A lipoma is a benign Benign Fibroadenoma neoplasm of fat cells ( adipocytes Adipocytes Cells in the body that store fats, usually in the form of triglycerides. White adipocytes are the predominant type and found mostly in the abdominal cavity and subcutaneous tissue. Brown adipocytes are thermogenic cells that can be found in newborns of some species and hibernating mammals. Adipose Tissue: Histology) and the most common soft tissue Soft Tissue Soft Tissue Abscess tumor Tumor Inflammation in adults. The etiology is unknown, but obesity Obesity Obesity is a condition associated with excess body weight, specifically with the deposition of excessive adipose tissue. Obesity is considered a global epidemic. Major influences come from the western diet and sedentary lifestyles, but the exact mechanisms likely include a mixture of genetic and environmental factors. Obesity is a predisposing factor; genetics Genetics Genetics is the study of genes and their functions and behaviors. Basic Terms of Genetics also play a role, with multiple lipomas occurring in various inherited disorders. Lipomas can arise in any site with adipose tissue Adipose tissue Adipose tissue is a specialized type of connective tissue that has both structural and highly complex metabolic functions, including energy storage, glucose homeostasis, and a multitude of endocrine capabilities. There are three types of adipose tissue, white adipose tissue, brown adipose tissue, and beige or "brite" adipose tissue, which is a transitional form. Adipose Tissue: Histology (including the gastrointestinal tract, chest cavity, retroperitoneum, and glands), but are most common in subcutaneous tissues of the trunk or proximal extremities. The treatment is not necessary for small asymptomatic lipomas. Surgical excision is the treatment if there is a cosmetic, functional, or diagnostic concern.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Lipoma is a benign Benign Fibroadenoma neoplasm of fat cells ( adipocytes Adipocytes Cells in the body that store fats, usually in the form of triglycerides. White adipocytes are the predominant type and found mostly in the abdominal cavity and subcutaneous tissue. Brown adipocytes are thermogenic cells that can be found in newborns of some species and hibernating mammals. Adipose Tissue: Histology).
Anatomic sites:
