Monoamine oxidase Oxidase Neisseria inhibitors are a class of antidepressants that inhibit the activity of monoamine oxidase Oxidase Neisseria (MAO), thereby increasing the amount of monoamine neurotransmitters (particularly serotonin Serotonin A biochemical messenger and regulator, synthesized from the essential amino acid l-tryptophan. In humans it is found primarily in the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and blood platelets. Serotonin mediates several important physiological functions including neurotransmission, gastrointestinal motility, hemostasis, and cardiovascular integrity. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS, norepinephrine Norepinephrine Precursor of epinephrine that is secreted by the adrenal medulla and is a widespread central and autonomic neurotransmitter. Norepinephrine is the principal transmitter of most postganglionic sympathetic fibers, and of the diffuse projection system in the brain that arises from the locus ceruleus. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS, and dopamine Dopamine One of the catecholamine neurotransmitters in the brain. It is derived from tyrosine and is the precursor to norepinephrine and epinephrine. Dopamine is a major transmitter in the extrapyramidal system of the brain, and important in regulating movement. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS). The increase of these neurotransmitters can help in alleviating the symptoms of depression. Selective inhibitors Selective Inhibitors Pulmonary Hypertension Drugs of MAO type B can also be used for the treatment of Parkinson disease Parkinson disease Parkinson's disease (PD) is a chronic, progressive neurodegenerative disorder. Although the cause is unknown, several genetic and environmental risk factors are currently being studied. Individuals present clinically with resting tremor, bradykinesia, rigidity, and postural instability. Parkinson’s Disease. Other uses include for bulimia Bulimia Eating an excess amount of food in a short period of time, as seen in the disorder of bulimia nervosa. It is caused by an abnormal craving for food, or insatiable hunger also known as 'ox hunger'. Bulimia Nervosa nervosa and panic disorder Panic disorder