Loop diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication are a group of diuretic medications primarily used to treat fluid overload in edematous conditions such as heart failure Heart Failure A heterogeneous condition in which the heart is unable to pump out sufficient blood to meet the metabolic need of the body. Heart failure can be caused by structural defects, functional abnormalities (ventricular dysfunction), or a sudden overload beyond its capacity. Chronic heart failure is more common than acute heart failure which results from sudden insult to cardiac function, such as myocardial infarction. Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Return (TAPVR) and cirrhosis Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a late stage of hepatic parenchymal necrosis and scarring (fibrosis) most commonly due to hepatitis C infection and alcoholic liver disease. Patients may present with jaundice, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cirrhosis can also cause complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, and hepatorenal syndrome. Cirrhosis. Loop diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication also treat hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension, but not as a 1st-line agent. The medication inhibits sodium reabsorption Sodium reabsorption Tubular System through the NKCC2 NKCC2 Renal Potassium Regulation cotransporter in the thick ascending limb Thick ascending limb Renal Sodium and Water Regulation of the loop of Henle Loop of Henle The U-shaped portion of the renal tubule in the kidney medulla, consisting of a descending limb and an ascending limb. It is situated between the proximal kidney tubule and the distal kidney tubule. Tubular System ( TAL TAL Renal Sodium and Water Regulation), leading to significant diuresis. Careful monitoring is important because loop diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication result in increased excretion of sodium Sodium A member of the alkali group of metals. It has the atomic symbol na, atomic number 11, and atomic weight 23. Hyponatremia, potassium Potassium An element in the alkali group of metals with an atomic symbol k, atomic number 19, and atomic weight 39. 10. It is the chief cation in the intracellular fluid of muscle and other cells. Potassium ion is a strong electrolyte that plays a significant role in the regulation of fluid volume and maintenance of the water-electrolyte balance. Hyperkalemia, chloride Chloride Inorganic compounds derived from hydrochloric acid that contain the Cl- ion. Electrolytes, calcium Calcium A basic element found in nearly all tissues. It is a member of the alkaline earth family of metals with the atomic symbol ca, atomic number 20, and atomic weight 40. Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body and combines with phosphorus to form calcium phosphate in the bones and teeth. It is essential for the normal functioning of nerves and muscles and plays a role in blood coagulation (as factor IV) and in many enzymatic processes. Electrolytes, magnesium Magnesium A metallic element that has the atomic symbol mg, atomic number 12, and atomic weight 24. 31. It is important for the activity of many enzymes, especially those involved in oxidative phosphorylation. Electrolytes, and water. In addition to electrolyte and fluid abnormalities, loop diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication can lead to nephrotoxicity Nephrotoxicity Glycopeptides and ototoxicity Ototoxicity Damage to the ear or its function secondary to exposure to toxic substances such as drugs used in chemotherapy; immunotherapy; or radiation. Glycopeptides.
Last updated: Jan 28, 2025
Loop diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication are a group of medications primarily used to treat edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema (and sometimes hypertension Hypertension Hypertension, or high blood pressure, is a common disease that manifests as elevated systemic arterial pressures. Hypertension is most often asymptomatic and is found incidentally as part of a routine physical examination or during triage for an unrelated medical encounter. Hypertension) by inhibiting sodium reabsorption Sodium reabsorption Tubular System through the NKCC2 NKCC2 Renal Potassium Regulation cotransporter (as known as the Na+-K+-Cl– cotransporter) in the thick ascending limb Thick ascending limb Renal Sodium and Water Regulation of the loop of Henle Loop of Henle The U-shaped portion of the renal tubule in the kidney medulla, consisting of a descending limb and an ascending limb. It is situated between the proximal kidney tubule and the distal kidney tubule. Tubular System ( TAL TAL Renal Sodium and Water Regulation), which lead to significant diuresis.
