An abnormal amount of lipid in blood is called dyslipidemia, which includes abnormal levels of cholesterol Cholesterol The principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils. Cholesterol Metabolism, triglycerides Triglycerides Fatty Acids and Lipids, and/or lipoproteins Lipoproteins Lipid-protein complexes involved in the transportation and metabolism of lipids in the body. They are spherical particles consisting of a hydrophobic core of triglycerides and cholesterol esters surrounded by a layer of hydrophilic free cholesterol; phospholipids; and apolipoproteins. Lipoproteins are classified by their varying buoyant density and sizes. Lipid Metabolism. Dyslipidemia may be primary (familial) or secondary (acquired). Both primary and secondary causes can lead to the development of premature Premature Childbirth before 37 weeks of pregnancy (259 days from the first day of the mother's last menstrual period, or 245 days after fertilization). Necrotizing Enterocolitis cardiovascular ( atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis Atherosclerosis is a common form of arterial disease in which lipid deposition forms a plaque in the blood vessel walls. Atherosclerosis is an incurable disease, for which there are clearly defined risk factors that often can be reduced through a change in lifestyle and behavior of the patient. Atherosclerosis) disease. Familial causes are classified according to the Fredrickson system, which looks into the pathology and the lipids Lipids Lipids are a diverse group of hydrophobic organic molecules, which include fats, oils, sterols, and waxes. Fatty Acids and Lipids that are elevated. Certain types do not increase the risk of premature Premature Childbirth before 37 weeks of pregnancy (259 days from the first day of the mother's last menstrual period, or 245 days after fertilization). Necrotizing Enterocolitis atherosclerotic disease but still impact overall cardiac risk and chance of cardiovascular events in the future. Screening Screening Preoperative Care, early diagnosis, and strict control and management are the keys to prevention of cardiovascular events.
Last updated: Apr 25, 2025
Dyslipidemia: abnormal amounts of lipid in the blood
Causes of dyslipidemia can be divided into primary (familial) and secondary (acquired) causes.
Primary causes:
Secondary (acquired) causes:
| Type | Condition, mode of inheritance ( autosomal dominant Autosomal dominant Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal dominant diseases are expressed when only 1 copy of the dominant allele is inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance ( AD AD The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment. Advance Directives), autosomal recessive Autosomal recessive Autosomal inheritance, both dominant and recessive, refers to the transmission of genes from the 22 autosomal chromosomes. Autosomal recessive diseases are only expressed when 2 copies of the recessive allele are inherited. Autosomal Recessive and Autosomal Dominant Inheritance ( AR AR Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders. Aortic Regurgitation)), lipid abnormality | Pathology | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| I | Familial hyperchylomicronemia (
AR
AR
Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders.
Aortic Regurgitation) Elevated chylomicrons |
Deficiency in LPL or apolipoprotein C-II (ApoC-II) |
|
| IIa | Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) (
AD
AD
The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment.
Advance Directives) Elevated LDL |
Mutation Mutation Genetic mutations are errors in DNA that can cause protein misfolding and dysfunction. There are various types of mutations, including chromosomal, point, frameshift, and expansion mutations. Types of Mutations in PCSK-9, defective LDL receptors Receptors Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors or apolipoprotein B-100 (ApoB-100) |
|
| IIb | Familial combined hypercholesterolemia (
AD
AD
The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment.
Advance Directives) Elevated VLDL and LDL |
|
|
| III | Familial hyperlipoproteinemia (
AR
AR
Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders.
Aortic Regurgitation) Remnants of VLDL and chylomicrons |
Defective ApoE |
|
| IV | Familial hypertriglyceridemia (
AD
AD
The term advance directive (AD) refers to treatment preferences and/or the designation of a surrogate decision-maker in the event that a person becomes unable to make medical decisions on their own behalf. Advance directives represent the ethical principle of autonomy and may take the form of a living will, health care proxy, durable power of attorney for health care, and/or a physician’s order for life-sustaining treatment.
Advance Directives) Elevated VLDL |
Excessive VLDL production by the liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy |
|
| V | Mixed HLD (
AR
AR
Aortic regurgitation (AR) is a cardiac condition characterized by the backflow of blood from the aorta to the left ventricle during diastole. Aortic regurgitation is associated with an abnormal aortic valve and/or aortic root stemming from multiple causes, commonly rheumatic heart disease as well as congenital and degenerative valvular disorders.
