Measles (also known as rubeola) is caused by a single-stranded, linear, negative-sense RNA Negative-sense RNA RNA viruses that have their genetic material encoded in the form of single-stranded, negative-sense RNA. Unlike retroviruses they do not employ DNA intermediates in their life-cycle. Respiratory Syncytial Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology of the family Paramyxoviridae Paramyxoviridae A family of spherical viruses, of the order mononegavirales, somewhat larger than the orthomyxoviruses, and containing single-stranded RNA. Subfamilies include paramyxoviridae and pneumovirinae. Respiratory Syncytial Virus and the genus Morbillivirus. It is highly contagious and spreads only among humans by respiratory droplets Droplets Varicella-Zoster Virus/Chickenpox or direct-contact transmission from an infected person. Typically a disease of childhood, measles classically starts with cough, coryza Coryza Inflammation of the nasal mucosa, the mucous membrane lining the nasal cavities. Rhinitis, and conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis Conjunctivitis is a common inflammation of the bulbar and/or palpebral conjunctiva. It can be classified into infectious (mostly viral) and noninfectious conjunctivitis, which includes allergic causes. Patients commonly present with red eyes, increased tearing, burning, foreign body sensation, and photophobia. Conjunctivitis, followed by a maculopapular Maculopapular Dermatologic Examination rash Rash Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. Complications include diarrhea Diarrhea Diarrhea is defined as ≥ 3 watery or loose stools in a 24-hour period. There are a multitude of etiologies, which can be classified based on the underlying mechanism of disease. The duration of symptoms (acute or chronic) and characteristics of the stools (e.g., watery, bloody, steatorrheic, mucoid) can help guide further diagnostic evaluation. Diarrhea, pneumonia Pneumonia Pneumonia or pulmonary inflammation is an acute or chronic inflammation of lung tissue. Causes include infection with bacteria, viruses, or fungi. In more rare cases, pneumonia can also be caused through toxic triggers through inhalation of toxic substances, immunological processes, or in the course of radiotherapy. Pneumonia, and encephalitis Encephalitis Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain parenchyma caused by an infection, usually viral. Encephalitis may present with mild symptoms such as headache, fever, fatigue, and muscle and joint pain or with severe symptoms such as seizures, altered consciousness, and paralysis. Encephalitis. Measles can be prevented through vaccination Vaccination Vaccination is the administration of a substance to induce the immune system to develop protection against a disease. Unlike passive immunization, which involves the administration of pre-performed antibodies, active immunization constitutes the administration of a vaccine to stimulate the body to produce its own antibodies. Vaccination, and thanks to this, had largely been eradicated until recent years. Most cases are managed with supportive care, although in select patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship, antivirals can be indicated.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

RNA virus identification:
Viruses can be classified in many ways. Most viruses, however, will have a genome formed by either DNA or RNA. RNA genome viruses can be further characterized by either a single- or double-stranded RNA. “Enveloped” viruses are covered by a thin coat of cell membrane (usually taken from the host cell). If the coat is absent, the viruses are called “naked” viruses. Viruses with single-stranded genomes are “positive-sense” viruses if the genome is directly employed as messenger RNA (mRNA), which is translated into proteins. “Negative-sense,” single-stranded viruses employ RNA dependent RNA polymerase, a viral enzyme, to transcribe their genome into messenger RNA.
