Gregor Mendel (1822–1884), the "father of genetics", was an Augustine monk and mathematician who performed cross-breeding experiments with peas and beans from a monastery garden. Based on the experiments, Mendel deduced hereditary factors may be passed from the parental generation to the filial generation. From the deductions, the father of genetics Genetics Genetics is the study of genes and their functions and behaviors. Basic Terms of Genetics formed Mendel's laws of heredity: the law of segregation, the law of independent assortment, and the law of dominance. Mendel's laws described the inheritance of uncoupled autosomal genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure based on statistical predictions. The gene Gene A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. Basic Terms of Genetics traits follow the laws of mendelian inheritance.
Last updated: Feb 28, 2023
Mendel chose pea plants Plants Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic as the experimental model. Mendel reasoned pea plants Plants Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic were a good model of inheritance because of the following properties:
Mendel cross-fertilized plants Plants Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic truebred (purebred) for certain traits. Mendel selected 7 true-breeding traits:
True-breeding traits are referred to as homozygous alleles ( genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure). Example of determining true-breeding traits of flower color:
From the experiments, Mendel inferred:
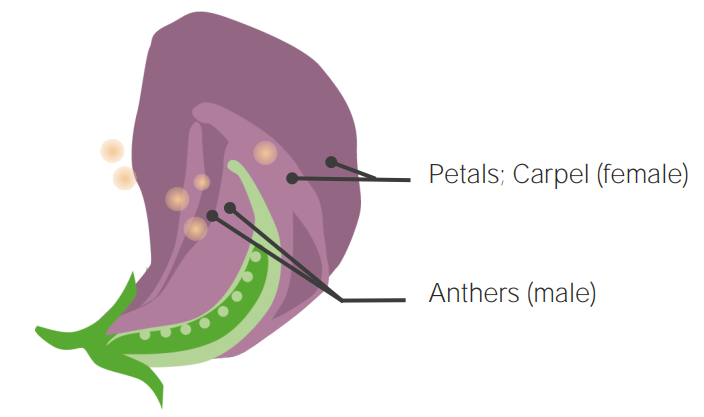
Anatomy of the pea plant
Image by Lecturio.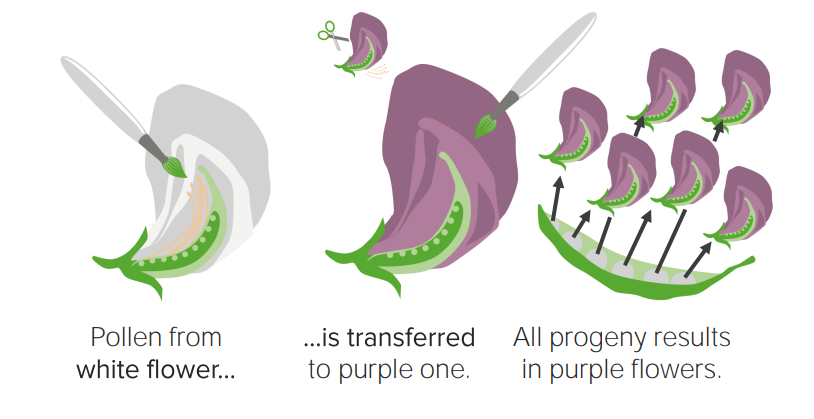
Cross-breeding between white and purple truebred pea plants: Purple is shown as the dominant trait.
