The mucopolysaccharidoses, a subset of the lysosomal storage diseases, are a group of inherited disorders characterized by absent or defective enzymes needed to break down carbohydrate chains called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), previously known as mucopolysaccharides. These disorders lead to the accumulation of GAGs within cell lysosomes Lysosomes A class of morphologically heterogeneous cytoplasmic particles in animal and plant tissues characterized by their content of hydrolytic enzymes and the structure-linked latency of these enzymes. The intracellular functions of lysosomes depend on their lytic potential. The single unit membrane of the lysosome acts as a barrier between the enzymes enclosed in the lysosome and the external substrate. The activity of the enzymes contained in lysosomes is limited or nil unless the vesicle in which they are enclosed is ruptured or undergoes membrane fusion. The Cell: Organelles, resulting in a variety of health problems. Most patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship appear healthy at birth, but physical and/or mental function deteriorates as accumulation progresses. With disease progression, multiple organ systems may be affected. The diagnosis can be made by measuring urine GAG concentrations and by performing enzyme assays to identify the enzyme deficiency. Management depends on the specific disorder, degree of GAG accumulation, and degree of deformity Deformity Examination of the Upper Limbs.
Last updated: Apr 23, 2025
Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPSs) are a group of genetic metabolic diseases due to absent or defective enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body’s constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes needed to break down carbohydrate chains called glycosaminoglycans (GAGs).
The MPSs are all inherited and classified on the basis of the enzyme deficiency.
Affected individuals are usually not affected at birth, but they experience disease progression as they age. Clinical features vary based on the MPS type.
Results in a continuous spectrum of disease that is divided into 3 clinical entities based on disease severity (less severe forms referred to as attenuated):
Distinguishing clinical features (more or less pronounced depending on severity):
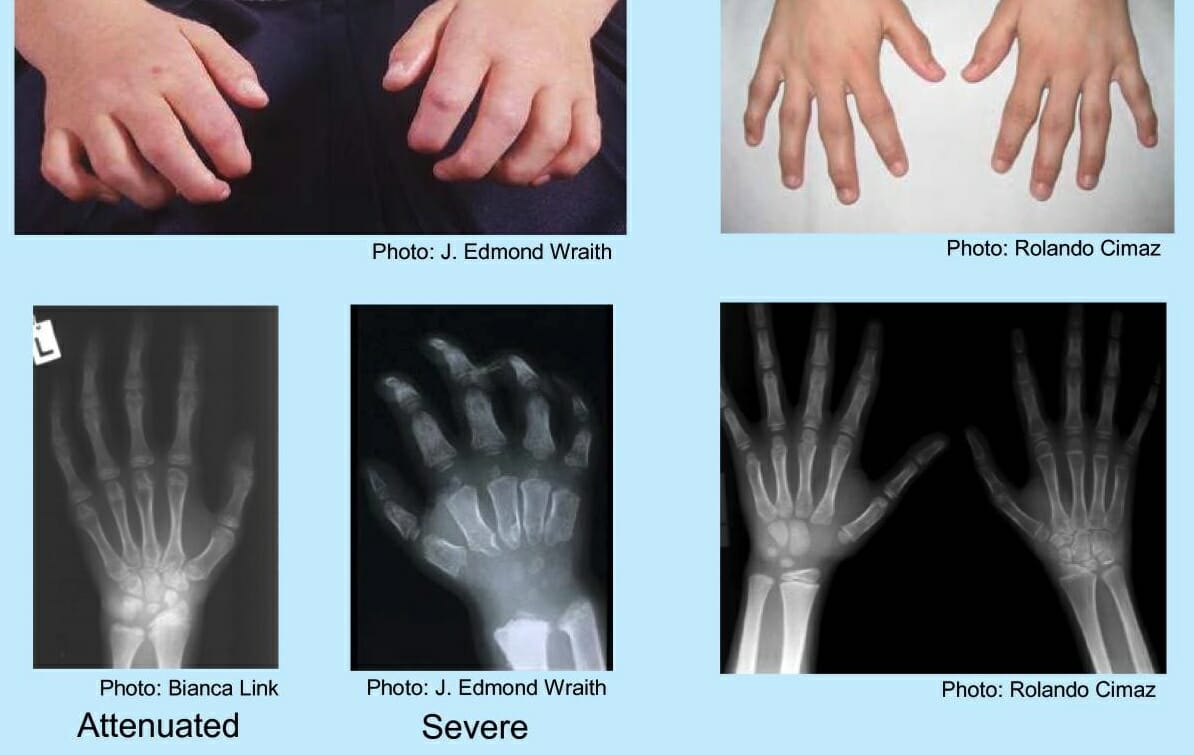
Hands of a child with mucopolysaccharidosis:
Findings include a curled “claw” hand, abnormal metacarpal bones, proximal widening of phalanges, and a V-shaped deformity in the distal radius and ulna.
