Malnutrition is a clinical state caused by an imbalance or deficiency of calories and/or micronutrients and macronutrients. The 2 main manifestations of acute severe malnutrition are marasmus (total caloric insufficiency) and kwashiorkor (protein malnutrition with characteristic edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema). Malnutrition is almost always associated with an underlying disease process, which can be classified into 4 categories: decreased nutrient intake, decreased absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption of micronutrients and macronutrients, increased nutrient loss, and increased energy expenditure Energy expenditure Energy expenditure is the sum of internal heat produced and external work. Energy Homeostasis. The clinical presentation of marasmus varies based on severity, duration of caloric restriction, and vitamin/mineral deficiencies. The clinical presentation of kwashiorkor includes peripheral pitting edema Pitting edema Edema caused by excess fluid without excess colloid. Leaves “pits” due to fluid displacement when pressure is applied to the area Edema, muscle atrophy Atrophy Decrease in the size of a cell, tissue, organ, or multiple organs, associated with a variety of pathological conditions such as abnormal cellular changes, ischemia, malnutrition, or hormonal changes. Cellular Adaptation, and abdominal distention Abdominal distention Megacolon. Anthropometry is essential in the diagnosis of malnutrition. The 3-step approach to treat malnutrition includes resuscitation Resuscitation The restoration to life or consciousness of one apparently dead. . Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome, rehabilitation, and relapse Relapse Relapsing Fever prevention.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Malnutrition is a clinical state with an imbalance, a deficiency, or an excess of a wide range of nutrients and energy.
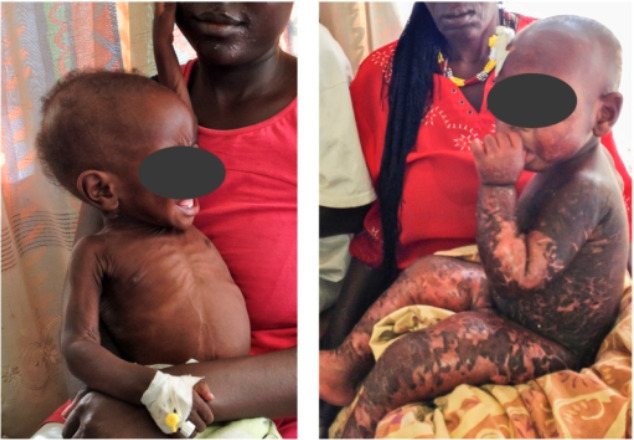
Two forms of severe acute malnutrition: nonedematous (marasmus) and edematous (kwashiorkor) malnutrition
Image: “Clinical picture” by Department of Nutrition, Exercise and Sports, Faculty of Science, University of Copenhagen, Frederiksberg, Denmark. License: CC BY 4.0Malnutrition is often associated with underlying disease and can be conceptually categorized into 4 broad etiological categories:
Clinical presentation varies based on severity, duration of caloric restriction, and presence of vitamin/mineral deficiencies.
Individuals present with:
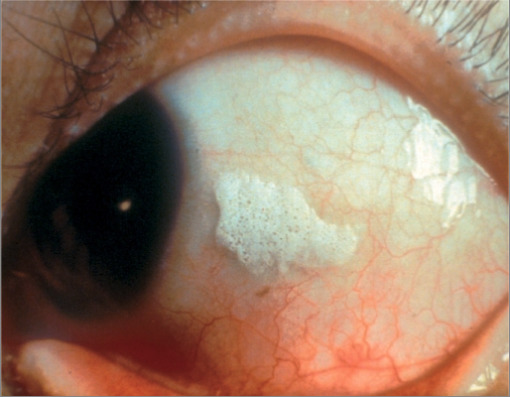
Bitot spots resulting from vitamin A deficiency
Image: “Bitot spots” by Professor of Ophthalmology, College of Medicine, University of Ibadan, Nigeria. License: CC BY 2.0Individuals present with:
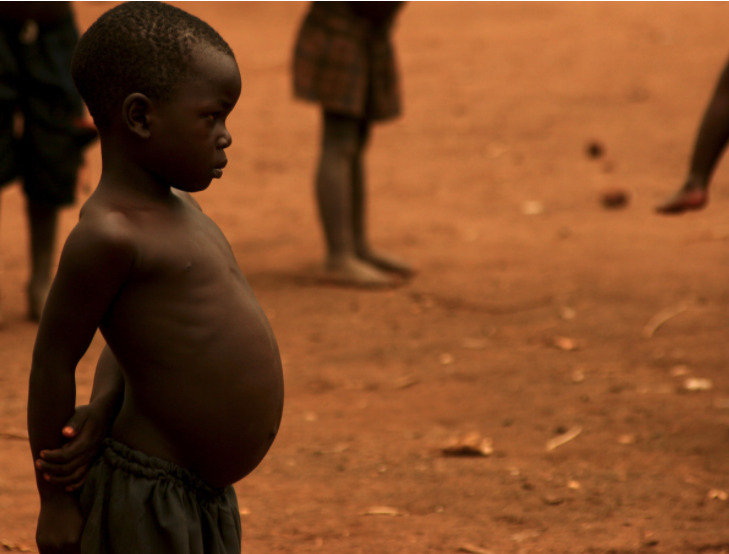

A child with kwashiorkor: Ascites lead to protruding abdomen.
Image: “Kwashiorkor” by Av TKnoxB/Flickr. License: CC BY 2.0Accurate anthropometry is essential in malnutrition diagnosis:
Laboratory tests to consider:
Diagnosis made if:
Divided into 3 main phases:
Key considerations: