Infectious mononucleosis (IM), also known as “the kissing disease,” is a highly contagious viral infection caused by the Epstein-Barr virus Epstein-Barr Virus Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the Herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus. Its common name is derived from its main method of transmission: the spread of infected saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy via kissing. Clinical manifestations of IM include fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, tonsillar pharyngitis Pharyngitis Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the back of the throat (pharynx). Pharyngitis is usually caused by an upper respiratory tract infection, which is viral in most cases. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, and hoarseness. Pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy Lymphadenopathy Lymphadenopathy is lymph node enlargement (> 1 cm) and is benign and self-limited in most patients. Etiologies include malignancy, infection, and autoimmune disorders, as well as iatrogenic causes such as the use of certain medications. Generalized lymphadenopathy often indicates underlying systemic disease. Lymphadenopathy. Diagnosis is clinical and confirmed through heterophile antibody testing or specific serologic antibody testing. There is currently no specific antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B therapy available for this condition.
Last updated: May 19, 2023
Infectious mononucleosis (IM) is a viral infectious disease most commonly caused by the Epstein-Barr virus Epstein-Barr Virus Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the Herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus ( EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus) and is characterized by a triad of fever Fever Fever is defined as a measured body temperature of at least 38°C (100.4°F). Fever is caused by circulating endogenous and/or exogenous pyrogens that increase levels of prostaglandin E2 in the hypothalamus. Fever is commonly associated with chills, rigors, sweating, and flushing of the skin. Fever, tonsillar pharyngitis Pharyngitis Pharyngitis is an inflammation of the back of the throat (pharynx). Pharyngitis is usually caused by an upper respiratory tract infection, which is viral in most cases. It typically results in a sore throat and fever. Other symptoms may include a runny nose, cough, headache, and hoarseness. Pharyngitis, and lymphadenopathy Lymphadenopathy Lymphadenopathy is lymph node enlargement (> 1 cm) and is benign and self-limited in most patients. Etiologies include malignancy, infection, and autoimmune disorders, as well as iatrogenic causes such as the use of certain medications. Generalized lymphadenopathy often indicates underlying systemic disease. Lymphadenopathy.
EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus belongs to the group of human herpesviruses (HHV-4).
EBV EBV Epstein-barr virus (EBV) is a linear, double-stranded DNA virus belonging to the herpesviridae family. This highly prevalent virus is mostly transmitted through contact with oropharyngeal secretions from an infected individual. The virus can infect epithelial cells and B lymphocytes, where it can undergo lytic replication or latency. Epstein-Barr Virus has an exceptionally high species specificity:
The disease is transmitted mainly via contact with body secretions, primarily oropharyngeal secretions.
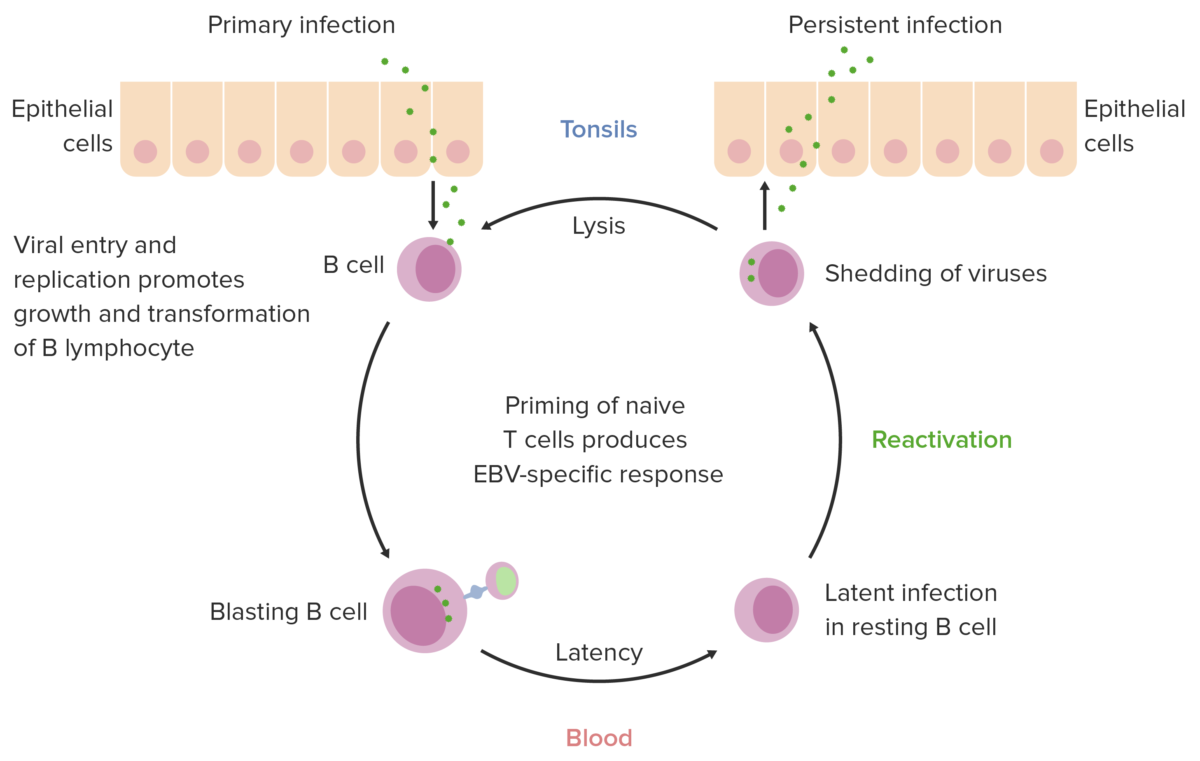
The Epstein-Barr virus can infect both B cells and oropharyngeal epithelial cells. EBV enters B cells by binding to the cellular receptor CD21, allowing fusion of the viral envelope with the cell membrane. The lytic cycle results in the production of infectious virions in both B cells and oropharyngeal epithelial cells. In B cells, lytic replication normally only takes place after reactivation from latency, whereas in oropharyngeal epithelial cells the lytic replication often directly follows viral entry. During lytic replication, viral DNA polymerase is responsible for synthesizing the viral genome. This contrasts with latency, in which host-cell DNA polymerase copies the viral genome. However, latency does not result in the production of virions, since only a portion of EBV’s genes are expressed.
Image by Lecturio.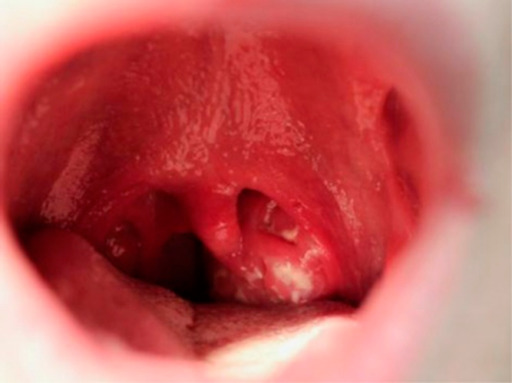
Pharyngitis demonstrating exudative tonsillitis and an enlarged uvula in an adolescent patient 5 days after the onset of infectious mononucleosis
Image: “Infectious mononucleosis” by University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, MN, USA. License: CC BY 4.0Diagnosis is based on clinical symptoms noted above with confirmatory testing.
If IM is suspected from history and physical examination, order a WBC count with differential and a heterophile test.