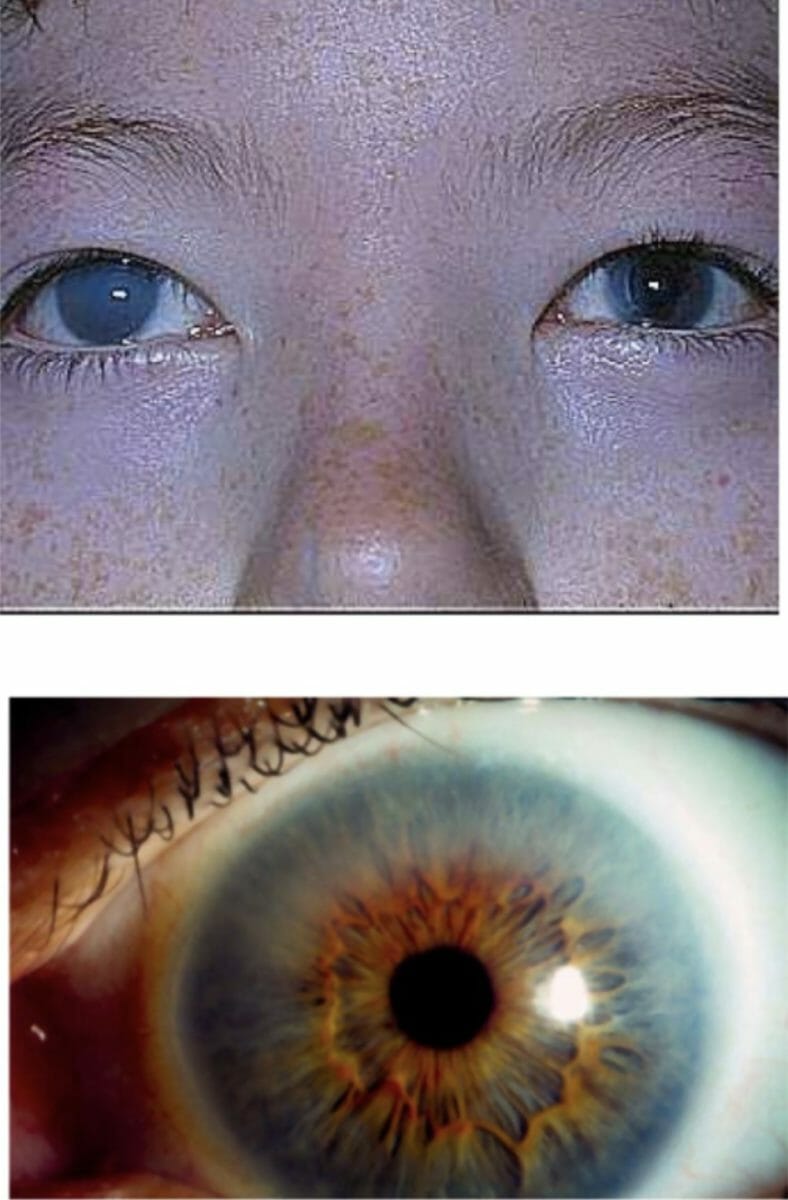
Corneal clouding in a patient with MPS I:
This finding can be severe, as shown in the upper image, or it can be less noticeable, as shown in the bottom image.
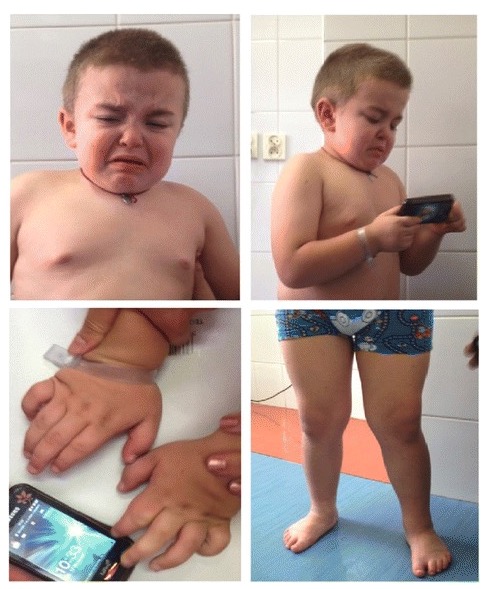
Clinical features of mucopolysaccharidosis IIIA:
Facial dysmorphism (coarse facial features, slightly depressed nasal bridge, prominent eyebrows, low-set ears, malocclusion, full cheeks, wiry and dry hair, and short neck) and skeletal symptoms (genu valga, varus feet, and stocky hands) are shown.
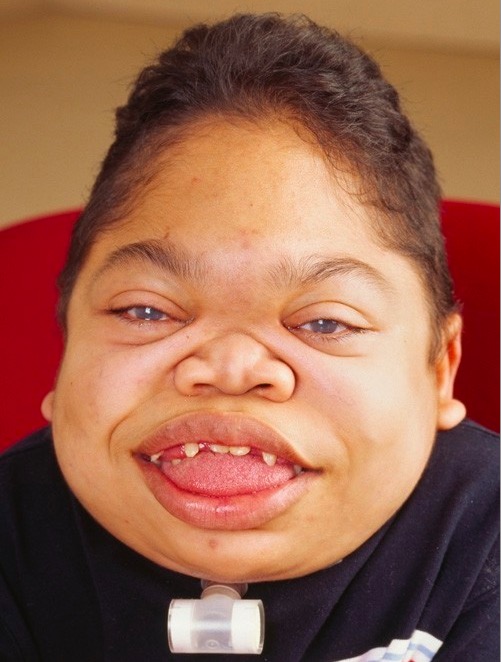
Rapidly progressing MPS VI in a 16-year-old patient:
Face shows coarse facies, with frontal bossing, enlarged tongue, thick lips, abnormal dentition, and gingival hyperplasia.
Clinical history and examination:
Laboratory analysis:
There is no cure for MPS. Medical care Medical care Conflict of Interest is aimed at treating systemic conditions and at improving quality Quality Activities and programs intended to assure or improve the quality of care in either a defined medical setting or a program. The concept includes the assessment or evaluation of the quality of care; identification of problems or shortcomings in the delivery of care; designing activities to overcome these deficiencies; and follow-up monitoring to ensure effectiveness of corrective steps. Quality Measurement and Improvement of life. At this time, eventual decline in function is inevitable.