Lymphocytes are heterogeneous WBCs involved in immune response. Lymphocytes develop from the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis, starting from hematopoietic stem cells Hematopoietic stem cells Progenitor cells from which all blood cells derived. They are found primarily in the bone marrow and also in small numbers in the peripheral blood. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis (HSCs) and progressing to common lymphoid progenitors Common lymphoid progenitors Stem cells from which B-lymphocytes; T-lymphocytes; natural killer cells; and some dendritic cells derive. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis ( CLPs CLPs Stem cells from which B-lymphocytes; T-lymphocytes; natural killer cells; and some dendritic cells derive. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis). B and T lymphocytes T lymphocytes Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions and natural killer (NK) cells arise from the lineage. B and T lymphocytes T lymphocytes Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions play a role in adaptive immunity, and NK cells provide host defense against atypical proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis such as tumor Tumor Inflammation cells. While all developmental stages begin in bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis, lymphocyte maturation differs. B lymphocytes B lymphocytes Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions and NK cells differentiate in bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis before migrating to secondary lymphoid organs Lymphoid organs A system of organs and tissues that process and transport immune cells and lymph. Primary Lymphatic Organs (such as lymph nodes Lymph Nodes They are oval or bean shaped bodies (1 - 30 mm in diameter) located along the lymphatic system. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy). T lymphocytes T lymphocytes Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified - cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions, however, proceed to the thymus Thymus A single, unpaired primary lymphoid organ situated in the mediastinum, extending superiorly into the neck to the lower edge of the thyroid gland and inferiorly to the fourth costal cartilage. It is necessary for normal development of immunologic function early in life. By puberty, it begins to involute and much of the tissue is replaced by fat. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy for further maturation.
Last updated: Dec 18, 2025
Lymphocytes are blood cells involved in immune response, which arise from the common lymphoid progenitor (CLP).
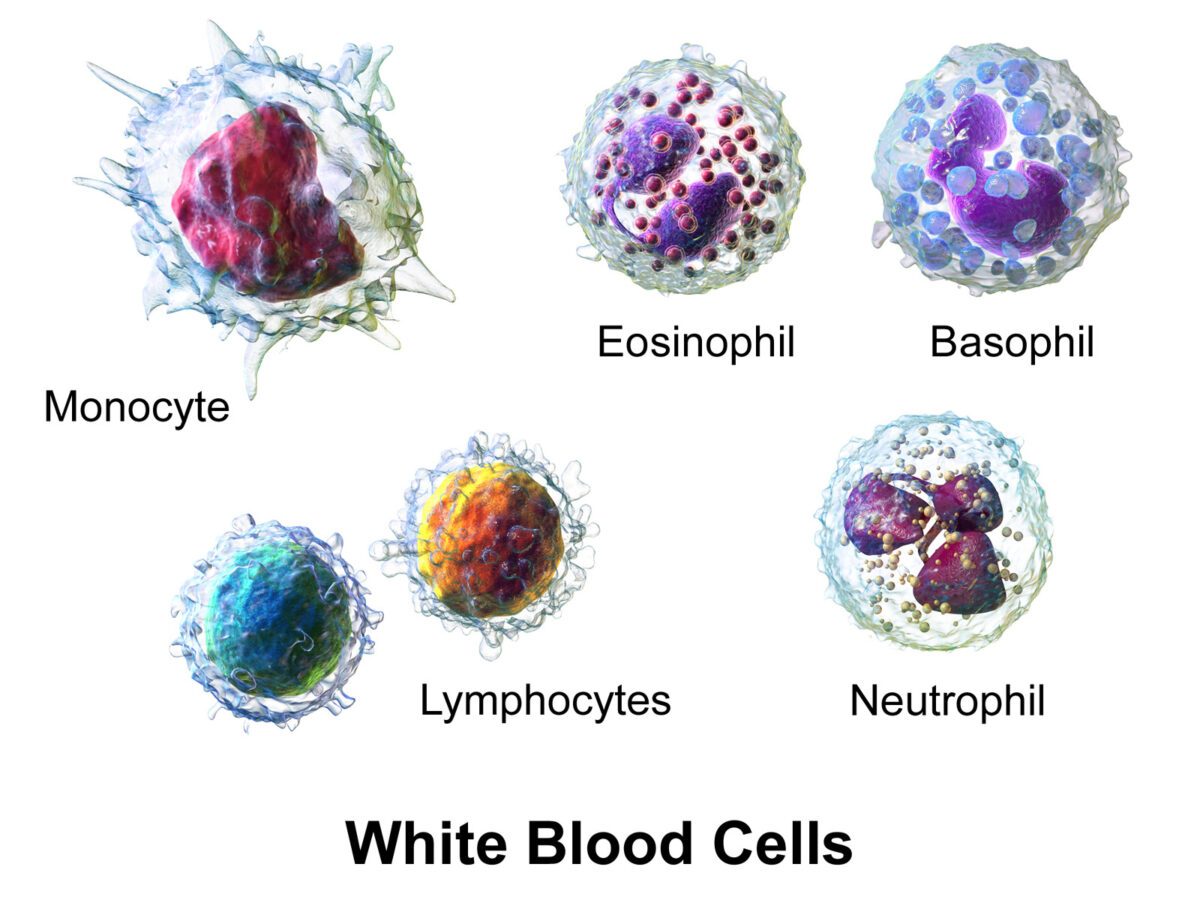
White blood cells (WBCs), or leukocytes, in the blood:
Granulocytes include basophil, eosinophil, and neutrophil; agranulocytes include lymphocytes and monocytes.
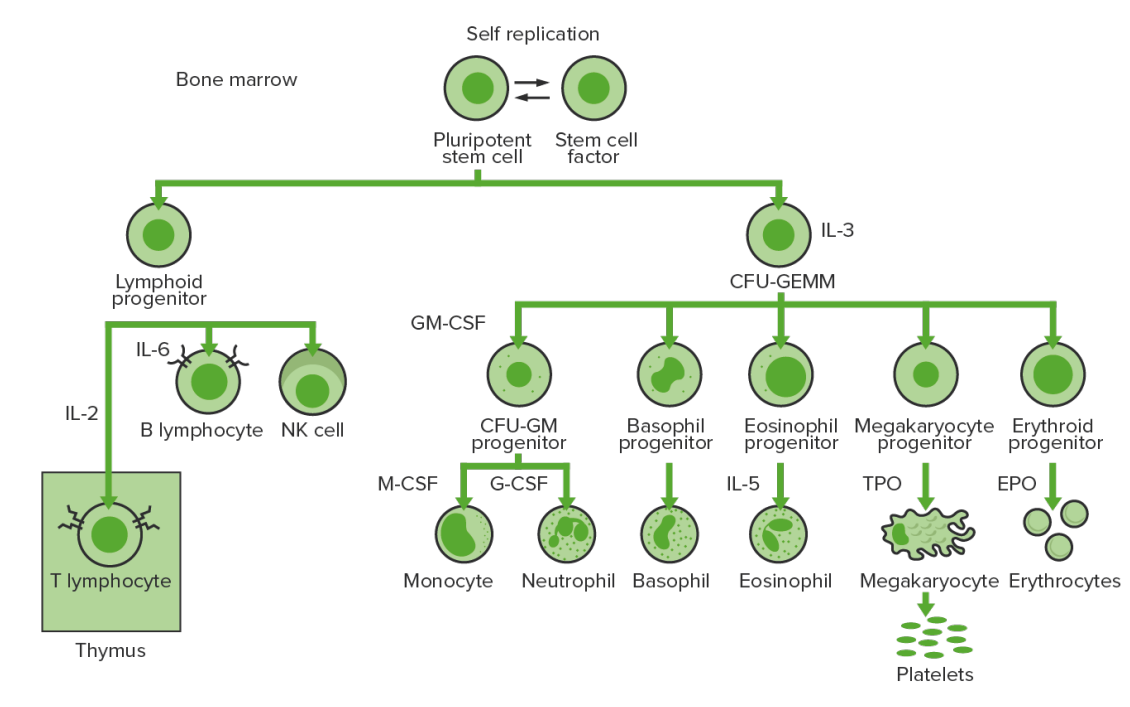
Bone-marrow hematopoiesis: proliferation and differentiation of the formed elements of blood.
IL-3: interleukin-3
CFU-GEMM: colony-forming unit–granulocyte, erythrocyte, monocyte, megakaryocyte
IL-2: interleukin-2
IL-6: interleukin-6
CFU-GM: colony-forming unit–granulocyte-macrophage
GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor
M-CSF: macrophage colony-stimulating factor
G-CSF: granulocyte colony-stimulating factor
IL-5: interleukin-5
NK: natural killer
TPO: thrombopoietin
EPO: erythropoietin
| Cytokines Cytokines Non-antibody proteins secreted by inflammatory leukocytes and some non-leukocytic cells, that act as intercellular mediators. They differ from classical hormones in that they are produced by a number of tissue or cell types rather than by specialized glands. They generally act locally in a paracrine or autocrine rather than endocrine manner. Adaptive Immune Response | Activities | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Stem cell factor Stem cell factor A hematopoietic growth factor and the ligand of the cell surface c-kit protein (proto-oncogene proteins c-kit). It is expressed during embryogenesis and is a growth factor for a number of cell types including the mast cells and the melanocytes in addition to the hematopoietic stem cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis (SCF) | Stimulates all hematopoietic progenitor cells | Bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis stromal cells |
| Interleukin-2 Interleukin-2 A soluble substance elaborated by antigen- or mitogen-stimulated T-lymphocytes which induces DNA synthesis in naive lymphocytes. Interleukins (IL-2) |
|
T helper cells |
| Interleukin-4 Interleukin-4 A soluble factor produced by activated T-lymphocytes that induces the expression of mhc class II genes and fc receptors on B-lymphocytes and causes their proliferation and differentiation. It also acts on T-lymphocytes, mast cells, and several other hematopoietic lineage cells. Interleukins (IL-4) |
|
T helper cells |
| Interleukin-6 Interleukin-6 A cytokine that stimulates the growth and differentiation of B-lymphocytes and is also a growth factor for hybridomas and plasmacytomas. It is produced by many different cells including T-lymphocytes; monocytes; and fibroblasts. Interleukins (IL-6) |
|
|
| Interleukin-7 ( IL-7 IL-7 A proinflammatory cytokine produced primarily by T-lymphocytes or their precursors. Several subtypes of interleukin-17 have been identified, each of which is a product of a unique gene. Severe Combined Immunodeficiency (SCID)) | Stimulation of all lymphoid stem cells | Bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis stromal cells |
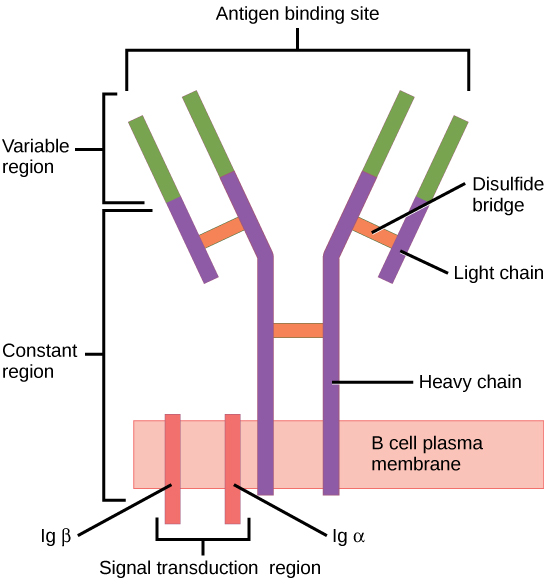
The B cell receptor (BCR) consists of the immunoglobulin (Ig) molecule and the signaling molecule. Immunoglobin contains 2 identical heavy chains and 2 identical light chains linked by a disulfide bridge; the membrane-bound Ig is anchored to the cell surface.
Image: “Figure 42 02 06” by OpenStax. License: CC BY 4.0To reach functionality, the B cell goes through stages in the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis and the secondary lymphoid organs Lymphoid organs A system of organs and tissues that process and transport immune cells and lymph. Primary Lymphatic Organs.