Image by Lecturio.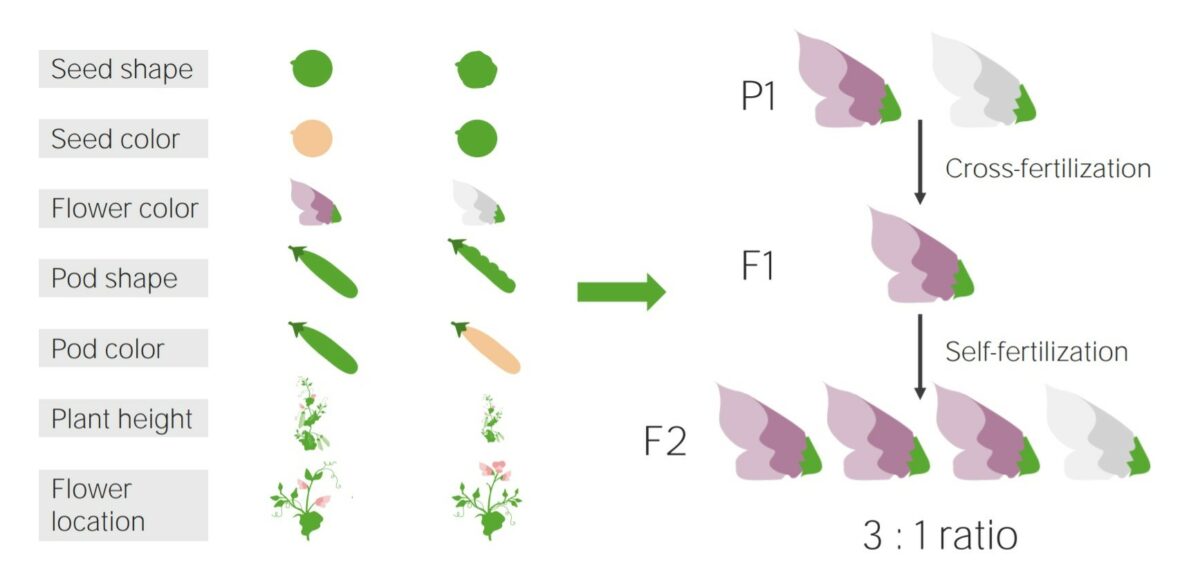
True-breeding traits and an example of a monohybrid cross
Image by Lecturio.A Punnett square is a statistical analysis tool based on Mendel’s research Research Critical and exhaustive investigation or experimentation, having for its aim the discovery of new facts and their correct interpretation, the revision of accepted conclusions, theories, or laws in the light of newly discovered facts, or the practical application of such new or revised conclusions, theories, or laws. Conflict of Interest:
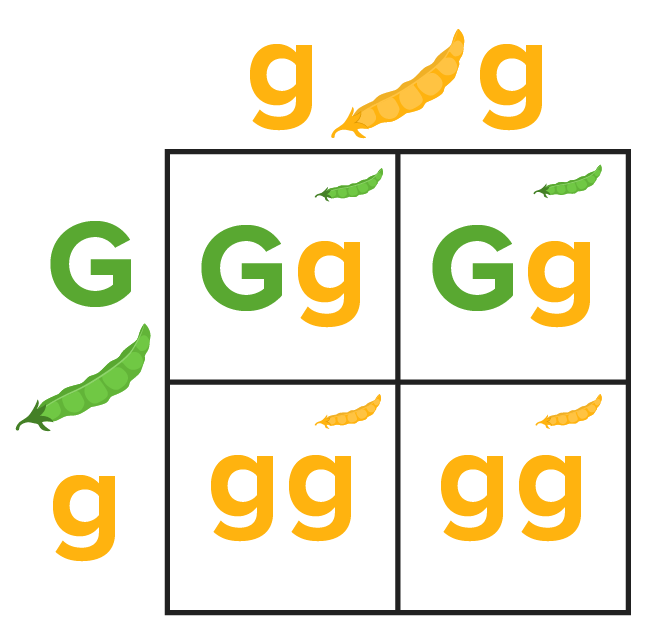
A Punnett square showing a typical test cross:
Green pod color is dominant over yellow for peapods. In contrast, yellow cotyledon color is dominant over green for pea seeds.
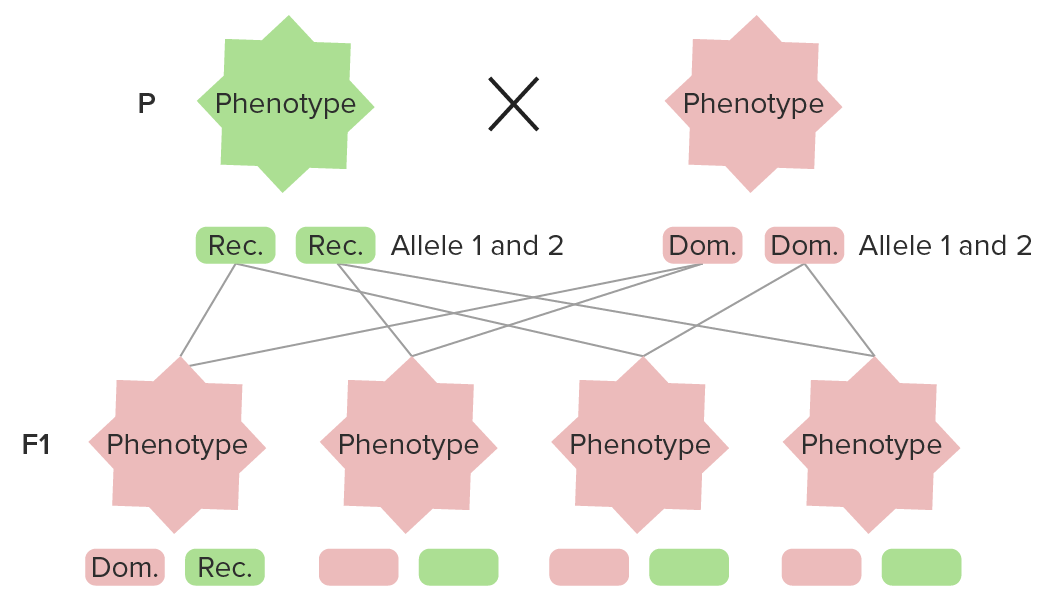
The diagram represents the 1st law of dominance:
All individuals in the 1st generation have the same genotype and phenotype, expressing the dominant trait (red).
P: Parental generation (homozygous genotype)
F1: 1st generation (heterozygous genotype)
Dom.: dominant
Rec.: recessive
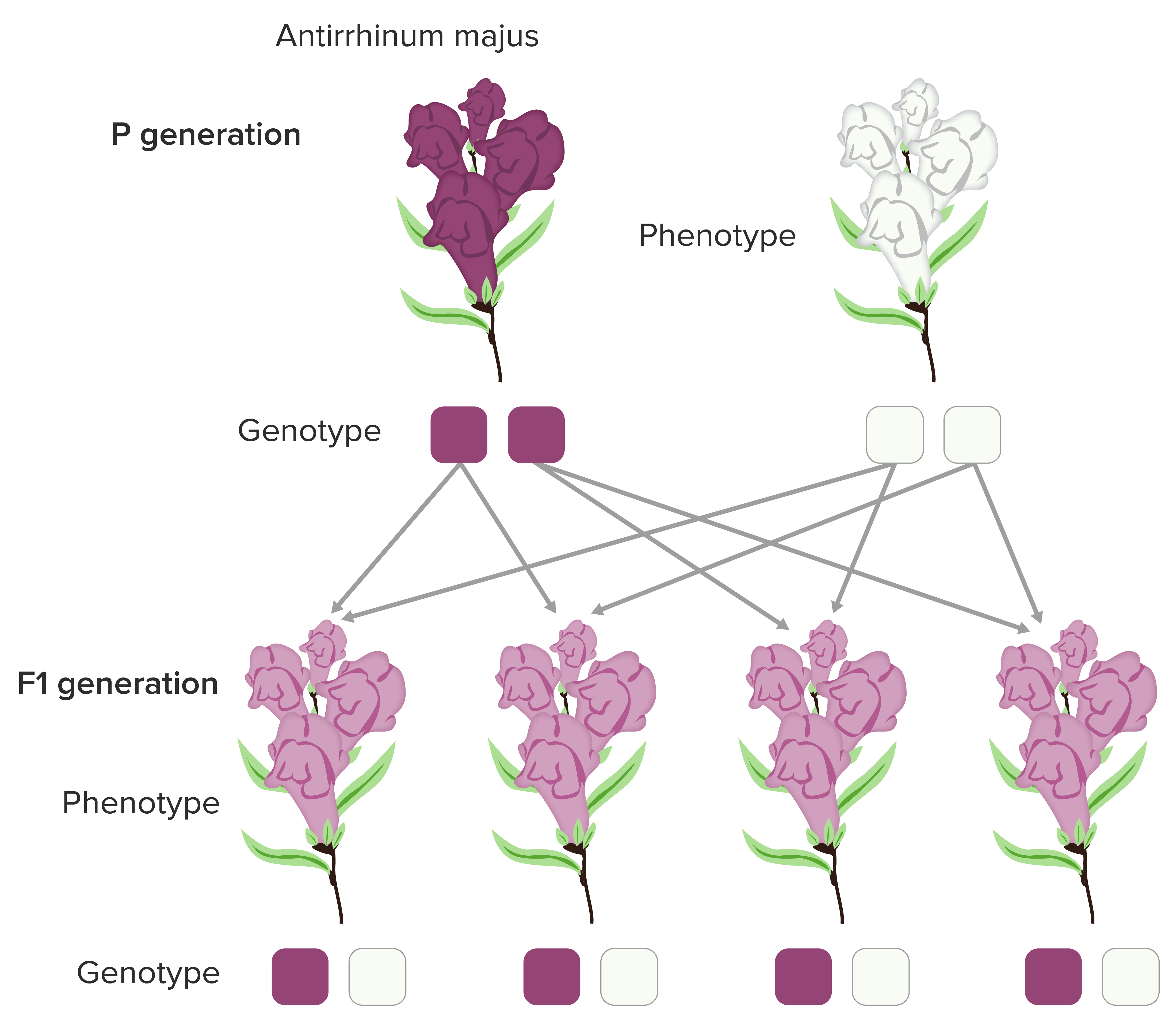
