Magnetic resonance imaging is a technique that utilizes magnetic fields and radiofrequency pulses to produce highly detailed images of the human anatomy. Magnetic resonance imaging can detect minute changes, reliably delineate lesions, and characterize vascular malformations. Soft tissues, such as abnormalities affecting non-bony structures, can be evaluated using MRI. Images can be obtained in most planes (commonly used are sagittal Sagittal Computed Tomography (CT), coronal Coronal Computed Tomography (CT), and axial Axial Computed Tomography (CT)). Contrary to CT, MRI does not expose patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship to ionizing radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma. There are some limitations Limitations Conflict of Interest of this imaging modality: MRI is expensive, time consuming, and not readily available in some centers. Additionally, patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with ferromagnetic implants or devices cannot be exposed to the MRI equipment, which has magnets. Contrast studies may result in renal complications; thus, the determination of renal function is necessary before using certain contrast agents Contrast agents Substances used to allow enhanced visualization of tissues. Computed Tomography (CT).
Last updated: Mar 29, 2023
MRI
Image: “MRI-Philips” by Jan Ainali. License: CC BY 3.0| Tissue | T1-weighted images T1-Weighted Images Imaging of the Head and Brain | T2-weighted images T2-Weighted Images Imaging of the Head and Brain |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid (e.g., CSF) | Dark | Bright |
| White matter White Matter The region of central nervous system that appears lighter in color than the other type, gray matter. It mainly consists of myelinated nerve fibers and contains few neuronal cell bodies or dendrites. Brown-Séquard Syndrome | Light gray | Dark gray |
| Gray matter Gray matter Region of central nervous system that appears darker in color than the other type, white matter. It is composed of neuronal cell bodies; neuropil; glial cells and capillaries but few myelinated nerve fibers. Cerebral Cortex: Anatomy | Gray | Light gray |
| Fat | Bright | Bright |
| Inflammation Inflammation Inflammation is a complex set of responses to infection and injury involving leukocytes as the principal cellular mediators in the body’s defense against pathogenic organisms. Inflammation is also seen as a response to tissue injury in the process of wound healing. The 5 cardinal signs of inflammation are pain, heat, redness, swelling, and loss of function. Inflammation | Dark | Bright |
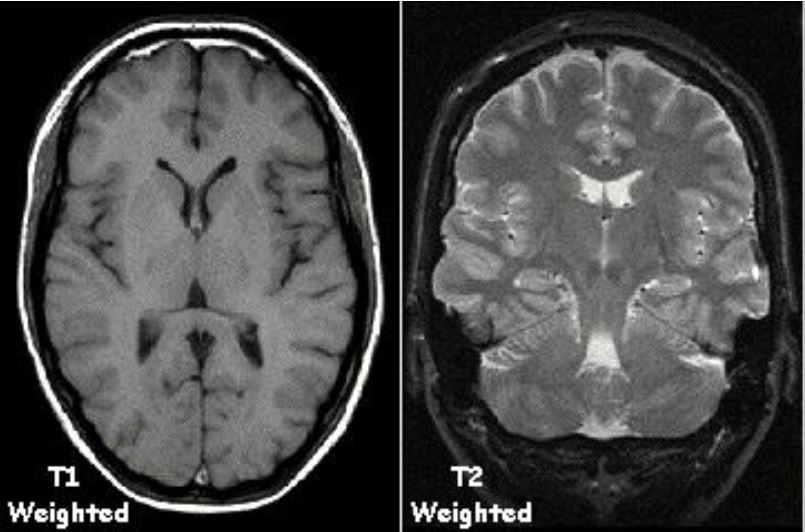
Note the appearance of white matter, gray matter, CSF, and fat (within the subcutaneous tissue) in T1 sequence and T2 sequence.
Image: “T1t2PD” by Kieran Maher. License: Public Domain, edited by Lecturio.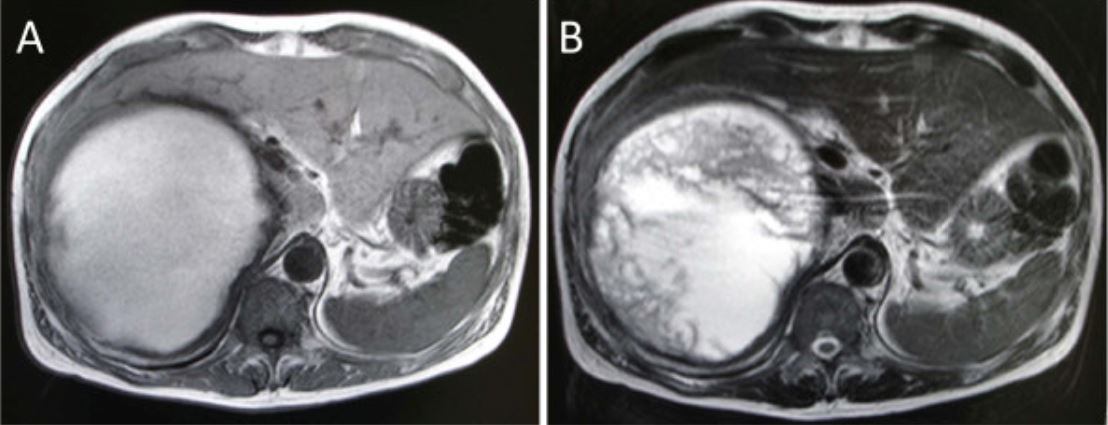
Abdominal MRI reveals a well-defined high-intensity mass that appears homogeneously intense in the T1-weighted image (A), but heterogeneously intense in the T2-weighted image (B).
Note that the liver, which is present between the abdominal wall and the mass, appears bright in T1 sequence and dark in T2 sequence.
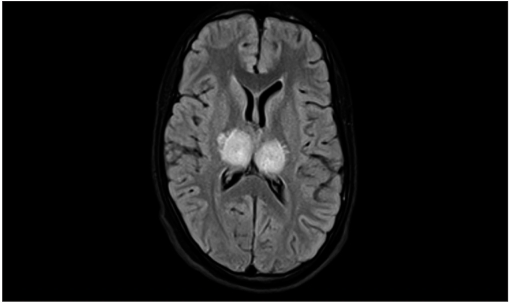
MRI T2-weighted FLAIR image showing bilateral thalamic hyperintensities in a case of viral encephalitis
Image: “Bilateral thalamic hyperintensities in a case of viral encephalitis” by Mohanasundaram K, Narayanan S, Kumarasamy S. License: CC BY 2.0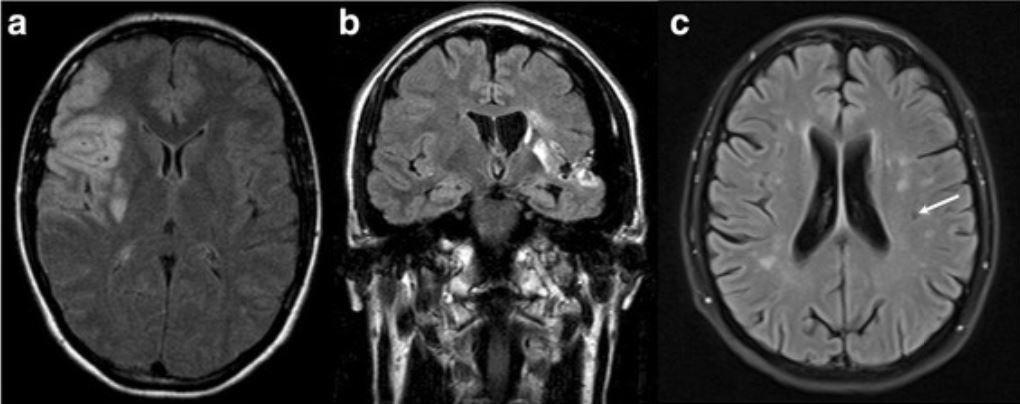
Magnetic resonance imaging scans of patients with cerebrovascular events:
a: axial MRI of the index woman (30 years of age) suffering from an embolic stroke within the vascular territory of the right middle cerebral artery
b: coronal fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR)-MRI of a male patient (38 years of age) suffering from an embolic stroke within the vascular territory of the left middle cerebral artery
c: FLAIR MRI of a female patient (46 years of age) with transient ischemic stroke and periventricular and subcortical microangiopathic and lacunar ischemic lesions (white arrow)
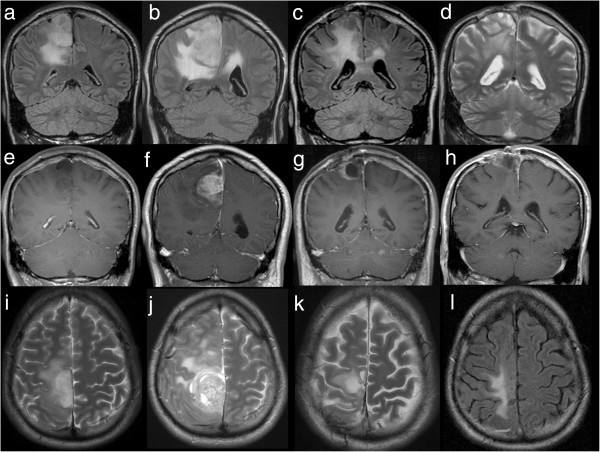
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain at 4 time points:
Each row represents an examination with coronal acquisition of FLAIR (or T2 (d)), coronal contrast-enhanced T1 and axial T2 (or FLAIR (l)).