| Maturation stage | Ig Ig X-linked Agammaglobulinemia genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure | BCR | Associated events |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-pro-B cell | Germline DNA DNA A deoxyribonucleotide polymer that is the primary genetic material of all cells. Eukaryotic and prokaryotic organisms normally contain DNA in a double-stranded state, yet several important biological processes transiently involve single-stranded regions. DNA, which consists of a polysugar-phosphate backbone possessing projections of purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (thymine and cytosine), forms a double helix that is held together by hydrogen bonds between these purines and pyrimidines (adenine to thymine and guanine to cytosine). DNA Types and Structure | None | No heavy or light chain expression |
| Pro-B cell | IGH D-J rearranged | None | Starts to express CD19, CD34, and HLA-DR (class II histocompatibility antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination) |
| Pre-B cell | IGH V-D-J rearranged | Pre-BCR is formed:
|
Other markers appear (e.g., CD79, CD10, CD20, CD40 CD40 Members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily with specificity for CD40 ligand. They are found on mature B-lymphocytes, some epithelial cells; and lymphoid dendritic cells. Evidence suggests that CD40-dependent activation of B-cells is important for generation of memory B-cells within the germinal centers. Mutations in the CD40 antigen gene result in hyper-igm immunodeficiency syndrome, type 3. Signaling of the receptor occurs through its association with tnf receptor-associated factors. Hyper-IgM Syndrome, TdT TdT Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia) |
| Immature B cell |
|
Mature BCR ( IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions molecule) | HLA-DR, CD19, CD20, and CD40 CD40 Members of the tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily with specificity for CD40 ligand. They are found on mature B-lymphocytes, some epithelial cells; and lymphoid dendritic cells. Evidence suggests that CD40-dependent activation of B-cells is important for generation of memory B-cells within the germinal centers. Mutations in the CD40 antigen gene result in hyper-igm immunodeficiency syndrome, type 3. Signaling of the receptor occurs through its association with tnf receptor-associated factors. Hyper-IgM Syndrome expression continues, but not other markers (e.g., CD10, CD34, TdT TdT Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia) |
| Mature B cell (naive) |
|
With mature BCR ( IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions) → exit bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis | Expression of CD19 and CD20 by all |
| Maturation stage | BCR | Associated events |
|---|---|---|
| Mature B cell (in secondary lymphoid tissues) | Mature (expresses IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions and IgD IgD An immunoglobulin which accounts for less than 1% of plasma immunoglobulin. It is found on the membrane of many circulating B lymphocytes. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions when in the secondary lymphoid tissues) | Cells can rest, or B cell activation B cell activation Humoral Adaptive Immunity can occur ( B cells B cells Lymphoid cells concerned with humoral immunity. They are short-lived cells resembling bursa-derived lymphocytes of birds in their production of immunoglobulin upon appropriate stimulation. B cells: Types and Functions interact with exogenous antigen Antigen Substances that are recognized by the immune system and induce an immune reaction. Vaccination and/or T helper cells). |