Panic disorder is a condition marked by recurrent and episodic panic attacks that occur abruptly and without a trigger. These episodes are time-limited and present with cardiorespiratory (palpitations, shortness of breath, choking), GI (nausea, abdominal distress), and neurologic (paresthesias, lightheadedness) symptoms. Panic Disorder. The major adverse effects include serotonin Serotonin A biochemical messenger and regulator, synthesized from the essential amino acid l-tryptophan. In humans it is found primarily in the central nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, and blood platelets. Serotonin mediates several important physiological functions including neurotransmission, gastrointestinal motility, hemostasis, and cardiovascular integrity. Receptors and Neurotransmitters of the CNS syndrome and hypertensive crisis Hypertensive Crisis Oxazolidinones. Special care should be taken to avoid other serotonergic medications and tyramine-containing foods.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The monoamine oxidase Oxidase Neisseria inhibitors (MAOIs) have variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables chemical structures.
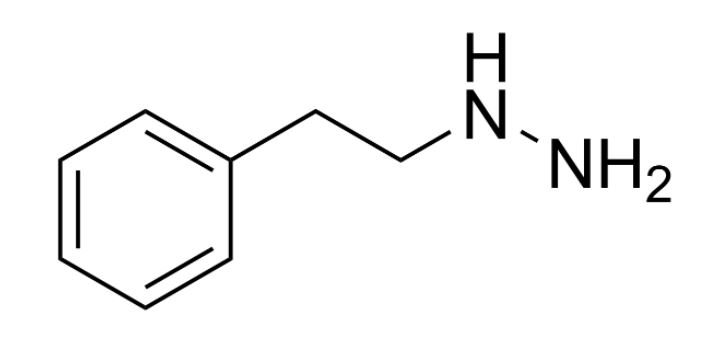
Chemical structure of phenelzine, a derivative of hydralazine
Image: “Phenelzine” by Edgar181. License: Public Domain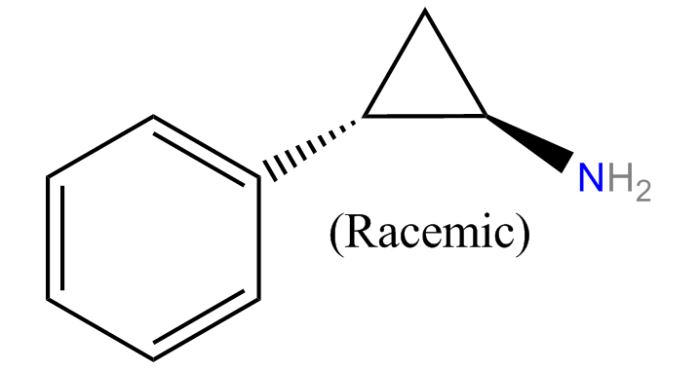
Chemical structure of tranylcypromine
Image: “Tranylcypromine” by Mykhal. License: Public Domain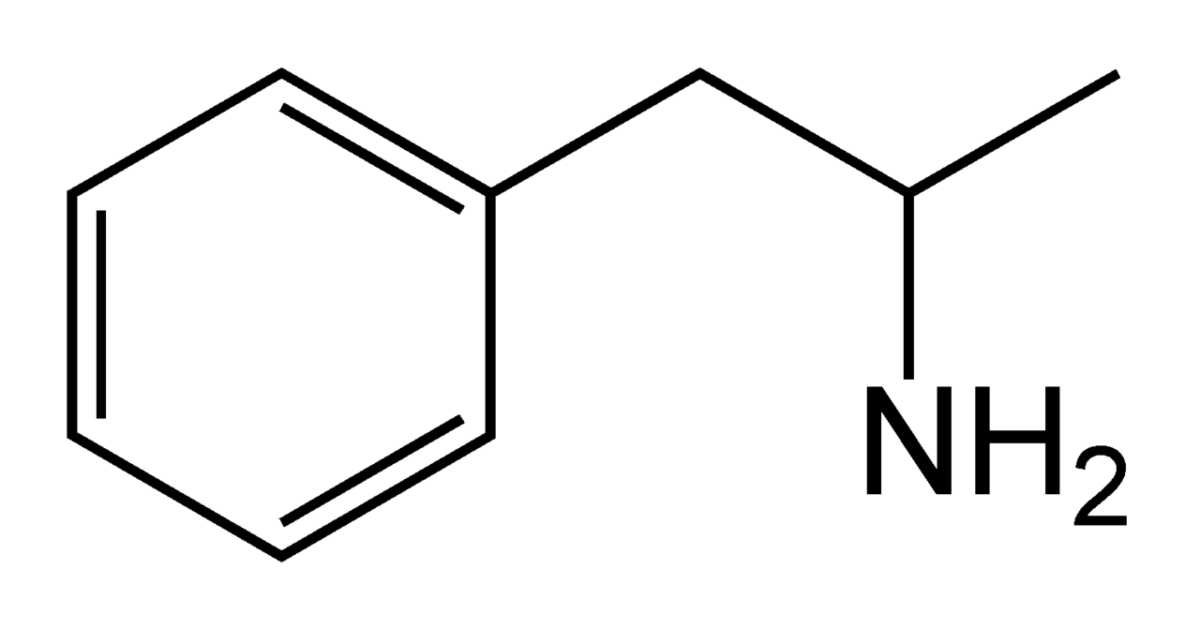
Chemical structure of amphetamine:
Note the similarity between this structure and that of tranylcypromine.Monoamine oxidase Oxidase Neisseria (MAO):
MAOIs:
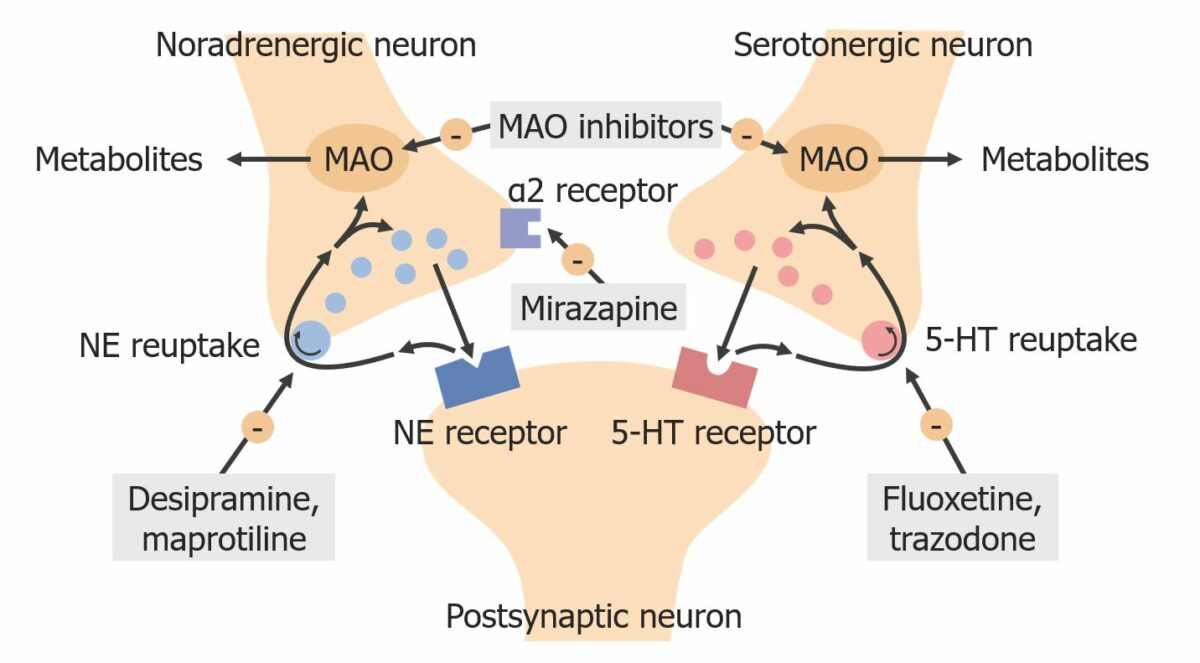
Mechanisms of antidepressants:
The basic mechanisms of action of commonly prescribed antidepressants are listed. These medications include monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, the α-2 antagonist mirtazapine, the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor fluoxetine, the serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor trazodone, the tricyclic antidepressant desipramine, and the tetracyclic drug maprotiline.
MAOIs are classified based on their selectivity for MAO-A and MAO-B.