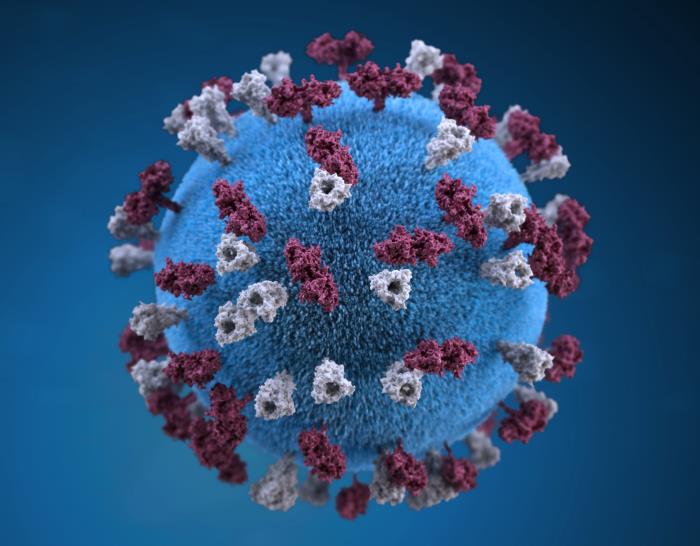
Three-dimensional graphic representation of a spherical-shaped measles virus particle
Image: “21074” by Allison M. Maiuri. License: Public Domain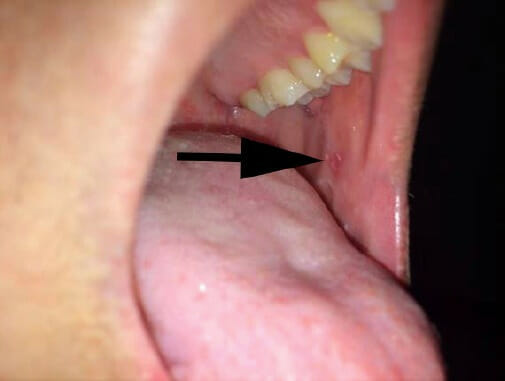
An individual with measles showing Koplik spots
Image: “Koplik spots” by Michael J Burns. License: CC BY 4.0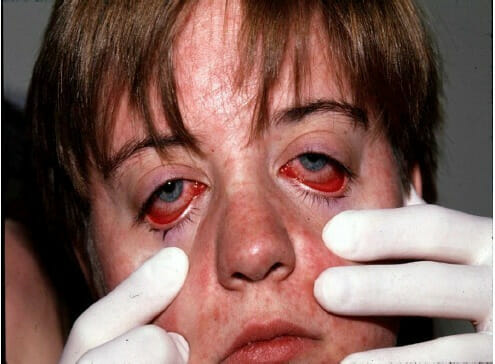
A child with nonpurulent conjunctivitis and facial rash due to measles
Image: “ Nonpurulent conjunctivitis and facial rash of measles one day after rash began” by Michael J Burns. License: CC BY 4.0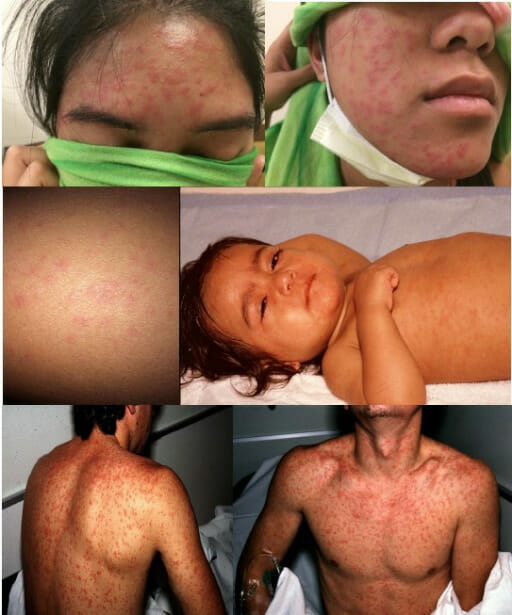
Rash from measles
Image: “Measles rash” by Michael J Burns. License: CC BY 4.0At least 1 complication occurs in 30% of cases:
The disease is diagnosed on clinical suspicion followed by confirmatory laboratory testing. Suspected cases should be isolated until confirmed.
| Number | Other names for the disease | Etiology | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st disease |
|
Measles morbillivirus |
|
| 2nd disease |
|
Streptococcus Streptococcus Streptococcus is one of the two medically important genera of gram-positive cocci, the other being Staphylococcus. Streptococci are identified as different species on blood agar on the basis of their hemolytic pattern and sensitivity to optochin and bacitracin. There are many pathogenic species of streptococci, including S. pyogenes, S. agalactiae, S. pneumoniae, and the viridans streptococci. Streptococcus pyogenes |
|
| 3rd disease 3rd disease An acute infectious disease caused by the rubella virus. The virus enters the respiratory tract via airborne droplet and spreads to the lymphatic system. Rubella Virus |
|
Rubella Rubella An acute infectious disease caused by the rubella virus. The virus enters the respiratory tract via airborne droplet and spreads to the lymphatic system. Rubella Virus virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology |
|
| 4th disease |
|
Due to Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess strains that make epidermolytic (exfoliative) toxin |
|
| 5th disease | Erythema Erythema Redness of the skin produced by congestion of the capillaries. This condition may result from a variety of disease processes. Chalazion infectiosum | Erythrovirus or parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or “slapped cheek syndrome.” Parvovirus B19 (Primate erythroparvovirus Erythroparvovirus Parvovirus B19 1) |
|
| 6th disease |
|
Human herpesvirus 6B or 7 |
|