Multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes are autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance inherited conditions characterized by 2 or more hormone-producing tumors involving the endocrine organs. There are different types of MEN, namely MEN1–4. The MEN1 syndrome is associated with MEN1 gene mutation Gene Mutation Myotonic Dystrophies and has a predilection for primary hyperparathyroidism Primary hyperparathyroidism A condition of abnormally elevated output of parathyroid hormone due to parathyroid hyperplasia or parathyroid neoplasms. It is characterized by the combination of hypercalcemia, phosphaturia, elevated renal 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 synthesis, and increased bone resorption. Hyperparathyroidism, pituitary Pituitary A small, unpaired gland situated in the sella turcica. It is connected to the hypothalamus by a short stalk which is called the infundibulum. Hormones: Overview and Types adenomas, and pancreatic tumors (the 3 P’s). Due to the RET proto-oncogene mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations, MEN2 syndrome can be further categorized as MEN2A and MEN2B. Medullary thyroid carcinoma Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma Thyroid Cancer and pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma Pheochromocytoma is a catecholamine-secreting tumor derived from chromaffin cells. The majority of tumors originate in the adrenal medulla, but they may also arise from sympathetic ganglia (also referred to as paraganglioma). Symptoms are associated with excessive catecholamine production and commonly include hypertension, tachycardia, headache, and sweating. Pheochromocytoma are common features. The MEN2A variant is associated with primary hyperparathyroidism Primary hyperparathyroidism A condition of abnormally elevated output of parathyroid hormone due to parathyroid hyperplasia or parathyroid neoplasms. It is characterized by the combination of hypercalcemia, phosphaturia, elevated renal 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin d3 synthesis, and increased bone resorption. Hyperparathyroidism, whereas MEN2B (also considered MEN3) is associated with neuromas and Marfanoid habitus. The newer and rare entity, MEN4, has features of MEN1 but results from CDKN1B mutations. The diagnosis is clinical, and tumors are detected based on imaging and correlating hormone levels. Genetic testing Genetic Testing Detection of a mutation; genotype; karyotype; or specific alleles associated with genetic traits, heritable diseases, or predisposition to a disease, or that may lead to the disease in descendants. It includes prenatal genetic testing. Myotonic Dystrophies plays a crucial role in MEN2 syndromes in determining further management. Treatment is dependent on the tumors that are present and genetic mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) syndromes are genetic disorders characterized by the presence of ≥ 2 endocrine tumors.
