Extranodal marginal zone lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum (EMZL) of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy (also called MALToma, MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum, and pseudolymphoma) is a group of non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas that have historically been grouped together because they appear to arise from postgerminal center marginal zone B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions and share a similar immunophenotype. MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum is thought to arise in the setting of chronic immune stimulation, which is usually due to bacterial, viral, or autoimmune stimuli. MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphomas present with symptoms due to localized involvement of glandular epithelial tissues in the specific site where they develop. Diagnosis of MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum is made by morphologic, immunophenotypic, and genetic analysis of biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma samples. Helicobacter pylori Helicobacter pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter–positive gastric MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum is treated with H. pylori H. pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter eradication therapy, and H. pylori H. pylori A spiral bacterium active as a human gastric pathogen. It is a gram-negative, urease-positive, curved or slightly spiral organism initially isolated in 1982 from patients with lesions of gastritis or peptic ulcers in Western Australia. Helicobacter pylori was originally classified in the genus campylobacter, but RNA sequencing, cellular fatty acid profiles, growth patterns, and other taxonomic characteristics indicate that the micro-organism should be included in the genus Helicobacter. It has been officially transferred to Helicobacter gen. Helicobacter–negative gastric MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum is treated with radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma therapy. Nongastric MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum is treated based on the involved area and extent of disease. MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship have a good prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas, with a median survival of > 10 years.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum is a clinically indolent non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum postulated to arise from postgerminal center memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions with the capacity to differentiate into marginal zone cells and plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products cells.
Clinical presentation varies depending on the location where the MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy lymphoma Lymphoma A general term for various neoplastic diseases of the lymphoid tissue. Imaging of the Mediastinum develops.
Dissemination to other sites of MALT MALT Colon, Cecum, and Appendix: Anatomy tissue:
Peripheral blood is usually not involved.
Systemic B symptoms are uncommon:
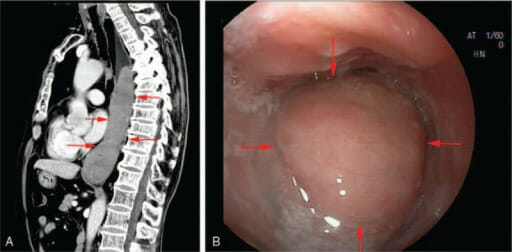
Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma of the esophagus:
Computed tomography (image A) and endoscopy (image B) show a neoplasm of the middle and lower esophagus.
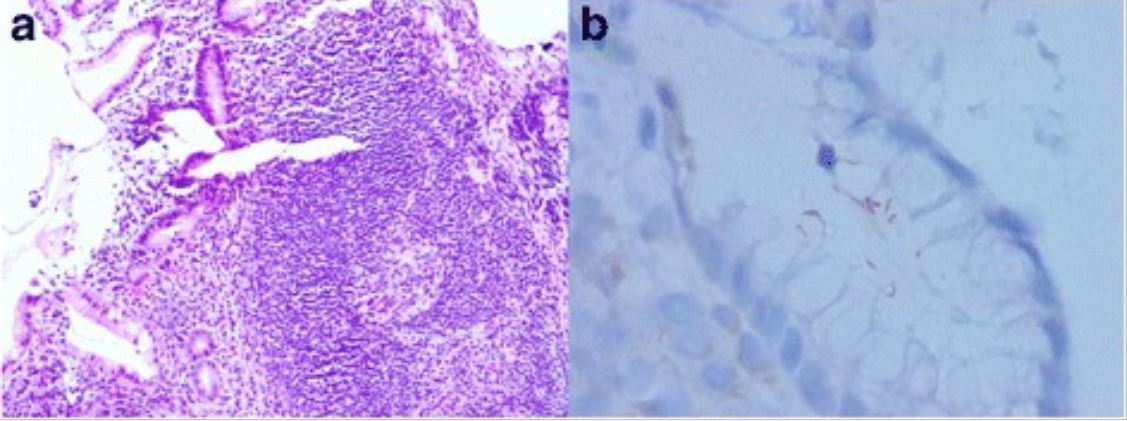
Gastric MALT lymphoma associated with H. pylori:
a: Lymphoid follicle with a reactive germinal center and a slightly expanded marginal zone (H&E, original magnification, 100X)
b: Immunostaining of H. pylori shows intra-foveolar bacteria with curving configuration, characteristic of H. pylori.
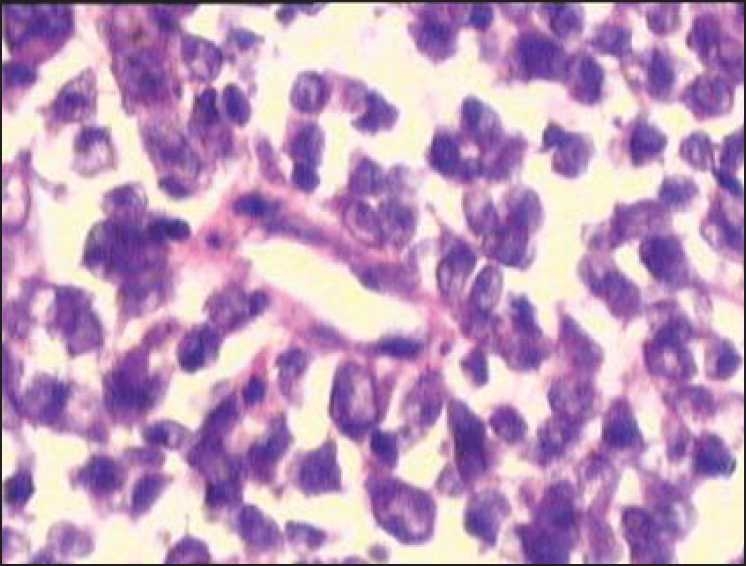
MALT lymphoma of the colon:
Infiltration of malignant-looking lymphoid cells in the lamina propria suggestive of malt lymphoma