After the 1st MRI in 2006 (a, e, i), showing a non-enhancing tumor, the patient underwent surgery, and astrocytoma WHO II° was diagnosed.
In 2008, recurrent tumor (b ,f ,j) with striking contrast enhancement (f), correlating with histologically proven malignization to glioblastoma WHO IV°, was proven using MRI. Again, tumor recurrence with rim-enhancing tumor (c, g, k), was documented in 04/2011 and surgery was performed.
In 08/2011 (d, h, l) MRI of the brain showed that the local contrast-enhancing tumor was under control and not responsible for deteriorating neurological status.
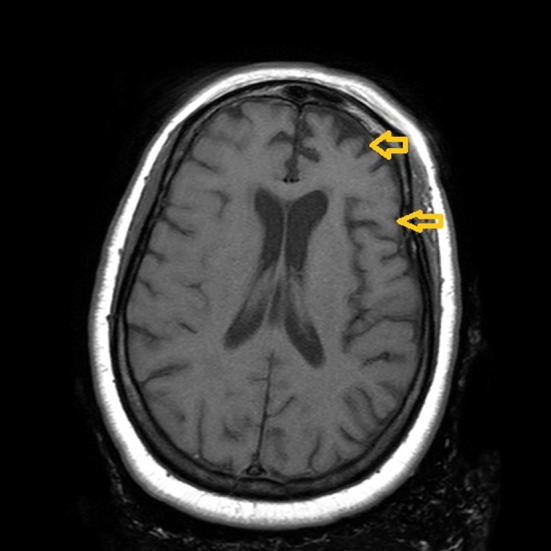
Atrophy of frontal and temporal lobes (arrows) bilaterally, left more prominent than right (frontotemporal dementia)
Image: “Paranoid personality masking an atypical case of frontotemporal dementia” by Iroka N, Jehangir W, Ii JL, Pattan V, Yousif A, Mishra AK. License: CC BY 2.0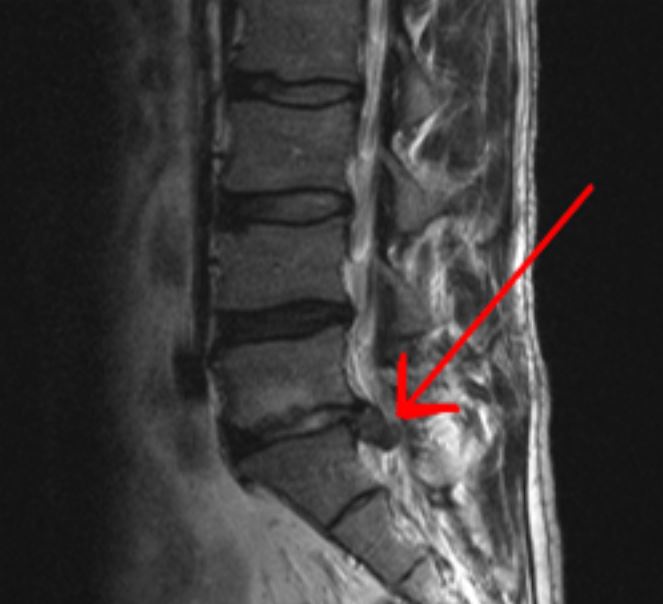
Magnetic resonance imaging scan of large extrusion (on the right) of the disk between L5 and S1 vertebrae
Image: “Lagehernia” by Mjorter. License: Public Domain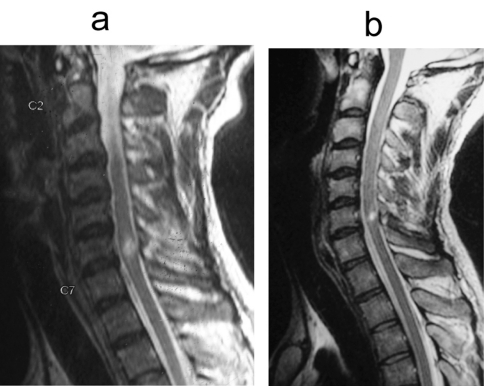