Image demonstrating the nonmendelian form of inheritance:
Intermediate inheritance of flower color in Antirrhinum majus due to incomplete dominance
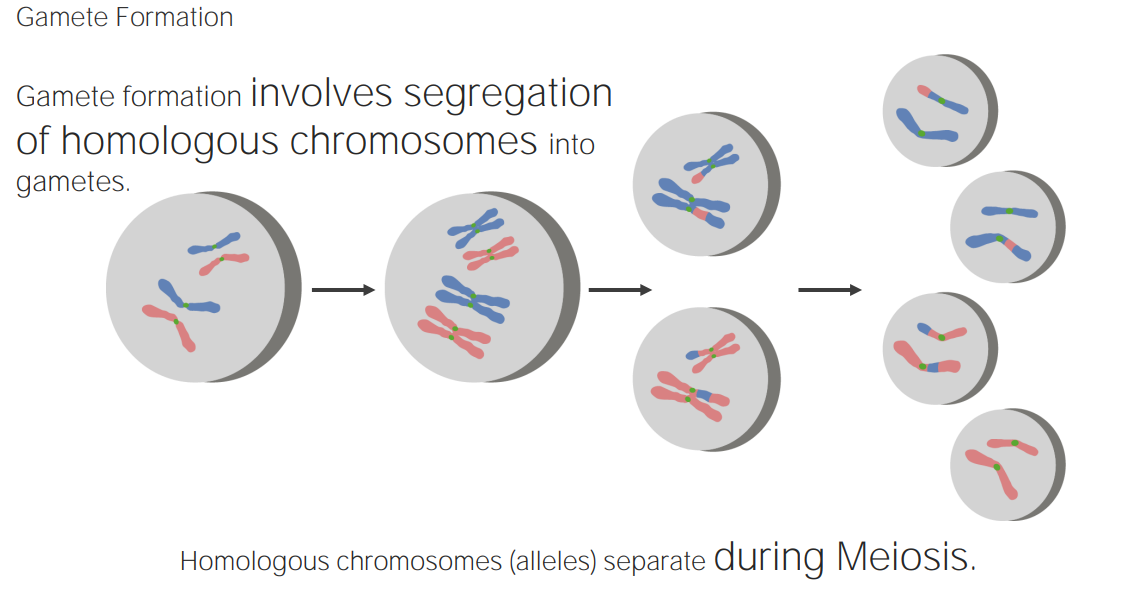
Segregation of alleles during gamete formation
Image by Lecturio.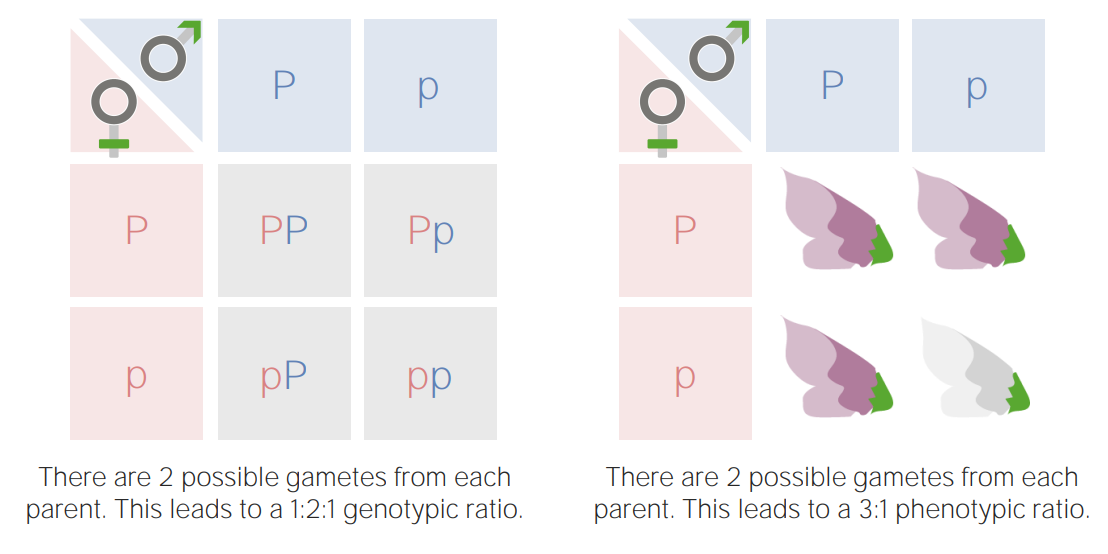
