Lynch syndrome, also called hereditary non-polyposis colorectal cancer (HNPCC), is the most common inherited colon cancer syndrome, and carries a significantly increased risk for endometrial cancer and other malignancies. Lynch syndrome has an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern involving pathogenic variants in one of the mismatch repair (MMR) genes or epithelial cell adhesion molecule (EpCAM). Diagnosis is made by genetic testing of the index patient and their family members. Management consists of an earlier screening of individuals with defective MMR genes, as well as total colectomy if colorectal neoplasia is discovered. Prophylactic hysterectomy plus salpingo-oophorectomy are recommended for women beyond reproductive age.
Last updated: Jan 18, 2024
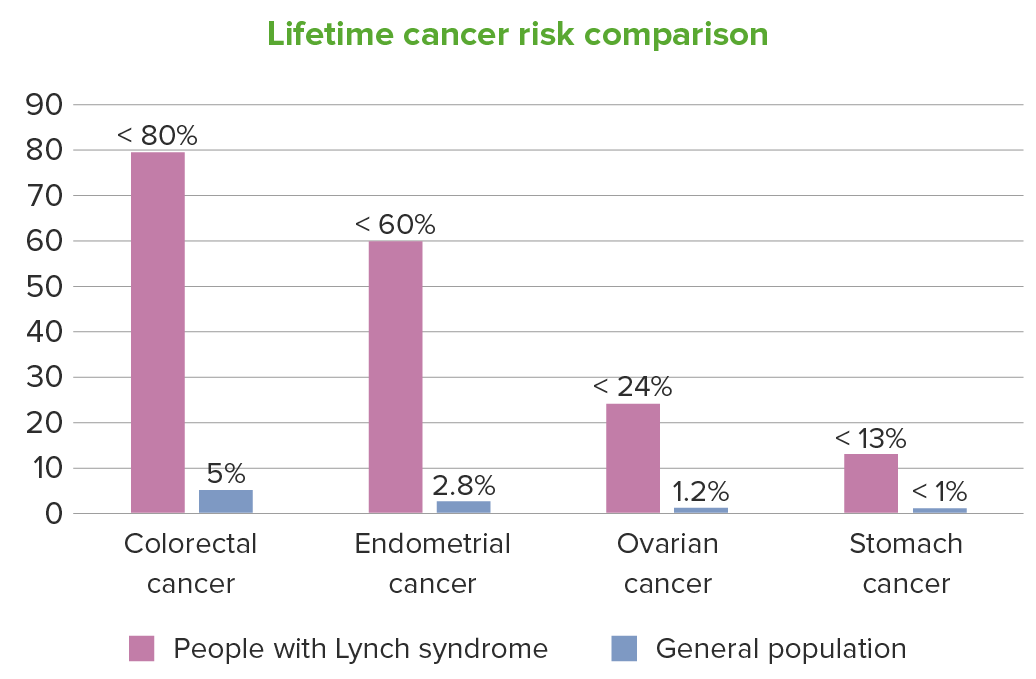
For people with Lynch syndrome, the lifetime cancer risk is also increased to a lesser extent for other cancers, including: renal pelvis, ureters, bladder, brain, small bowel, hepatobiliary tract, pancreas, prostate, and skin. In the figure, the upper ranges of the individual risks are given.
Image by Lecturio.Lynch syndrome patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship inherit one or more mutant MMR genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure and the respective normal allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics/alleles; the 2nd allele Allele Variant forms of the same gene, occupying the same locus on homologous chromosomes, and governing the variants in production of the same gene product. Basic Terms of Genetics then becomes mutated or loses function by epigenetic silencing so often that the inheritance pattern is effectively autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance.
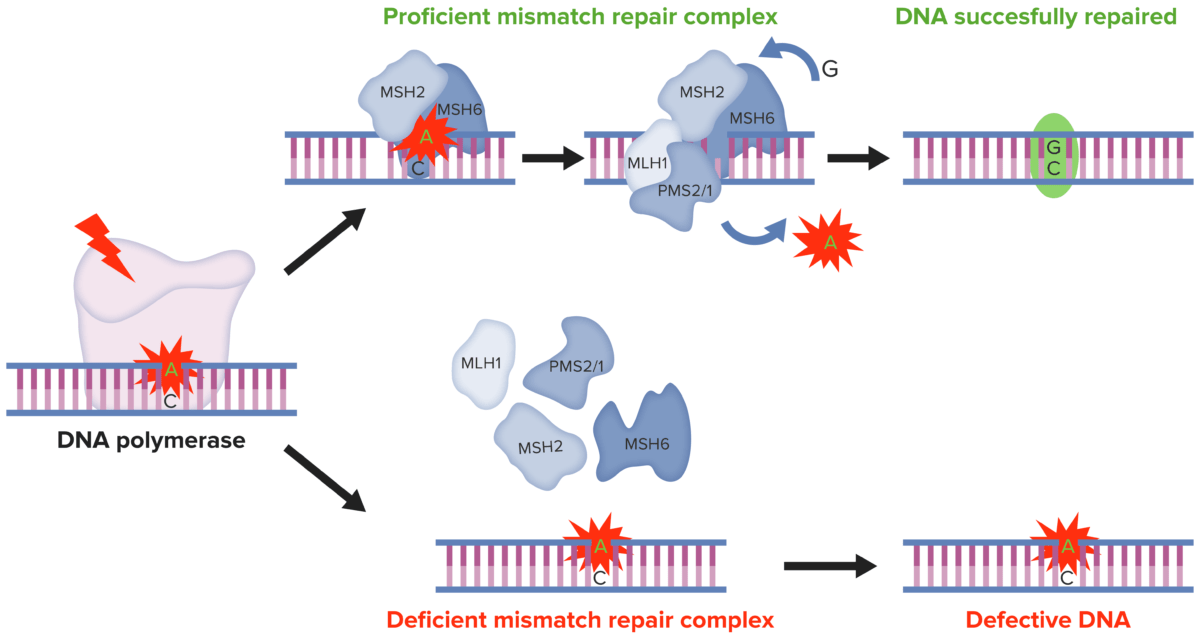
DNA MMR:
In normal cells, DNA MMR recognizes and repairs genetic mismatches generated during DNA replication. Conversely, in MSI tumor cells the presence of a deficient MMR system results in faulty DNA MMR in microsatellites, determining the accumulation of mutations in different genomic codons.
MMR: mismatch repair
MSI: microsatellite instability
For CRC:
For endometrial cancer Endometrial Cancer Endometrial carcinoma (EC) is the most common gynecologic malignancy in the developed world, and it has several histologic types. Endometrioid carcinoma (known as type 1 EC) typically develops from atypical endometrial hyperplasia, is hormonally responsive, and carries a favorable prognosis. Endometrial Hyperplasia and Endometrial Cancer:
Chemoprevention:
Immunotherapy: