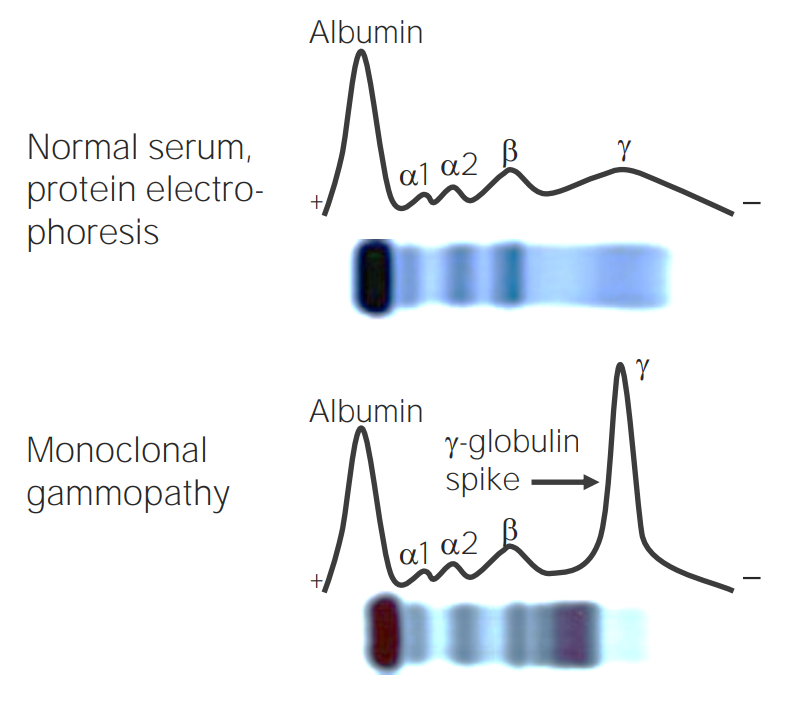
SPEP showing the M spike in patients with MM
Image by Lecturio.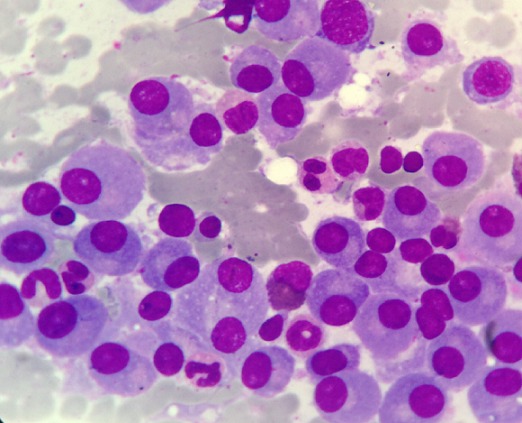
Multiple myeloma:
Bone marrow infiltration with mature plasma cells: Note the eccentric nuclei and perinuclear pale zones.