| Activated B cell | Class-switch | Once activated, can remain as IgM IgM A class of immunoglobulin bearing mu chains (immunoglobulin mu-chains). Igm can fix complement. The name comes from its high molecular weight and originally being called a macroglobulin. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions or switch to IgE IgE An immunoglobulin associated with mast cells. Overexpression has been associated with allergic hypersensitivity. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions, IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, or IgA IgA Represents 15-20% of the human serum immunoglobulins, mostly as the 4-chain polymer in humans or dimer in other mammals. Secretory iga is the main immunoglobulin in secretions. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions |
| Memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment B cell |
|
|
| Plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products cell |
|
|
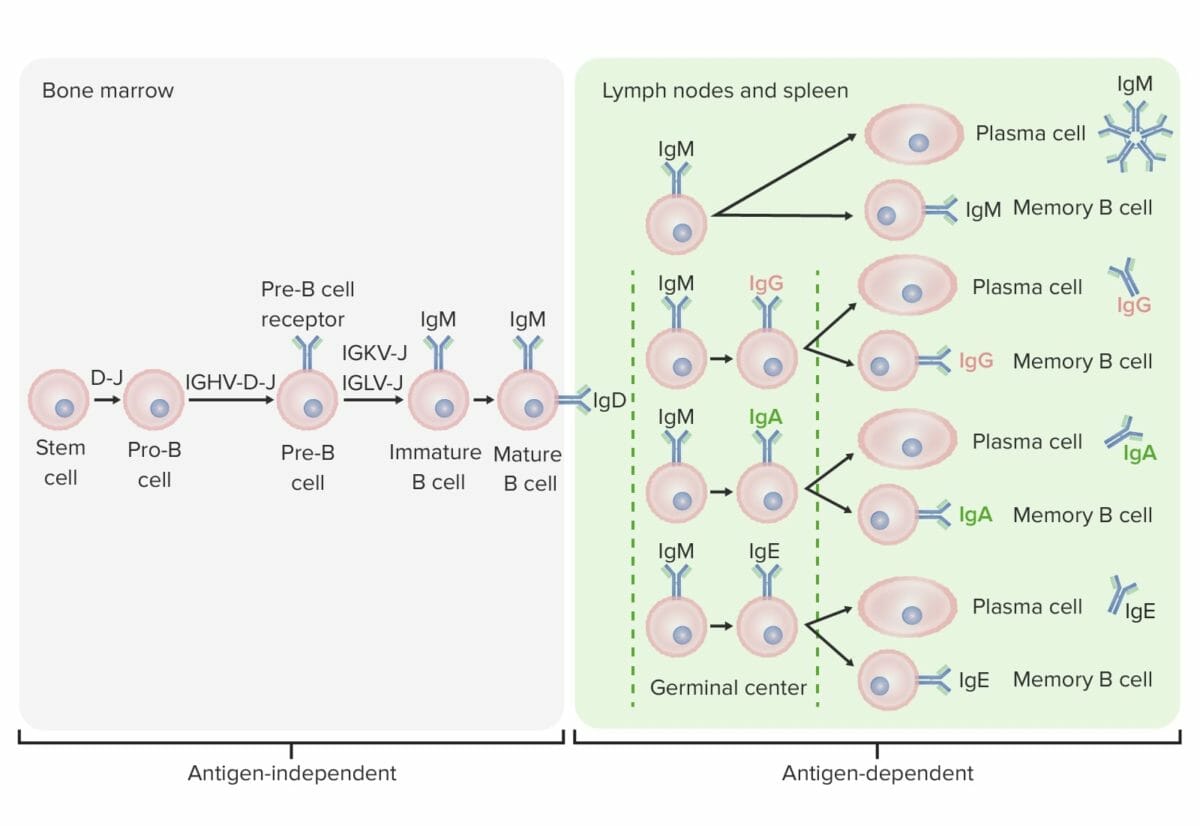
Differentiation stages of the B cell:
In antigen-independent stages, B-cell production starts with the hematopoietic stem cell (HSC), which becomes a common lymphoid progenitor (CLP) and then a pre-pro-B cell or B-progenitor cell. The next steps include gene rearrangement to assemble the Ig molecule. Ig heavy chains start with rearrangement of diversity and joining segments to form the pro-B cell. In the next step (pre-B cell), Ig heavy-chain recombination (variable, diversity, joining) is completed and the pre-B-cell receptor is formed. Light-chain (kappa (κ) or lambda (λ)) rearrangement occurs, resulting in the expression of a complete IgM-antibody molecule by an immature B cell. Formation of the mature B cell (naive) with both IgM and IgD follows.
Antigen-dependent stages take place in secondary lymphoid tissues. Once the mature B cell produce IgM and IgD, a class switch can take place to make IgE, IgG, and IgA. B cells are activated and become plasma cells or memory cells.
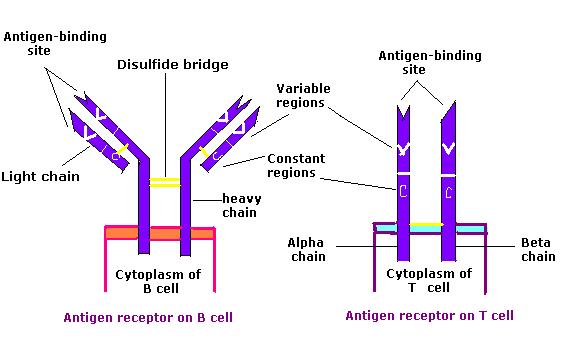
Comparison of the B cell receptor (BCR) and the T cell receptor (TCR)
Image: “Antigen receptor chem114A” by Tinastella. License: Public DomainTo reach functionality, the T cell goes through stages, released from the bone marrow Bone marrow The soft tissue filling the cavities of bones. Bone marrow exists in two types, yellow and red. Yellow marrow is found in the large cavities of large bones and consists mostly of fat cells and a few primitive blood cells. Red marrow is a hematopoietic tissue and is the site of production of erythrocytes and granular leukocytes. Bone marrow is made up of a framework of connective tissue containing branching fibers with the frame being filled with marrow cells. Bone Marrow: Composition and Hematopoiesis as progenitor cells to continue development in the thymus Thymus A single, unpaired primary lymphoid organ situated in the mediastinum, extending superiorly into the neck to the lower edge of the thyroid gland and inferiorly to the fourth costal cartilage. It is necessary for normal development of immunologic function early in life. By puberty, it begins to involute and much of the tissue is replaced by fat. Lymphatic Drainage System: Anatomy.
