Liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy function tests, also known as hepatic function panels, are one of the most commonly performed screening Screening Preoperative Care blood tests. Such tests are also used to detect, evaluate, and monitor acute and chronic liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy diseases. Liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy function tests assess the levels of various hepatic proteins Proteins Linear polypeptides that are synthesized on ribosomes and may be further modified, crosslinked, cleaved, or assembled into complex proteins with several subunits. The specific sequence of amino acids determines the shape the polypeptide will take, during protein folding, and the function of the protein. Energy Homeostasis and enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body's constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes to determine the state of liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy metabolic activity, homeostasis Homeostasis The processes whereby the internal environment of an organism tends to remain balanced and stable. Cell Injury and Death, bile Bile An emulsifying agent produced in the liver and secreted into the duodenum. Its composition includes bile acids and salts; cholesterol; and electrolytes. It aids digestion of fats in the duodenum. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy metabolism, and protein synthesis Synthesis Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) capacity. The standard hepatic panel includes the levels of total protein, bilirubin Bilirubin A bile pigment that is a degradation product of heme. Heme Metabolism, albumin, ALT, AST, AST/ALT ratio, and alkaline phosphatase Alkaline Phosphatase An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of an orthophosphoric monoester and water to an alcohol and orthophosphate. Osteosarcoma ( ALP ALP An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of an orthophosphoric monoester and water to an alcohol and orthophosphate. Osteosarcoma). Note: The laboratory values presented on this page are intended for illustrative purposes only. Value ranges may differ based on the units of measurement, reagents, techniques, or instruments employed by a specific laboratory facility.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
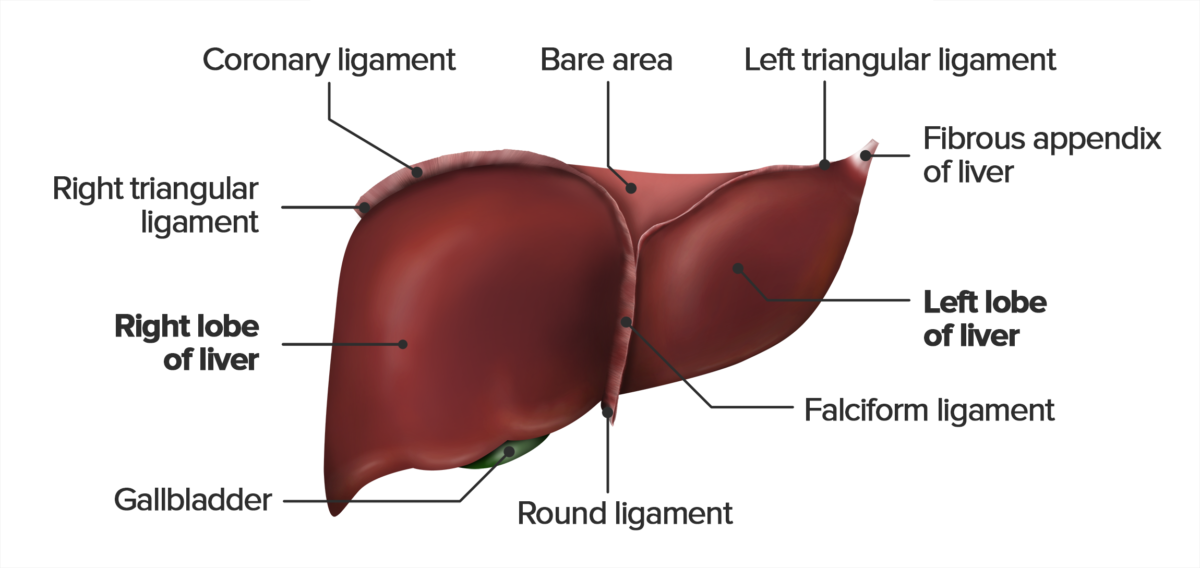
View of the diaphragmatic surface of the liver
| Liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease | ALT and AST | ALP ALP An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of an orthophosphoric monoester and water to an alcohol and orthophosphate. Osteosarcoma | Bilirubin Bilirubin A bile pigment that is a degradation product of heme. Heme Metabolism | GGTP | PT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acute liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy damage (e.g., viral hepatitis) | > 10 times normal level Usually ALT > AST |
Normal or ↑ | Normal or ↑ | Normal | |
| Chronic liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy damage (e.g., fatty liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy) | Normal or ↑ | Normal or ↑ | Normal | ||
| Alcoholic Alcoholic Persons who have a history of physical or psychological dependence on ethanol. Mallory-Weiss Syndrome (Mallory-Weiss Tear) liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy disease (ALD) | AST/ALT > 2 |
Normal or ↑ | Normal or ↑ | Normal | |
| Cholestasis | > 4 times |
Normal | |||
| Cirrhosis Cirrhosis Cirrhosis is a late stage of hepatic parenchymal necrosis and scarring (fibrosis) most commonly due to hepatitis C infection and alcoholic liver disease. Patients may present with jaundice, ascites, and hepatosplenomegaly. Cirrhosis can also cause complications such as hepatic encephalopathy, portal hypertension, portal vein thrombosis, and hepatorenal syndrome. Cirrhosis | AST > ALT |