a:T2-weighted sagittal MRI image of a 29-year-old male showing cord contusion opposite C6–7 level and multiple disk bulges
b: T2-weighted sagittal MRI image of the same patient performed after a year, showing that the contusion has decreased in size
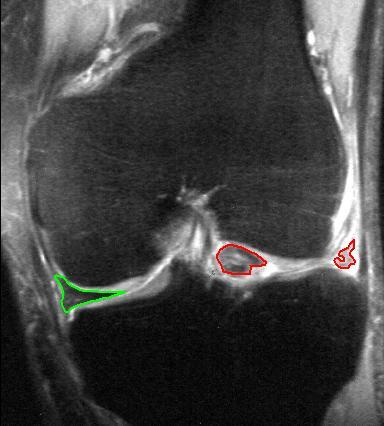
Coronal T2*-weighted gradient recalled echo sequence MRI:
Bucket-handle tear of the lateral meniscus (red)
Medial meniscus intact (green)
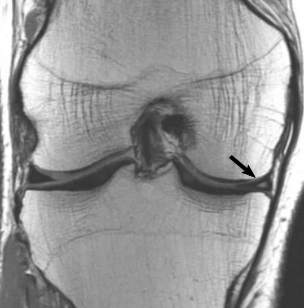
Proton density MRI in a coronal plane of the knee showing a grade 2 medial meniscal tear
Image: “Proton density MRI of a grade 2 medial meniscal tear” by Nicolas Lefevre, et al. License: CC BY 4.0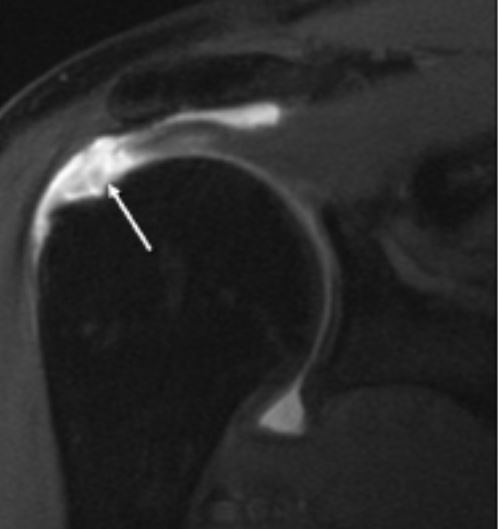
An MRI of rotator cuff full-thickness tear of the supraspinatus
Image: “Full-thickness Tear” by Medscape. License: Public Domain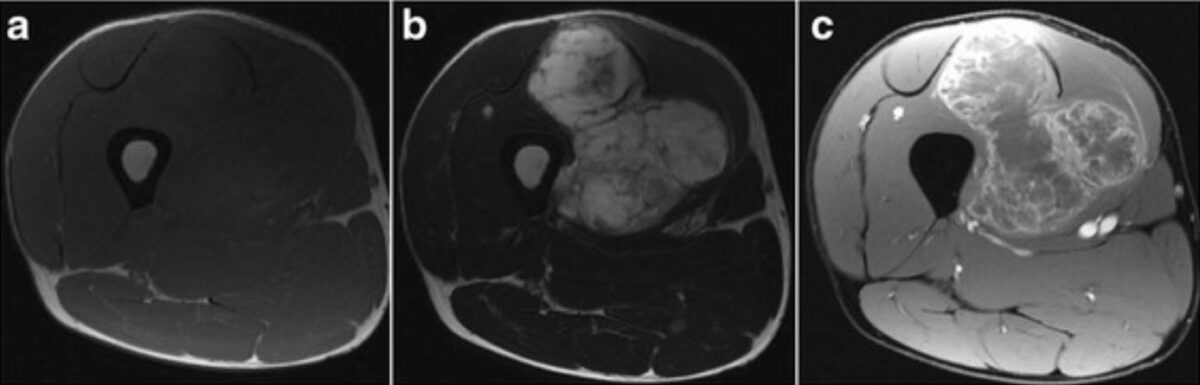
Magnetic resonance imaging findings:
a: T1-weighted axial imaging reveals a soft tissue tumor with an isointense signal.
b: T2-weighted axial imaging reveals a soft tissue tumor with a high-intensity signal.
