Malignant mesothelioma (usually referred to as simply "mesothelioma") is the malignant growth of mesothelial cells, most commonly affecting the pleura Pleura The pleura is a serous membrane that lines the walls of the thoracic cavity and the surface of the lungs. This structure of mesodermal origin covers both lungs, the mediastinum, the thoracic surface of the diaphragm, and the inner part of the thoracic cage. The pleura is divided into a visceral pleura and parietal pleura. Pleura: Anatomy. The majority of cases are associated with occupational exposure to asbestos that occurred > 20 years before clinical onset, which includes dyspnea Dyspnea Dyspnea is the subjective sensation of breathing discomfort. Dyspnea is a normal manifestation of heavy physical or psychological exertion, but also may be caused by underlying conditions (both pulmonary and extrapulmonary). Dyspnea, chest pain Pain An unpleasant sensation induced by noxious stimuli which are detected by nerve endings of nociceptive neurons. Pain: Types and Pathways, coughing, fatigue Fatigue The state of weariness following a period of exertion, mental or physical, characterized by a decreased capacity for work and reduced efficiency to respond to stimuli. Fibromyalgia, and weight loss Weight loss Decrease in existing body weight. Bariatric Surgery. Chest computed tomography Chest Computed Tomography Hemothorax (CT) scan shows multifocal Multifocal Retinoblastoma pleural thickening and pleural effusion Pleural Effusion Pleural effusion refers to the accumulation of fluid between the layers of the parietal and visceral pleura. Common causes of this condition include infection, malignancy, autoimmune disorders, or volume overload. Clinical manifestations include chest pain, cough, and dyspnea. Pleural Effusion. Pleural biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma is required for confirmation and to rule out metastases from lung or breast cancer Breast cancer Breast cancer is a disease characterized by malignant transformation of the epithelial cells of the breast. Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer and 2nd most common cause of cancer-related death among women. Breast Cancer. Treatment is rarely effective, with an average survival time of < 1 year.
Last updated: May 17, 2024
Pleural mesothelioma
Peritoneal mesothelioma
Pericardial mesothelioma
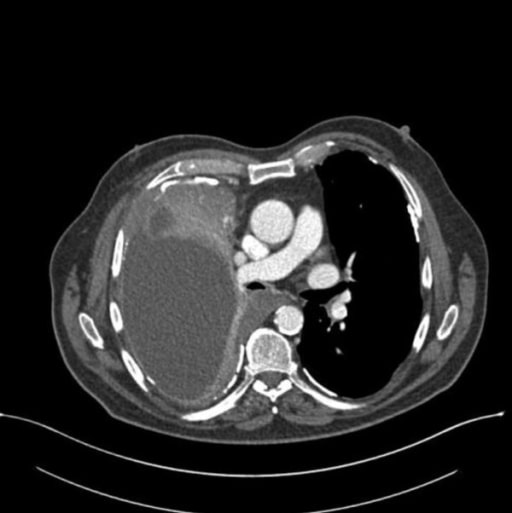
Chest CT scan showing mesothelioma
Image: “Chest CT presenting the mesothelioma” by University Hospital Zurich, Department of Craniomaxillofacial and Oral Surgery, Plattenstrasse 15, CH-8032 Zurich, Switzerland. License: CC BY 2.0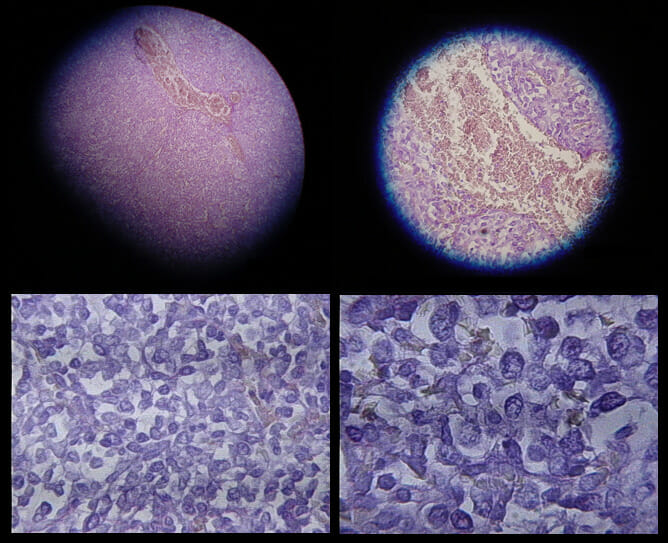
Histopathology of mesothelioma, which is caused due to exposure to asbestos: Mesothelioma cells and psammoma bodies can be seen.
Image: “Mesothelioma” by Robertolyra. License: Public DomainPrognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual’s condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas: Median survival time is 8–14 months.
The following conditions are differential diagnoses for mesothelioma.