| MEN1 | MEN2A and MEN2B | MEN4 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pattern | Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance | Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance | Autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance |
| Genetic mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations | MEN1 gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics on chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 11 (11q13) | RET proto-oncogene on chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 10 (10q11.2) | CDKN1B on chromosome Chromosome In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. Basic Terms of Genetics 12 (12p13) |
| Clinical features |
|
MEN2A
MEN2B
|
|
| Treatment |
|
|
|

Image summary of the main types of multiple endocrine neoplasia syndromes
Image: “Multiple endocrine neoplasia” by Mikael Häggström. License: CC0 1.0, edited by Lecturio.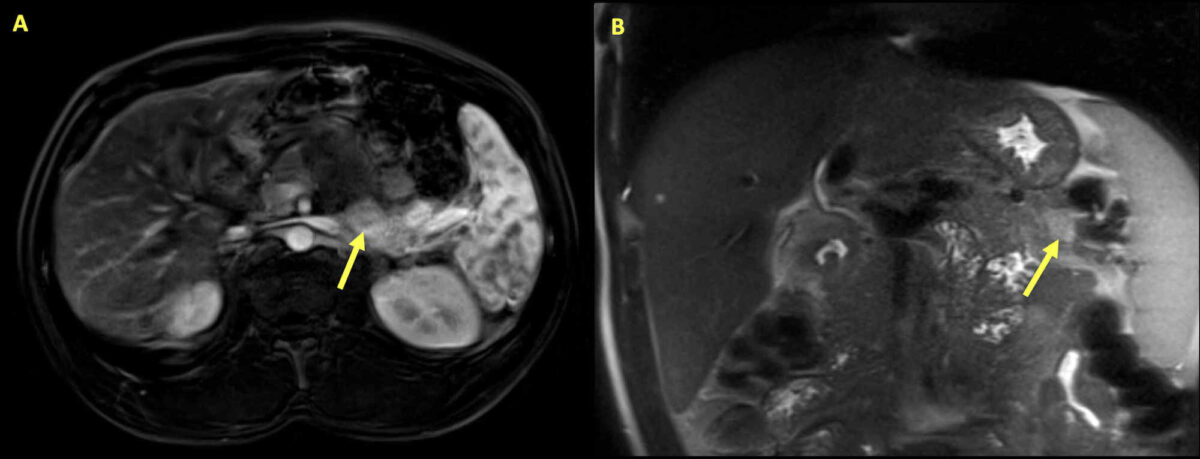
Insulinoma:
Magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen of a 34-year-old man presenting with hypoglycemia and hypercalcemia. Multiple pancreatic lesions are seen with the arrows highlighting the largest lesion. The mass is a 2.8 cm x 1.3 cm area of variable enhancement and diffusion restriction within the pancreas, consistent with insulinoma.
Further tests revealed elevated intact parathyroid hormone. With primary hyperparathyroidism and insulinoma, genetic testing was performed, which showed MEN1 gene mutation that confirmed the presence of MEN1 syndrome.
To recall the locations of tumor Tumor Inflammation development in MEN1, remember the 3 Ps PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation:
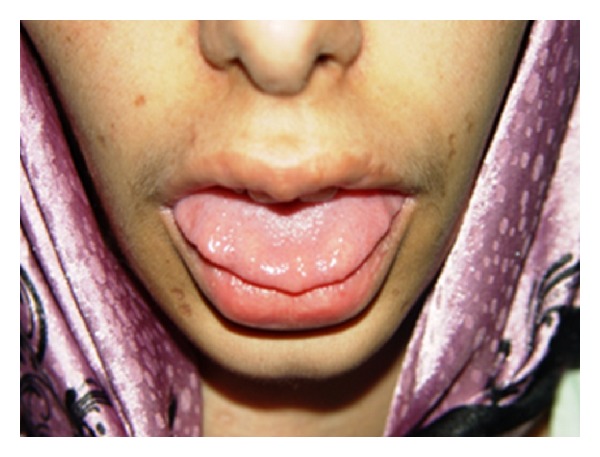
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN)2B:
Image shows neuromas on the anterior third of the tongue in a patient with MEN2B
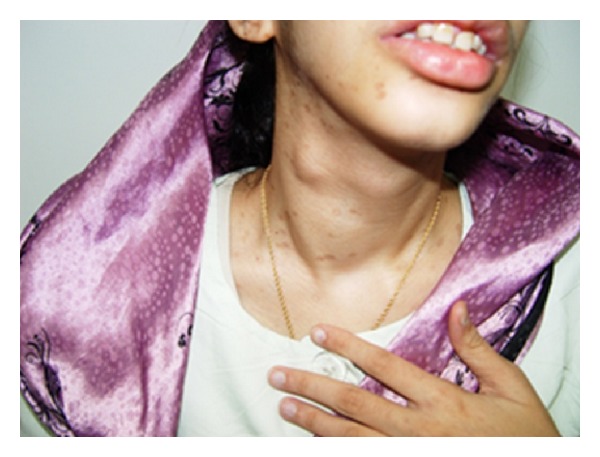
Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN)2B:
Image shows that the patient has a goiter with a thyroid nodule on the right lobe. Biopsy later revealed medullary thyroid carcinoma.
To recall the location of tumor Tumor Inflammation development in MEN2, remember the 3 Ps PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation: