Locked-in syndrome (LIS) is a rare neurological disorder in which patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are awake and conscious but are unable to move their limbs or speak. The disorder is a result of brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification injury to the ventral aspect of the pons Pons The front part of the hindbrain (rhombencephalon) that lies between the medulla and the midbrain (mesencephalon) ventral to the cerebellum. It is composed of two parts, the dorsal and the ventral. The pons serves as a relay station for neural pathways between the cerebellum to the cerebrum. Brain Stem: Anatomy and caudal ventral midbrain Midbrain The middle of the three primitive cerebral vesicles of the embryonic brain. Without further subdivision, midbrain develops into a short, constricted portion connecting the pons and the diencephalon. Midbrain contains two major parts, the dorsal tectum mesencephali and the ventral tegmentum mesencephali, housing components of auditory, visual, and other sensorimotor systems. Brain Stem: Anatomy; etiologies include brainstem stroke, tumors, intracranial bleeding, and demyelinating disorders Demyelinating disorders Conditions characterized by loss or dysfunction of myelin in the brain, spinal cord, or optic nerves secondary to autoimmune mediated processes. This may take the form of a humoral or cellular immune response directed toward myelin or oligodendroglia associated autoantigens. Posterior Cord Syndrome. Consciousness and the ability to think and reason remain intact, as do the abilities to blink and move the eyes. Diagnosis is made clinically, and the initial management is supportive care for breathing and feeding. Definitive management depends upon the underlying cause and is followed by several months of rehabilitation. Prognosis Prognosis A prediction of the probable outcome of a disease based on a individual's condition and the usual course of the disease as seen in similar situations. Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas is generally poor, although some patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are able to achieve significant improvement in some functions.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Locked-in syndrome (LIS) is a rare neurological disorder in which patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship are awake and conscious but are unable to move their limbs or speak due to pathology affecting the brainstem.
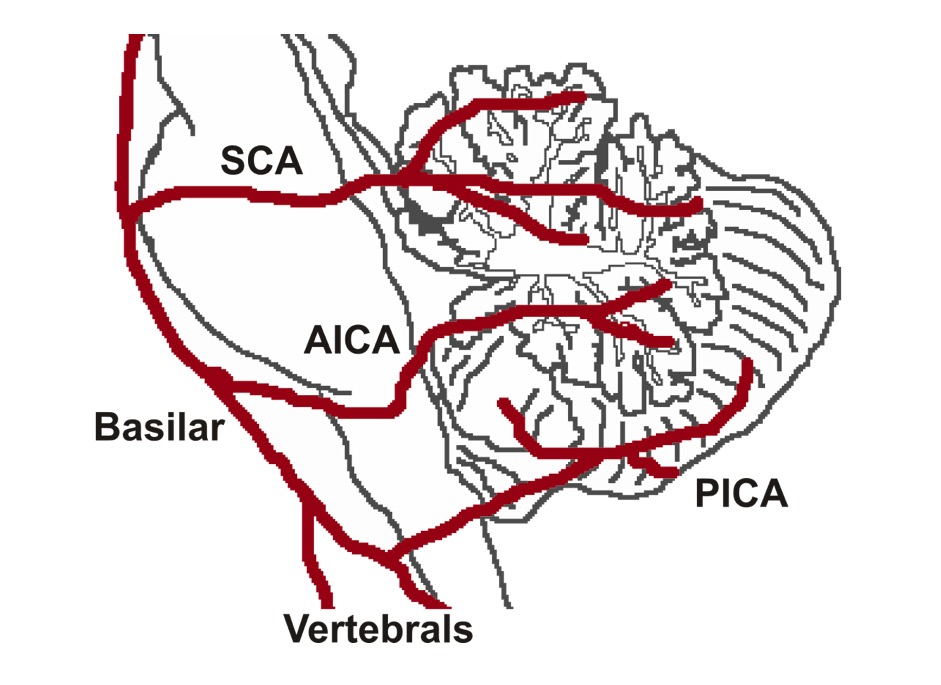
Cerebellar arteries:
Blood supply to the brainstem is shown; a stroke occurring in the pons due to occlusion of the basilar artery pontine branches may result in locked-in syndrome.
SCA: superior cerebellar artery
PICA: posterior inferior cerebellar artery
AICA: anterior inferior cerebellar artery
Ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke Hemorrhagic stroke Stroke due to rupture of a weakened blood vessel in the brain (e.g., cerebral hemispheres; cerebellum; subarachnoid space). Subarachnoid Hemorrhage can affect the vulnerable territory at the paramedian base of the pons Pons The front part of the hindbrain (rhombencephalon) that lies between the medulla and the midbrain (mesencephalon) ventral to the cerebellum. It is composed of two parts, the dorsal and the ventral. The pons serves as a relay station for neural pathways between the cerebellum to the cerebrum. Brain Stem: Anatomy. The tegmentum (ventral part of the midbrain Midbrain The middle of the three primitive cerebral vesicles of the embryonic brain. Without further subdivision, midbrain develops into a short, constricted portion connecting the pons and the diencephalon. Midbrain contains two major parts, the dorsal tectum mesencephali and the ventral tegmentum mesencephali, housing components of auditory, visual, and other sensorimotor systems. Brain Stem: Anatomy) has collateral supply that often spares the lateral and medial tegmentum.
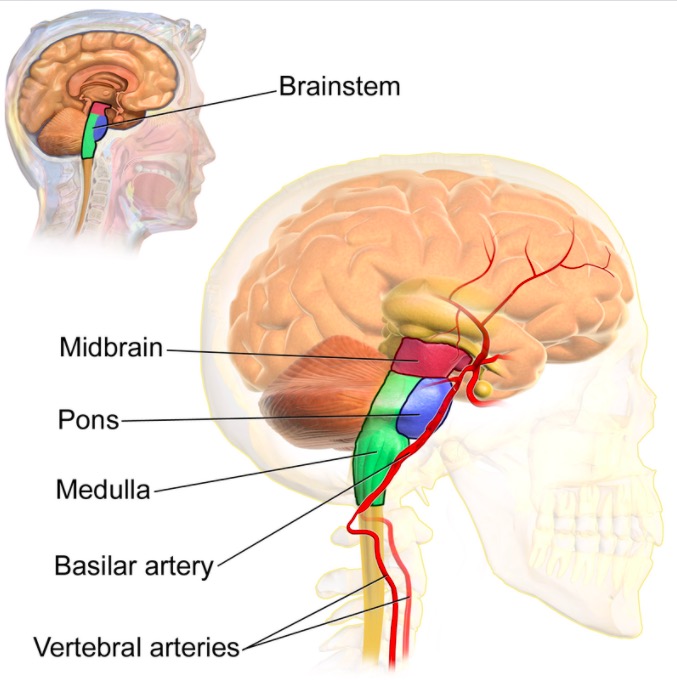
Anatomy involved in locked-in syndrome
Image: “The brainstem” by Blausen.com staff (2014). License: CC BY 3.0Diagnosis of LIS requires demonstration of preserved consciousness, alertness, and cognitive function in a patient with paralysis of the limbs and mouth.
Eye movement:
Physical exam:
Medical treatments to promote recovery from LIS are rehabilitative and supportive therapies.