c: axial imaging with gadolinium enhancement at the side edge of the partition structure

Sagittal view of the peritoneal reflection (red line) by rectal MRI
Image: “Is rectal MRI beneficial for determining the location of rectal cancer with respect to the peritoneal reflection?” by Jung EJ, Ryu CG, Kim G, Kim SR, Nam SE, Park HS, Kim YJ, Hwang DY. License: CC BY 3.0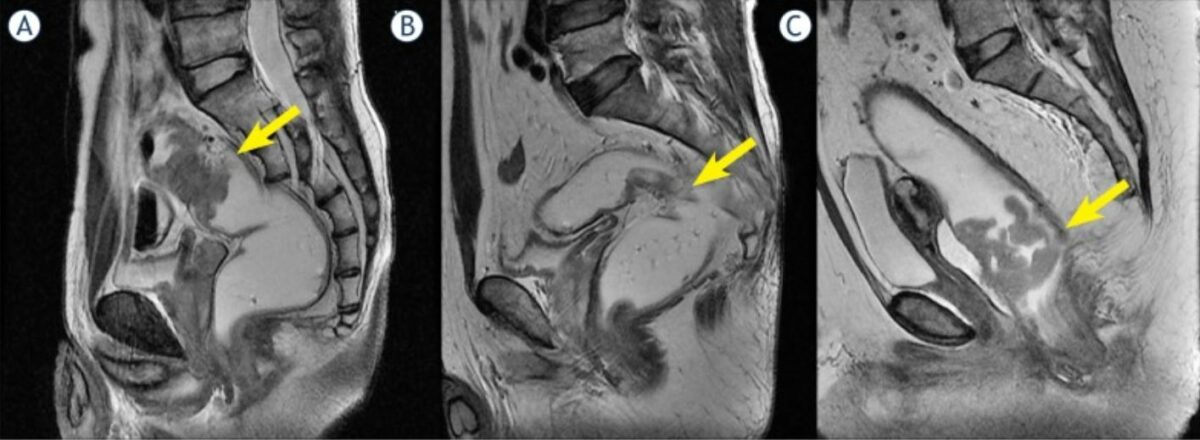
Tumor location with respect to the peritoneal reflection:
A: tumor above the peritoneal reflection
B: tumor at the peritoneal reflection
C: tumor below the peritoneal reflection
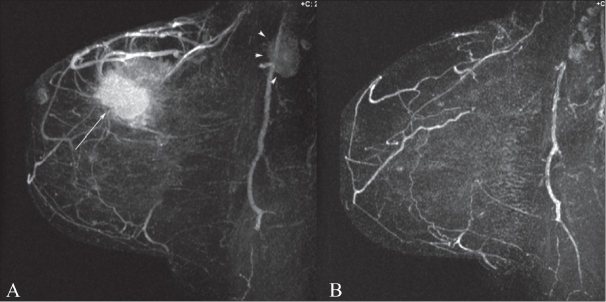
Maximum intensity projection (MIP) dynamic contrast enhanced (DCE)-MRI image before (A) and after chemotherapy (B) in a 53-year-old woman with invasive ductal carcinoma, grade 3. Note the primary tumor (arrow) as well as the axillary lymphadenopathy (arrowheads). A complete response to chemotherapy of the primary tumor as well as complete resolution of axillary lymphadenopathy is noted after chemotherapy (B).
Image: “MRI for breast cancer: Current indications” by Ojeda-Fournier H, Comstock CE. License: CC BY 2.0Contraindications Contraindications A condition or factor associated with a recipient that makes the use of a drug, procedure, or physical agent improper or inadvisable. Contraindications may be absolute (life threatening) or relative (higher risk of complications in which benefits may outweigh risks). Noninvasive Ventilation relevant in patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with:
| Radiography | CT | Ultrasound | MRI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanism of acquisition | Ionizing radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma | Ionizing radiation Radiation Emission or propagation of acoustic waves (sound), electromagnetic energy waves (such as light; radio waves; gamma rays; or x-rays), or a stream of subatomic particles (such as electrons; neutrons; protons; or alpha particles). Osteosarcoma | Acoustic energy | Ferromagnetic pulses |
| Relative cost | Inexpensive | Expensive | Very inexpensive | Very expensive |
| Portable | Yes | No | Yes | No |
| Length of exam | Seconds | < 1 minute | Seconds | Many minutes up to about 1 hour |
| Contrast | No | May be needed | May be needed | May be needed |