| Location of action | Class | Subclasses |
|---|---|---|
| Renal drugs | Drugs affecting the RAAS RAAS A blood pressure regulating system of interacting components that include renin; angiotensinogen; angiotensin converting enzyme; angiotensin i; angiotensin ii; and angiotensinase. Renin, an enzyme produced in the kidney, acts on angiotensinogen, an alpha-2 globulin produced by the liver, forming angiotensin I. Angiotensin-converting enzyme, contained in the lung, acts on angiotensin I in the plasma converting it to angiotensin II, an extremely powerful vasoconstrictor. Angiotensin II causes contraction of the arteriolar and renal vascular smooth muscle, leading to retention of salt and water in the kidney and increased arterial blood pressure. In addition, angiotensin II stimulates the release of aldosterone from the adrenal cortex, which in turn also increases salt and water retention in the kidney. Angiotensin-converting enzyme also breaks down bradykinin, a powerful vasodilator and component of the kallikrein-kinin system. Adrenal Hormones |
|
| Diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication |
|
|
| Extrarenal drugs | Direct vasodilators Vasodilators Drugs used to cause dilation of the blood vessels. Thromboangiitis Obliterans (Buerger Disease) |
|
| Agents acting via the sympathetic nervous system Nervous system The nervous system is a small and complex system that consists of an intricate network of neural cells (or neurons) and even more glial cells (for support and insulation). It is divided according to its anatomical components as well as its functional characteristics. The brain and spinal cord are referred to as the central nervous system, and the branches of nerves from these structures are referred to as the peripheral nervous system. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification |
|
Drugs include:
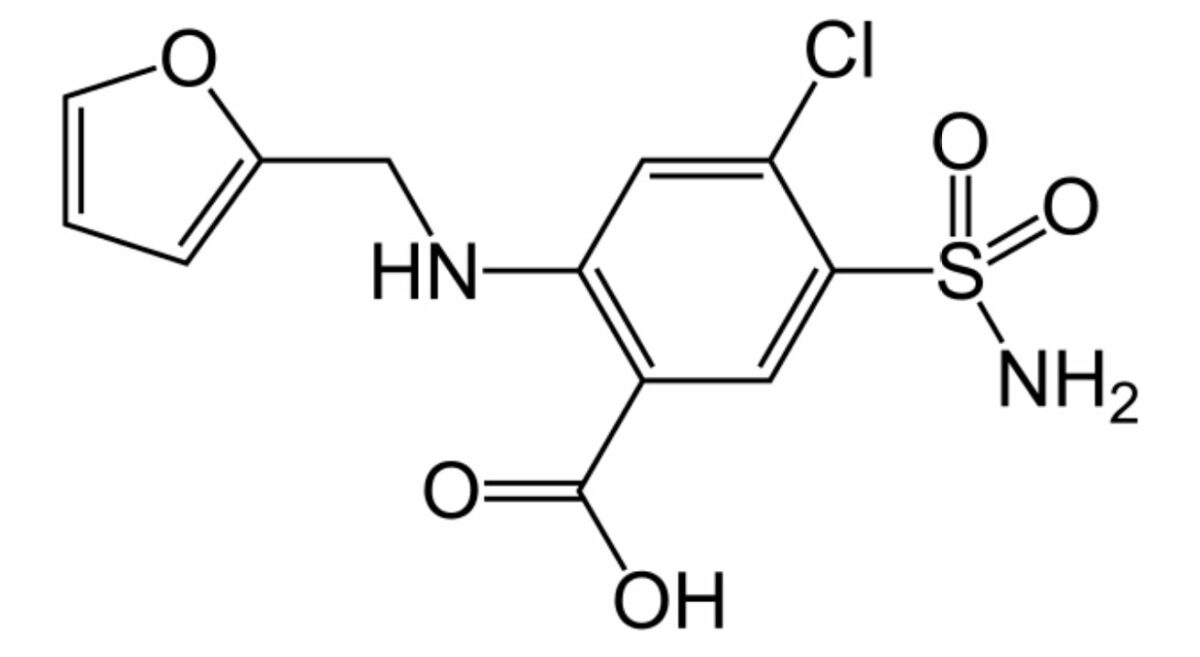
Chemical structure of furosemide
Image: “Furosemide” by Fvasconcellos. License: Public Domain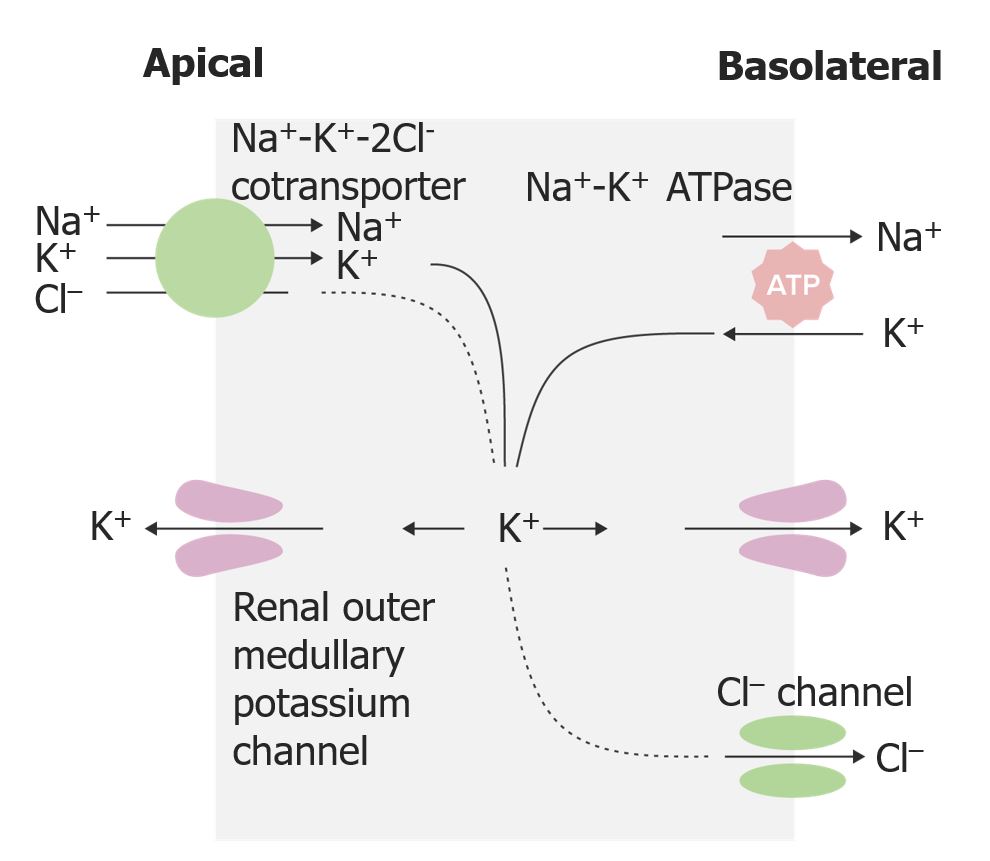
Action of loop diuretics in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle (TAL)
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0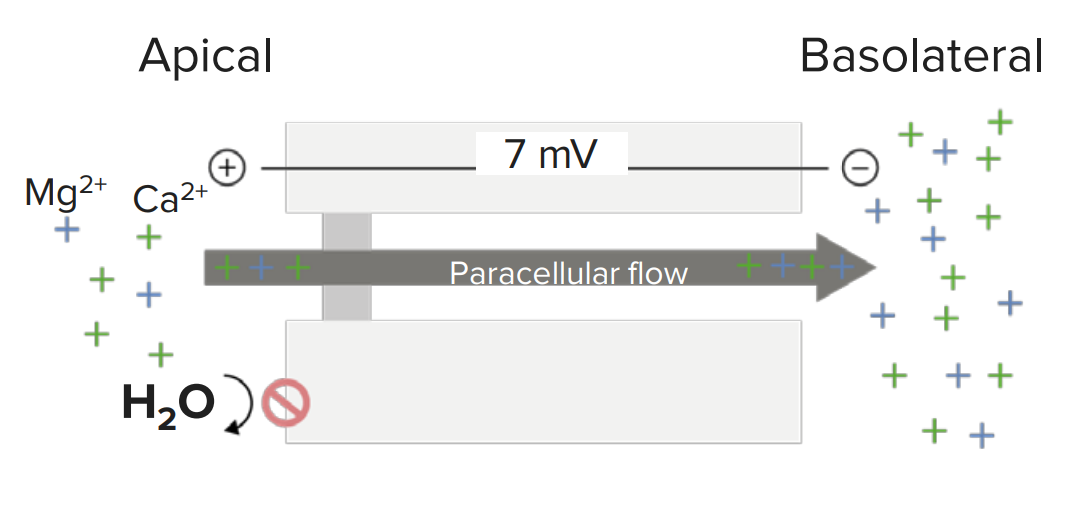