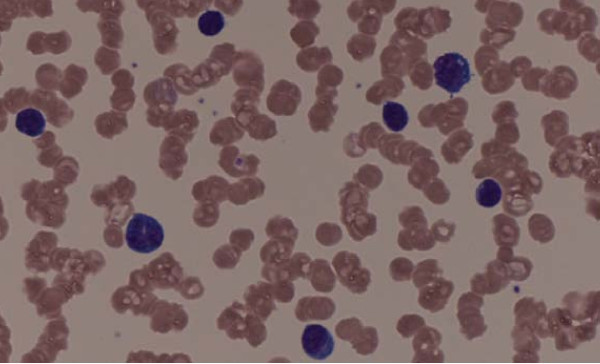
Peripheral blood smear shows rouleaux formation
Image: “Rouleaux formation” by Michail Charakidis, David Joseph Russell. License: CC BY 2.0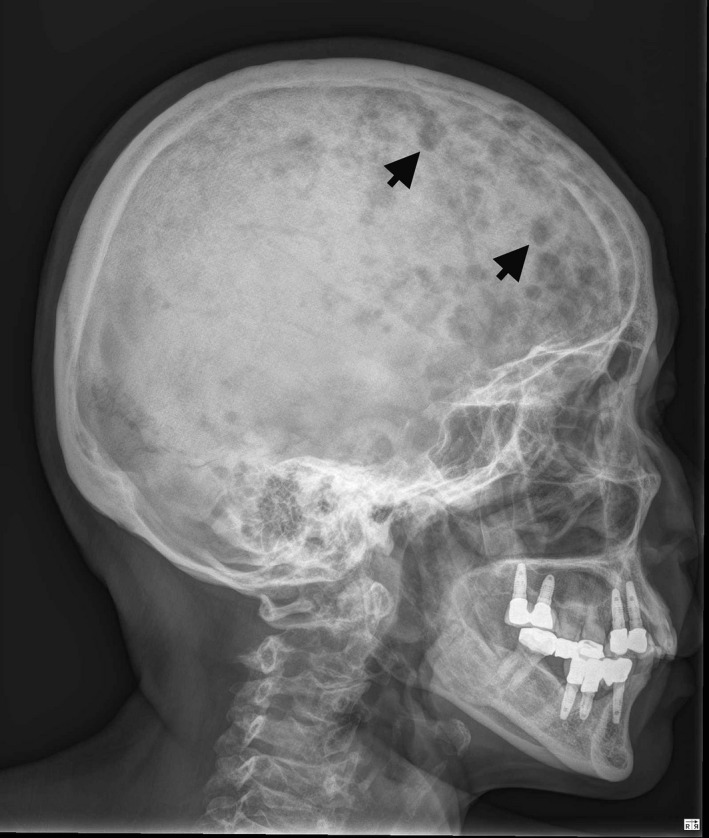
Multiple lytic lesions (arrows) on the skull
Image: “X‐ray of skull bone shows multiple punched‐out lesions (arrows)” by Ya‐Ting Hsu and Kung‐Chao Chang. License: CC BY 4.0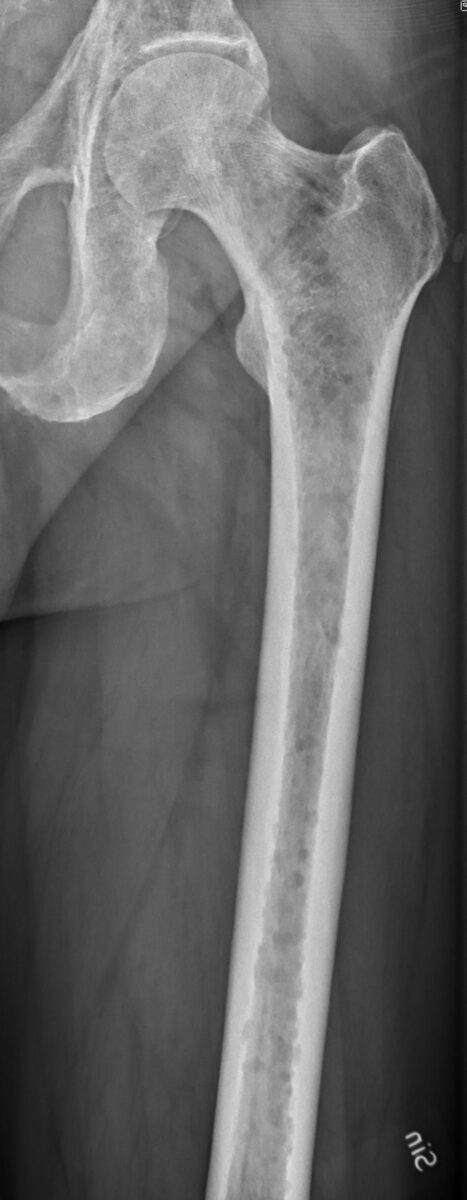
Multiple myeloma:
X-ray of the left femur shows lytic lesions with osteopenia.