Normal or ↑ | ↑ In advanced stages | Prolonged | |
| Liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy cancer | Normal or ↑ | Normal or ↑ | Prolonged | ||
| Autoimmune hepatitis Autoimmune hepatitis Autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) is a rare form of chronic liver disease in which the immune system attacks the liver causing inflammation. It predominantly affects women. Clinical presentation ranges from asymptomatic cases to patients that present with symptoms of acute liver failure (jaundice, right upper quadrant pain). Autoimmune Hepatitis | ALT > AST |
Normal or ↑ | Normal | ||
| Ischemic injury/ shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy | Normal or ↑ | Prolonged |
When hepatocytes Hepatocytes The main structural component of the liver. They are specialized epithelial cells that are organized into interconnected plates called lobules. Liver: Anatomy are damaged, they release their enzymes Enzymes Enzymes are complex protein biocatalysts that accelerate chemical reactions without being consumed by them. Due to the body’s constant metabolic needs, the absence of enzymes would make life unsustainable, as reactions would occur too slowly without these molecules. Basics of Enzymes into the circulation Circulation The movement of the blood as it is pumped through the cardiovascular system. ABCDE Assessment. The magnitude of enzyme level derangement reflects the severity of liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy damage.
| Parameter | Normal range | Function | Causes of elevation |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALT | 8–20 U/L |
|
> 1000 U/L:
|
| AST | 8–20 U/L |
|
|
| GLDH | 1–10 U/L |
|
|
| AST/ALT ratio | Approximately 0.8 | Used to differentiate between causes of hepatocellular damage |
|
| Parameter | Normal range | Function | Causes of elevation | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GGTP | 9–48 U/L |
|
|
|
| ALP ALP An enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of an orthophosphoric monoester and water to an alcohol and orthophosphate. Osteosarcoma | 44–147 IU/L | Responsible for dephosphorylating various compounds |
|
|
| Bilirubin Bilirubin A bile pigment that is a degradation product of heme. Heme Metabolism | Total | 0.1–1 mg/dL | Yellow pigment made during the breakdown of RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology via heme catabolism | Elevated by various diseases of the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy, gallbladder Gallbladder The gallbladder is a pear-shaped sac, located directly beneath the liver, that sits on top of the superior part of the duodenum. The primary functions of the gallbladder include concentrating and storing up to 50 mL of bile. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy, biliary tree Biliary tree The bile ducts and the gallbladder. Gallbladder and Biliary Tract: Anatomy, or RBCs RBCs Erythrocytes, or red blood cells (RBCs), are the most abundant cells in the blood. While erythrocytes in the fetus are initially produced in the yolk sac then the liver, the bone marrow eventually becomes the main site of production. Erythrocytes: Histology (e.g., hemolysis) |
| Direct | 0.0–0.3 mg/dL | Conjugated with glucuronic acid, water-soluble | Usually associated with causes of obstructive cholestasis | |
| Indirect | Usually measured as the difference between total and direct bilirubin Bilirubin A bile pigment that is a degradation product of heme. Heme Metabolism | Unconjugated with glucuronic acid, lipid-soluble |
|
|
| Parameter | Normal range | Function | Causes of elevation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin | 3.5–5.5 g/dL |
|
|
| Cholinesterase | 8–18 U/mL |
|
|
| PT | 9.5–13.5 seconds |
|
|