Punnett square of a monohybrid cross: The 1st square shows the possible genotypes; the 2nd square shows the possible phenotypes based on the dominance of purple flower color.
Image by Lecturio.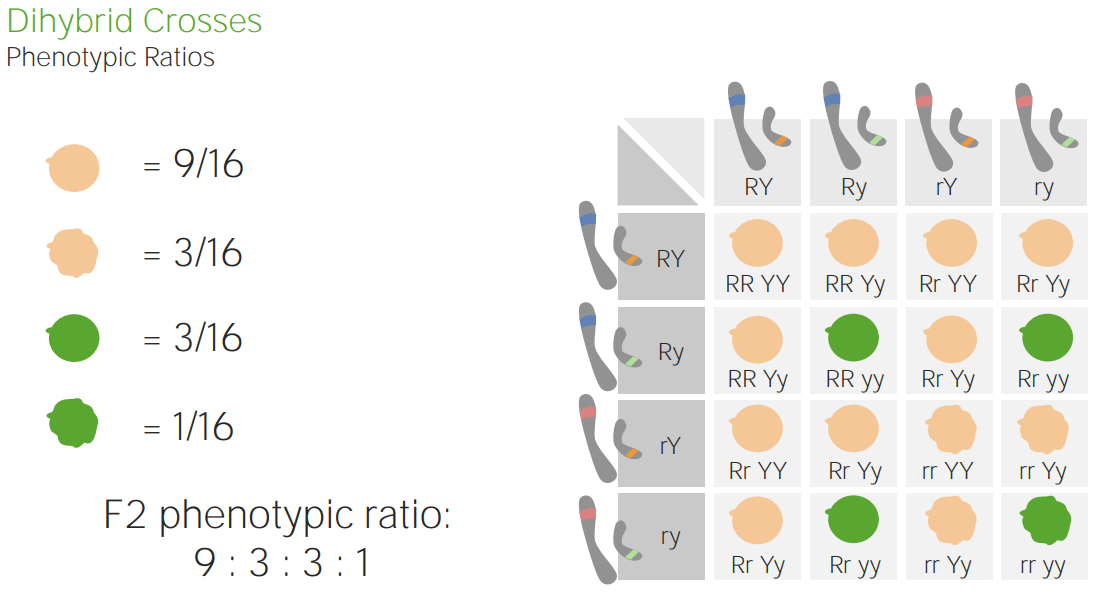
A Punnett square showing a dihybrid cross:
All possible genotypic and phenotypic combinations of the 2 alleles from 2 different genes are shown.