Passive paracellular reabsorption of magnesium and calcium in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle (TAL): driven by the voltage gradient between the tubular lumen (apical side) and the interstitial fluid (basolateral side)
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0| Drug | Absorption Absorption Absorption involves the uptake of nutrient molecules and their transfer from the lumen of the GI tract across the enterocytes and into the interstitial space, where they can be taken up in the venous or lymphatic circulation. Digestion and Absorption | Distribution | Metabolism | Excretion |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Furosemide (Lasix®) |
|
Protein binding: 95% | Minimal hepatic metabolism |
|
| Bumetanide (Bumex®) |
|
|
Partial hepatic metabolism |
|
| Torsemide (Demadex®) |
|
|
Hepatic (80%) via CYP2C9 CYP2C9 A cytochrome p-450 subtype that has specificity for acidic xenobiotics. It oxidizes a broad range of important clinical drugs that fall under the categories of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents; hypoglycemic agents; anticoagulants; and diuretics. Anticoagulants |
|
| Ethacrynic acid (Edecrin®) | Peak effect:
|
Protein binding: > 90% | Hepatic (40%) via active cysteine Cysteine A thiol-containing non-essential amino acid that is oxidized to form cystine. Synthesis of Nonessential Amino Acids conjugate |
|
Mnemonic:
To recall the adverse effects of loop diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication, remember “Ohh Daang”:
Loop diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication should be used with caution in the following situations:
Thiazide Thiazide Heterocyclic compounds with sulfur and nitrogen in the ring. This term commonly refers to the benzothiadiazines that inhibit sodium-potassium-chloride symporters and are used as diuretics. Hyponatremia diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication, potassium-sparing diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication, carbonic anhydrase Carbonic anhydrase A family of zinc-containing enzymes that catalyze the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide. They play an important role in the transport of carbon dioxide from the tissues to the lung. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors inhibitors, and osmotic diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication are also common diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication.
| Medication | Mechanism | Physiologic effect | Indication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thiazide Thiazide Heterocyclic compounds with sulfur and nitrogen in the ring. This term commonly refers to the benzothiadiazines that inhibit sodium-potassium-chloride symporters and are used as diuretics. Hyponatremia diuretic: Hydrochlorothiazide Hydrochlorothiazide A thiazide diuretic often considered the prototypical member of this class. It reduces the reabsorption of electrolytes from the renal tubules. This results in increased excretion of water and electrolytes, including sodium, potassium, chloride, and magnesium. It is used in the treatment of several disorders including edema, hypertension, diabetes insipidus, and hypoparathyroidism. Thiazide Diuretics | ↓ Reabsorption of NaCl in the DCT through the inhibition of Na+/Cl– cotransporter |
|
|
| Loop diuretic: Furosemide | Inhibits the luminal Na+/K+/Cl– cotransporter in the thick ascending limb Thick ascending limb Renal Sodium and Water Regulation of the loop of Henle Loop of Henle The U-shaped portion of the renal tubule in the kidney medulla, consisting of a descending limb and an ascending limb. It is situated between the proximal kidney tubule and the distal kidney tubule. Tubular System |
|
|
| Potassium-sparing diuretic: Spironolactone Spironolactone A potassium sparing diuretic that acts by antagonism of aldosterone in the distal renal tubules. It is used mainly in the treatment of refractory edema in patients with congestive heart failure, nephrotic syndrome, or hepatic cirrhosis. Its effects on the endocrine system are utilized in the treatments of hirsutism and acne but they can lead to adverse effects. Potassium-sparing Diuretics |
|
|
|
| Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor Glaucoma: Acetazolamide Acetazolamide One of the carbonic anhydrase inhibitors that is sometimes effective against absence seizures. It is sometimes useful also as an adjunct in the treatment of tonic-clonic, myoclonic, and atonic seizures, particularly in women whose seizures occur or are exacerbated at specific times in the menstrual cycle. However, its usefulness is transient often because of rapid development of tolerance. Its antiepileptic effect may be due to its inhibitory effect on brain carbonic anhydrase, which leads to an increased transneuronal chloride gradient, increased chloride current, and increased inhibition. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors | Inhibits both the hydration of CO2 in the PCT epithelial cells and the dehydration Dehydration The condition that results from excessive loss of water from a living organism. Volume Depletion and Dehydration of H2CO3 in the PCT lumen; results in ↑ HCO3– and Na+ excretion |
|
|
| Osmotic diuretics Diuretics Agents that promote the excretion of urine through their effects on kidney function. Heart Failure and Chronic Coronary Syndrome Medication: Mannitol Mannitol A diuretic and renal diagnostic aid related to sorbitol. It has little significant energy value as it is largely eliminated from the body before any metabolism can take place. It can be used to treat oliguria associated with kidney failure or other manifestations of inadequate renal function and has been used for determination of glomerular filtration rate. Mannitol is also commonly used as a research tool in cell biological studies, usually to control osmolarity. Osmotic Diuretics | ↑ Osmotic pressure Osmotic pressure The pressure required to prevent the passage of solvent through a semipermeable membrane that separates a pure solvent from a solution of the solvent and solute or that separates different concentrations of a solution. It is proportional to the osmolality of the solution. Intravenous Fluids in the glomerular filtrate → ↑ tubular fluid and prevents water reabsorption |
|
|
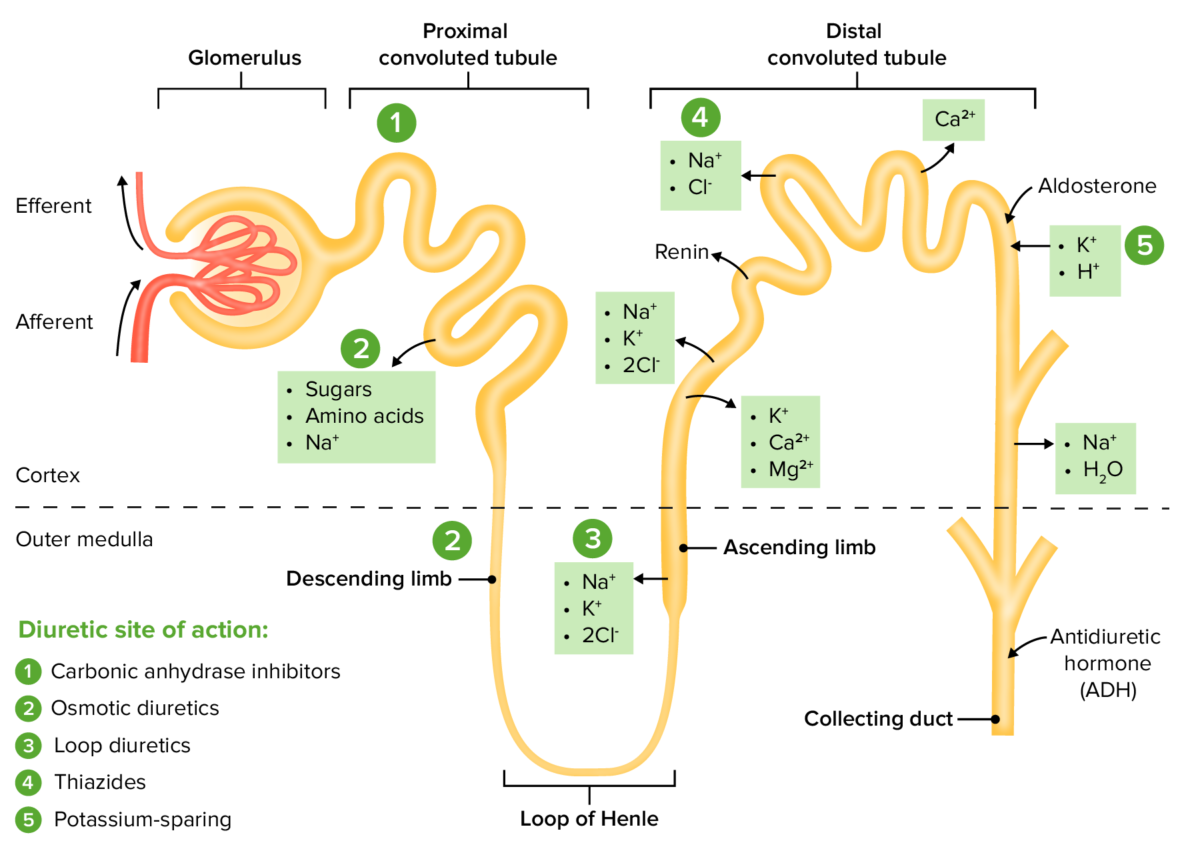
The sites of action within the nephron for the diuretic drug classes
Image by Lecturio. License: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0