Morphology:
Histology:
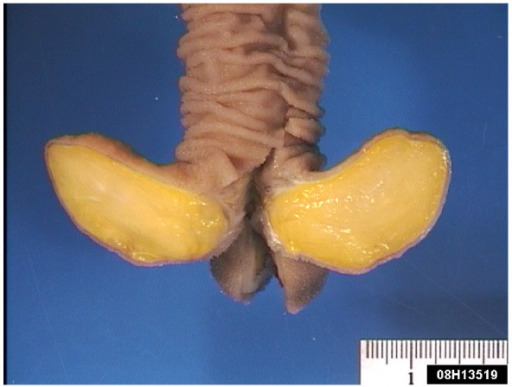
Pedunculated submucosal lipoma in the ileum, which was causing an obstruction
Image: “Gastric lipoma presenting as a giant bulging mass in an oligosymptomatic patient: a case report” by Abbasakoor NO, Kavanagh DO, Moran DC, Ryan B, Neary PC. License: CC BY 2.0.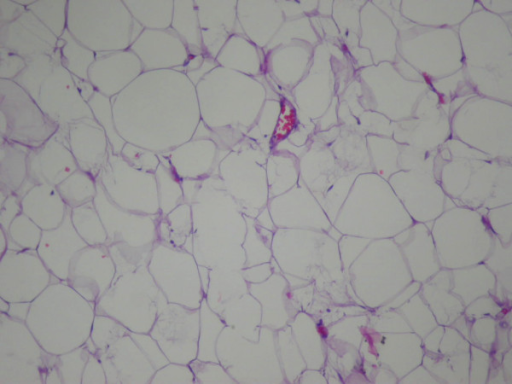
Photomicrograph of a conventional lipoma, showing mature adipocytes with scant vascularity
Image: “Gastric lipoma presenting as a giant bulging mass in an oligosymptomatic patient: a case report” by Neto FA, Ferreira MC, Bertoncello LC, Neto AA, de Aveiro WC, Bento CA, Cecchino GN, Rocha MA. License: CC BY 2.0.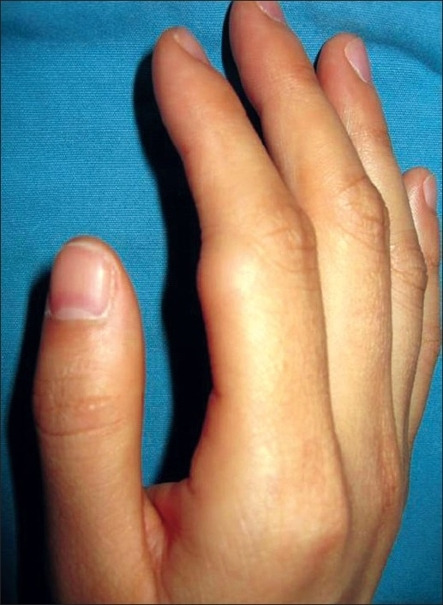
Subcutaneous 1.5-cm lipoma on the proximal interphalangeal joint of the right index finger of a 35-year-old woman
Image: “Lipoma of the finger presenting as restricted motion” by Yoon S, Jung SN. License: CC BY 2.0.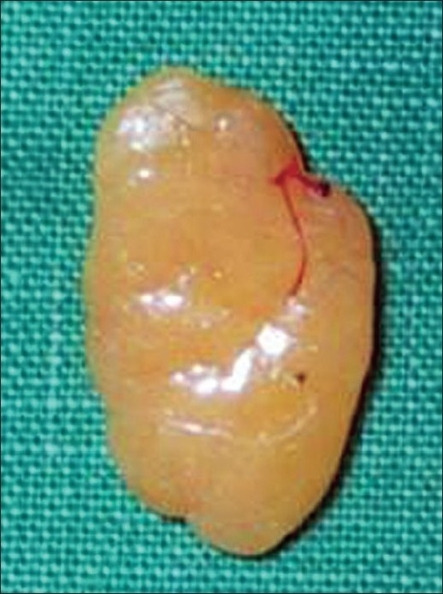
Subcutaneous 1.5-cm lipoma
Lipoma of the finger presents as restricted motion.
History:
Physical exam:
Imaging:
Endoscopy Endoscopy Procedures of applying endoscopes for disease diagnosis and treatment. Endoscopy involves passing an optical instrument through a small incision in the skin i.e., percutaneous; or through a natural orifice and along natural body pathways such as the digestive tract; and/or through an incision in the wall of a tubular structure or organ, i.e. Transluminal, to examine or perform surgery on the interior parts of the body. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD) and endoscopic ultrasound (EUS):
Biopsy Biopsy Removal and pathologic examination of specimens from the living body. Ewing Sarcoma:
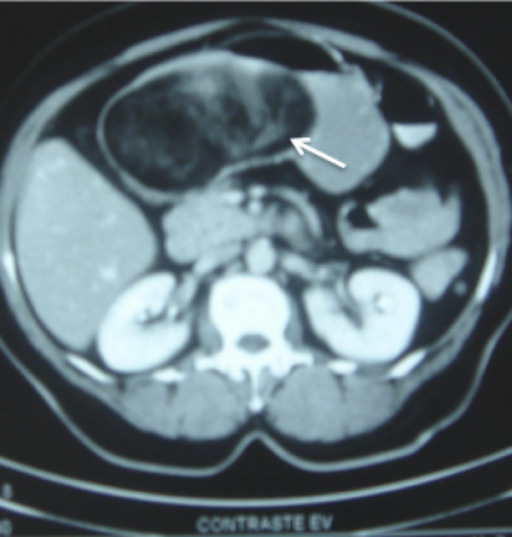
A large (12 x 8 x 6 cm) submucosal gastric lipoma (arrow)
Some contrast medium has leaked into the lipoma through focal ulcerated areas in the overlying mucosa, and can be seen tracking into the center from the surface.
Expectant management: appropriate for small (< 5 cm) subcutaneous asymptomatic lipomas
Surgical excision:
Complications of surgery:
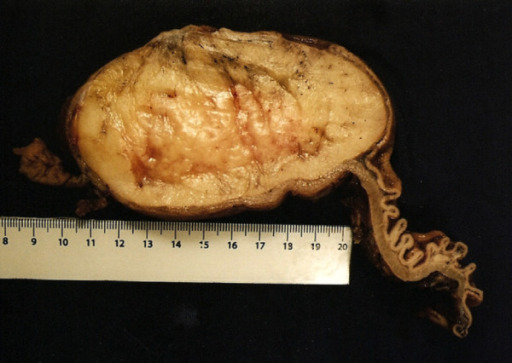
Submucosal gastric lipoma (surgical specimen)
Note the thickened wall of the proximal gastric wall on the right side, and the attenuated focally ulcerated overlying gastric mucosa.