The creation of eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotes can be single-celled or multicellular organisms and include plants, animals, fungi, and protozoa. Eukaryotic cells contain a well-organized nucleus contained by a membrane, along with other membrane-bound organelles. Cell Types: Eukaryotic versus Prokaryotic gametes involves a DNA replication DNA replication The entire DNA of a cell is replicated during the S (synthesis) phase of the cell cycle. The principle of replication is based on complementary nucleotide base pairing: adenine forms hydrogen bonds with thymine (or uracil in RNA) and guanine forms hydrogen bonds with cytosine. DNA Replication phase followed by 2 cellular division stages: meiosis I and meiosis II. Meiosis I separates homologous chromosomes Homologous chromosomes Basic Terms of Genetics into separate cells (1n, 2c), while meiosis II separates sister chromatids into gametes (1n, 1c). Unique combinations of gametes via sexual reproduction are a major driver of evolutionary fitness in complex organisms.
Last updated: Apr 17, 2025
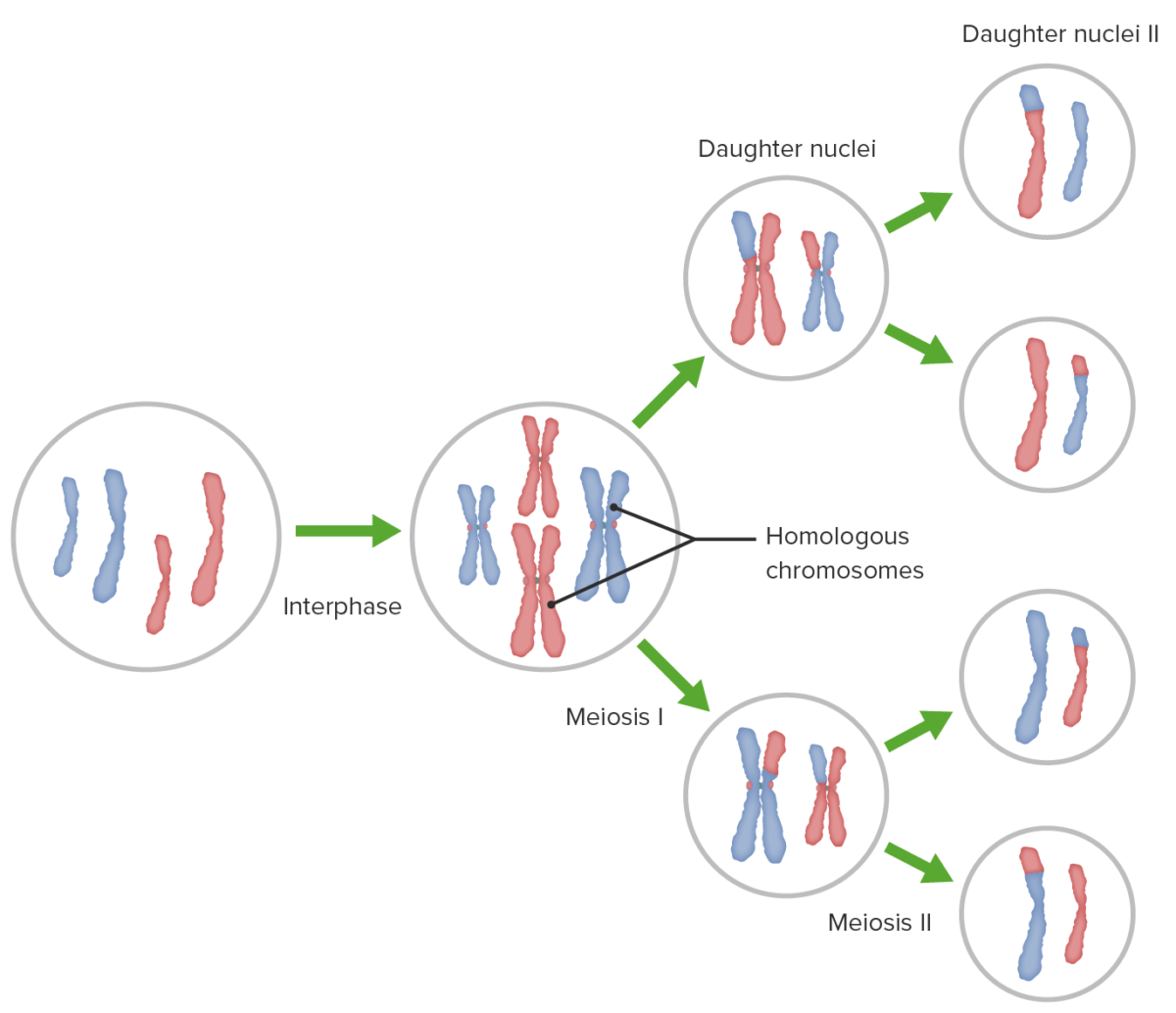
Overview of meiosis I and II, crossing over (homologous recombination), and independent assortment
Image by Lecturio.Following DNA replication DNA replication The entire DNA of a cell is replicated during the S (synthesis) phase of the cell cycle. The principle of replication is based on complementary nucleotide base pairing: adenine forms hydrogen bonds with thymine (or uracil in RNA) and guanine forms hydrogen bonds with cytosine. DNA Replication, meiosis I creates 2 daughter cells containing half the genetic information of the mother cell (1n) but the same number of chromosomes Chromosomes In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. DNA Types and Structure (2c) by segregating sister chromatids into the same daughter cell.
Reappearance of the nuclear membrane and nucleolus: the telophase
Image: “Reappearance of the nuclear membrane and nucleolus: the telophase” by Roy van Heesbeen. License: Public DomainMeiosis II is a cellular division event wherein the number of chromosomes Chromosomes In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. DNA Types and Structure in the daughter cells is halved from that of the mother cell.
The human karyotype Karyotype The full set of chromosomes presented as a systematized array of metaphase chromosomes from a photomicrograph of a single cell nucleus arranged in pairs in descending order of size and according to the position of the centromere. Congenital Malformations of the Female Reproductive System normally contains 23 pairs of chromosomes Chromosomes In a prokaryotic cell or in the nucleus of a eukaryotic cell, a structure consisting of or containing DNA which carries the genetic information essential to the cell. DNA Types and Structure.
Meiosis is important in the production of haploid Haploid The chromosomal constitution of cells, in which each type of chromosome is represented once. Symbol: n. Basic Terms of Genetics cells (gametes).
Spermatogenesis Spermatogenesis The process of germ cell development in the male from the primordial germ cells, through spermatogonia; spermatocytes; spermatids; to the mature haploid spermatozoa. Gametogenesis
Oogenesis Oogenesis The process of germ cell development in the female from the primordial germ cells through oogonia to the mature haploid ova (ovum). Gametogenesis
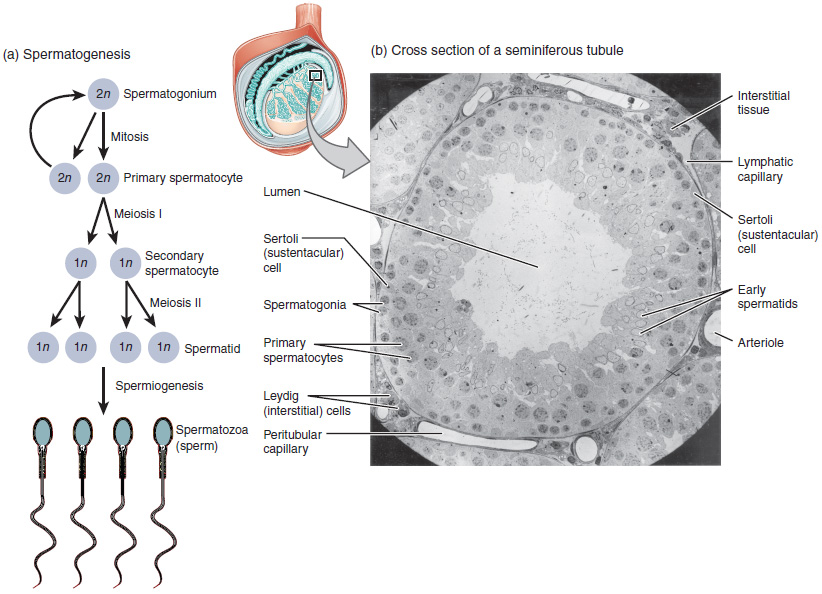
The process of spermatogenesis as the cells progress from primary spermatocytes to secondary spermatocytes to spermatids to sperm
Image: “Illustration from Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions” by OpenStax College. License: CC BY 3.0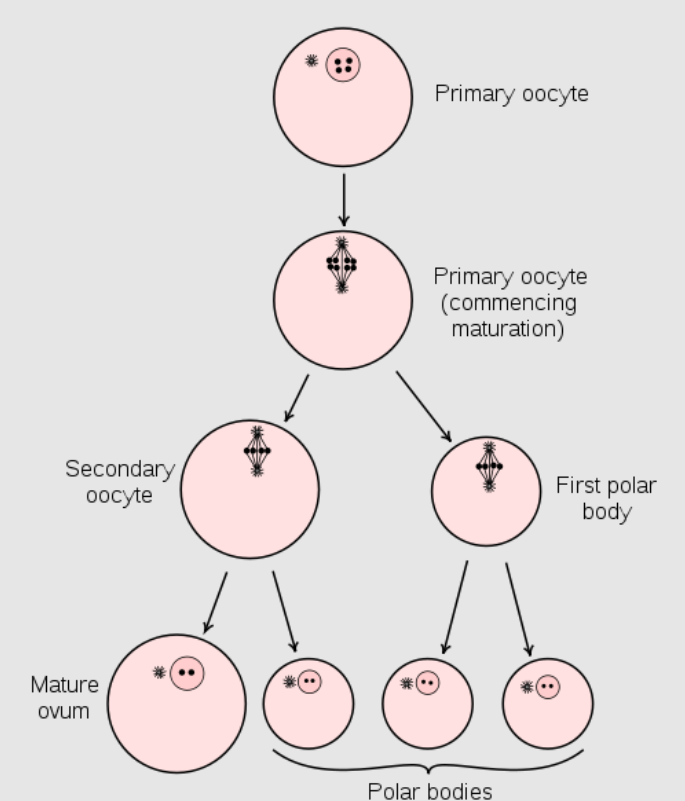
Diagram showing the reduction in number of the chromosomes in the process of maturation of the ovum. (In mammals, the 1st polar body normally disintegrates before dividing, so only 2 polar bodies are produced.)
Image: “Maturation of the ovum” by Henry Vandyke Carter et al. License: Public Domain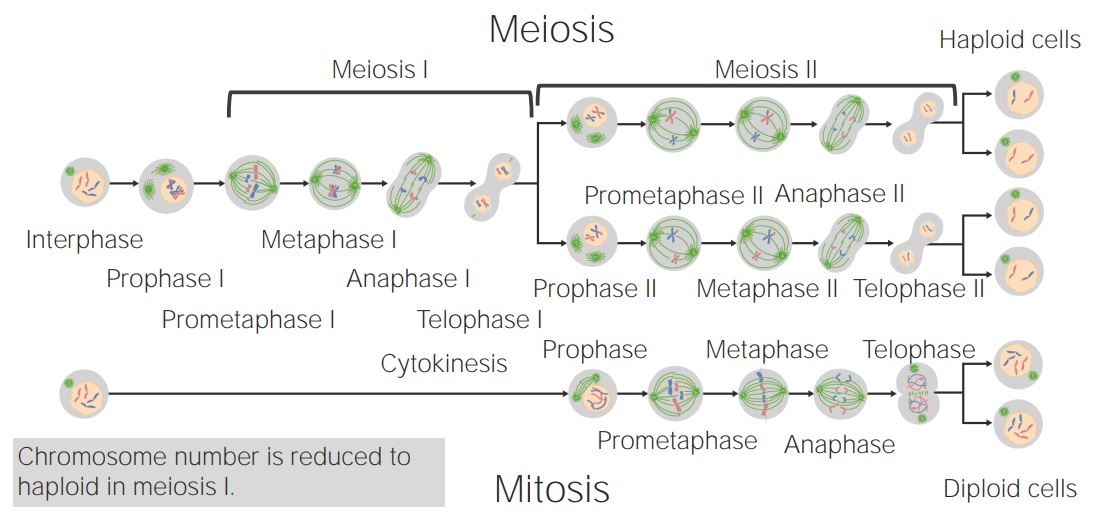
Comparing mitosis and meiosis
Image by Lecturio.