| Maturation stage | T cell receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors | Associated events |
|---|---|---|
| Progenitor cells | None |
|
| Double-negative cells | Rearrangement of β chain (pre-TCR) (failure to rearrange leads to apoptosis Apoptosis A regulated cell death mechanism characterized by distinctive morphologic changes in the nucleus and cytoplasm, including the endonucleolytic cleavage of genomic DNA, at regularly spaced, internucleosomal sites, I.e., DNA fragmentation. It is genetically-programmed and serves as a balance to mitosis in regulating the size of animal tissues and in mediating pathologic processes associated with tumor growth. Ischemic Cell Damage) |
|
| Double-positive cells | Rearrangement of ɑ chain → ɑ chains assemble with β chains → complete ɑ-β–TCR-CD3 complex (expressed on the surface) |
|
| Single-positive T cells T cells Lymphocytes responsible for cell-mediated immunity. Two types have been identified – cytotoxic (t-lymphocytes, cytotoxic) and helper T-lymphocytes (t-lymphocytes, helper-inducer). They are formed when lymphocytes circulate through the thymus gland and differentiate to thymocytes. When exposed to an antigen, they divide rapidly and produce large numbers of new T cells sensitized to that antigen. T cells: Types and Functions |
|
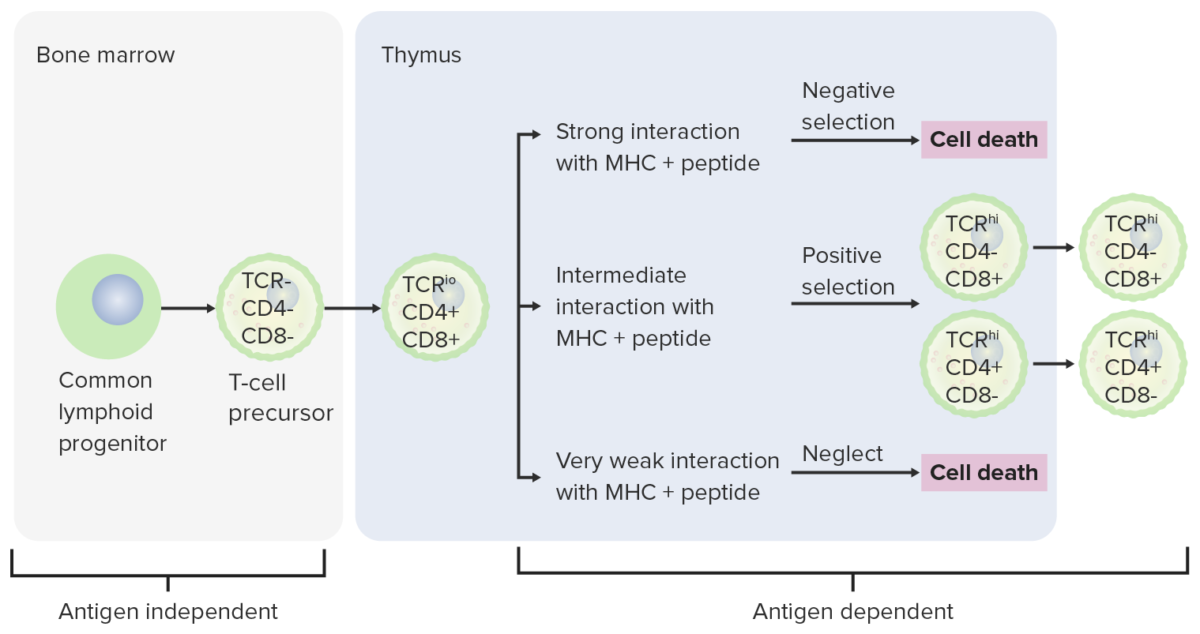
Differentiation stages of T cell:
From the bone marrow, progenitor cells go to the thymus for further maturation. The double-negative cells (no expression of CD4/CD8 or CD4-/CD8 -) have not developed the T-cell receptor (TCR). The double-negative cells undergo rearrangement of the TCR gene and become pro-T cells, then pre-T cells. Through the series, CD4 and CD8 are expressed, and the TCR becomes assembled through gene rearrangements (double-positive cells). The thymus then presents major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules to the developing T cells. Some cells undergo positive selection (intermediate interaction between MHC and TCR takes place) and produce functional cells. Some cells undergo negative selection (strong interaction between MHC and TCR), which results in cell death. The release of dysfunctional T cells, which can activate autoimmunity, is prevented. Some T cells fail to interact, leading to apoptosis. Mature T cells express either CD4 (T helper cells) or CD8 (cytotoxic T cells), not both.