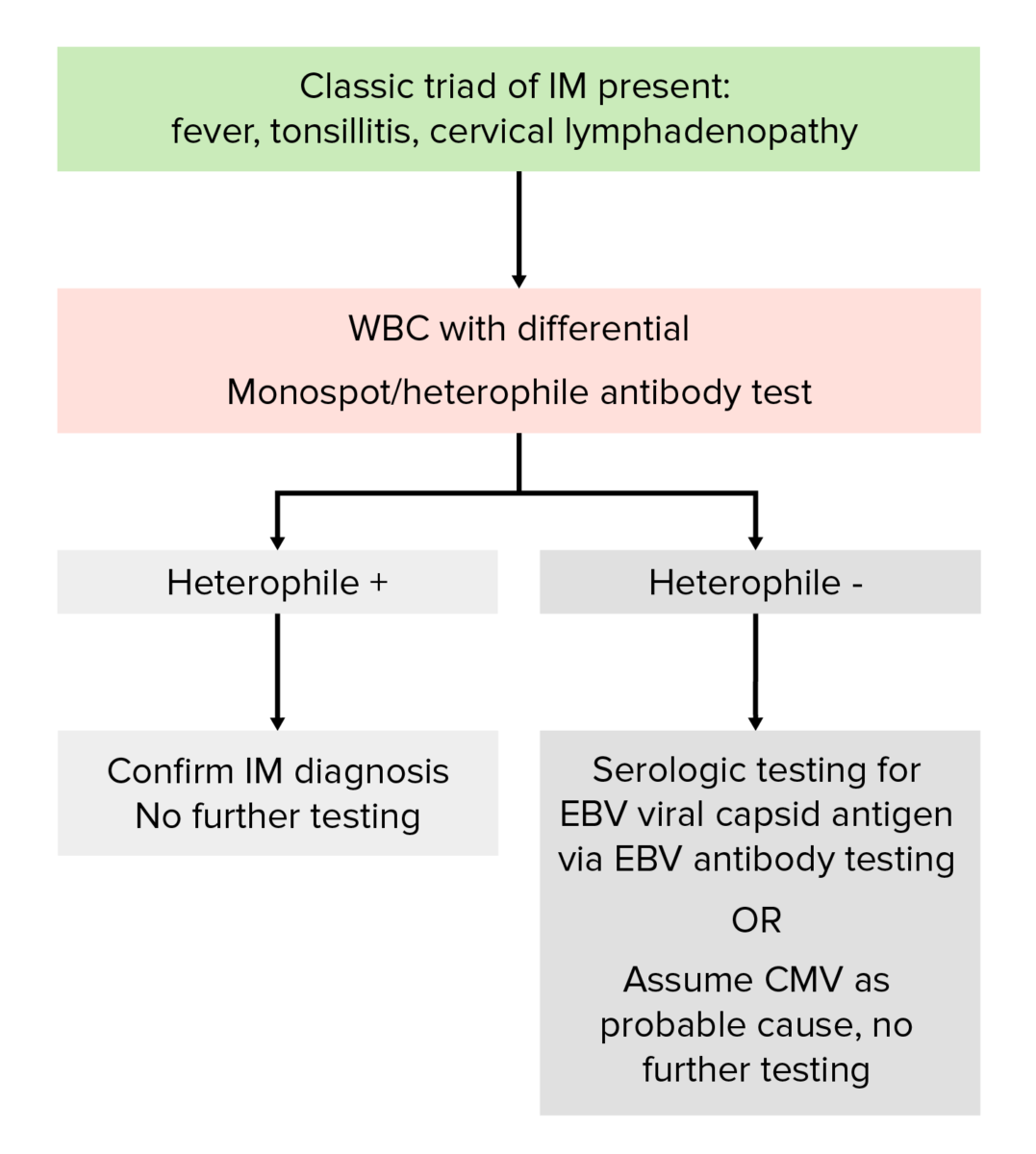
Diagnostic algorithm for infectious mononucleosis
Image by Lecturio.There is currently no specific antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B therapy available, so treatment is supportive.
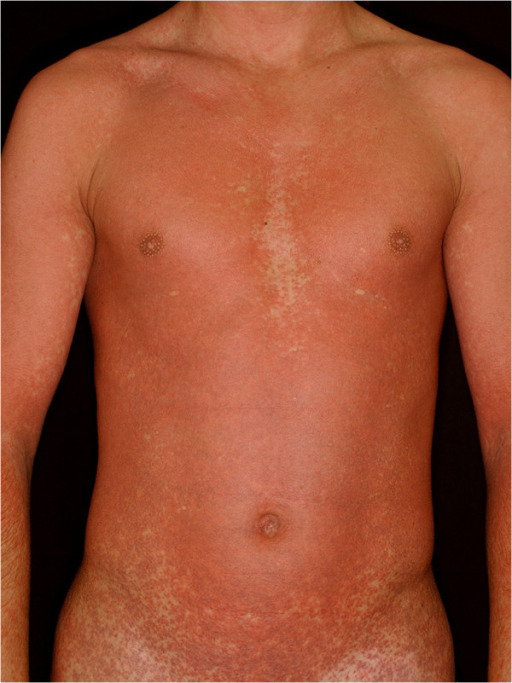
Amoxicillin rash in patients with infectious mononucleosis
Image: “Amoxicillin rash in a patient with infectious mononucleosis (patient 4)” by Department of Dermatology and Allergology, University of Szeged, Szeged, Hungary. License: CC BY 4.0Many patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship develop secondary streptococcal pharyngitis Streptococcal Pharyngitis Rheumatic Fever.
The following conditions are differential diagnoses for infectious mononucleosis:
References