Aortic Regurgitation) Elevated chylomicrons and VLDL |
Defective apolipoprotein A5 (ApoA5) |
|
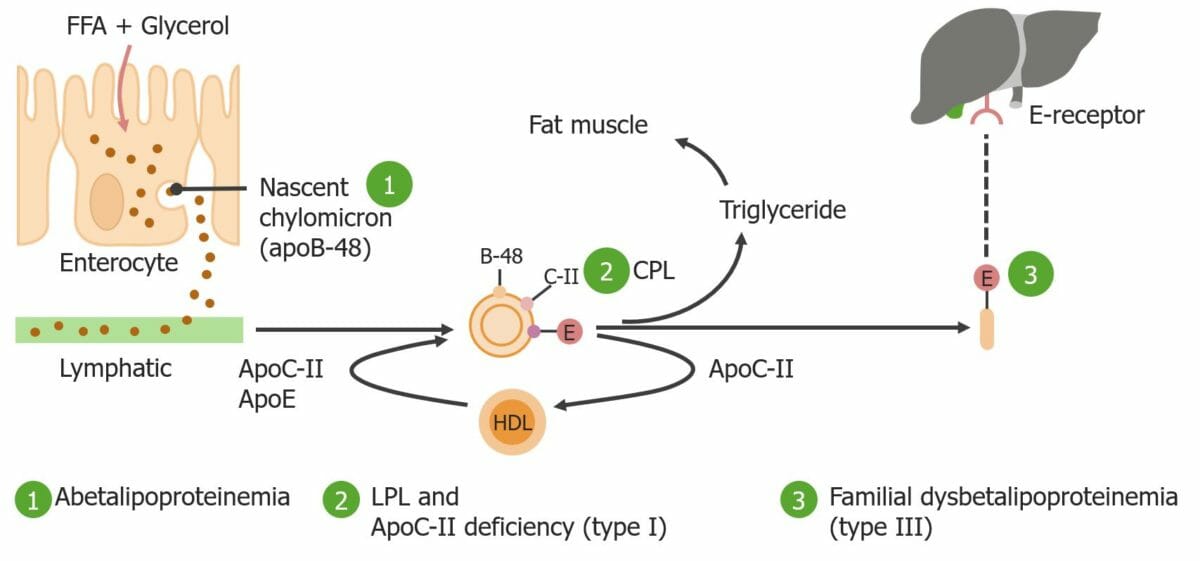
Schematic depiction of the Fredrickson classification types I and III
FFA: free fatty acid
ApoB-48: apolipoprotein-B-48
ApoC-II: apolipoprotein C-II
ApoE: apolipoprotein E
LPL: lipoprotein lipase
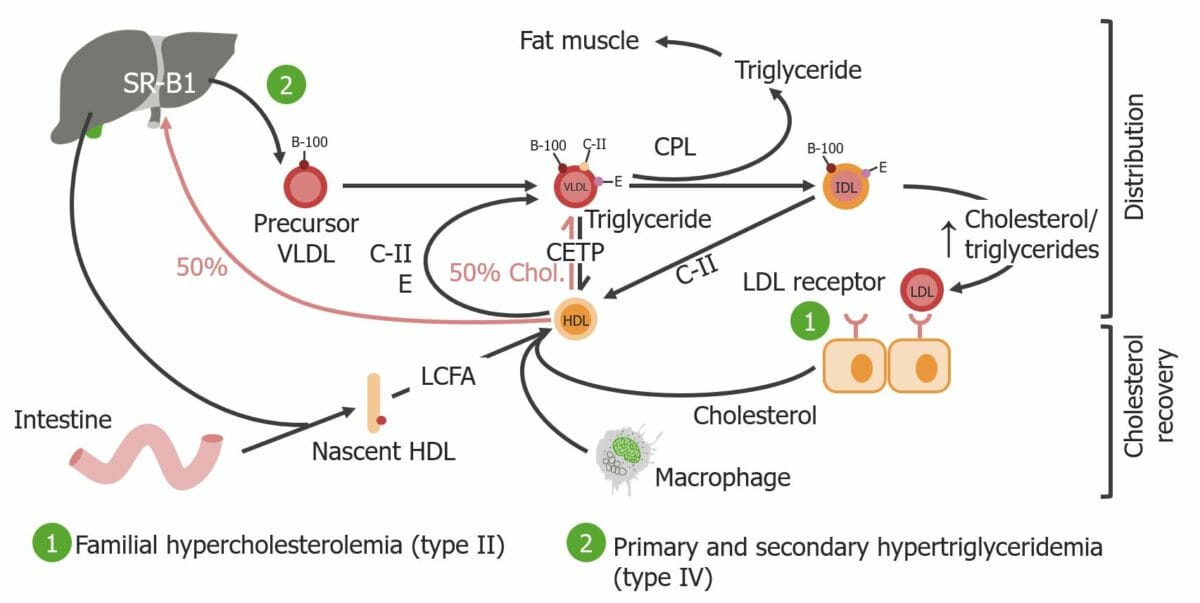
Schematic depiction of Fredrickson classification types II and IV
Image by Lecturio.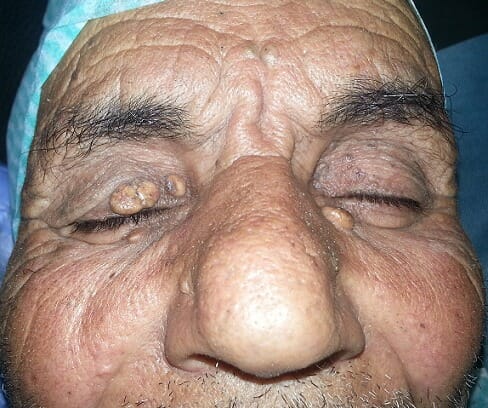
An elderly patient with yellow-tan deposits around the eyelids, most likely indicative of xanthelasma
Image: “Les différentes lésions jaunâtres au niveau des deux paupières en rapport avec le xanthélasma” by Elghazi, T. and Hafidi, Z. License: CC BY 2.0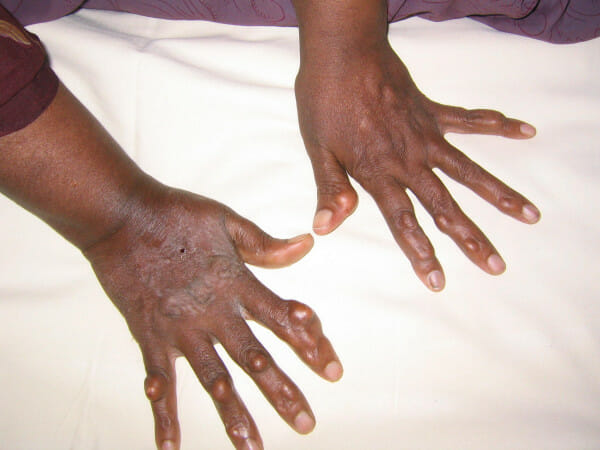
Multiple xanthomas on hands
Image: “Xanthomas” by Kumar, A.A. et al. License: CC BY 2.0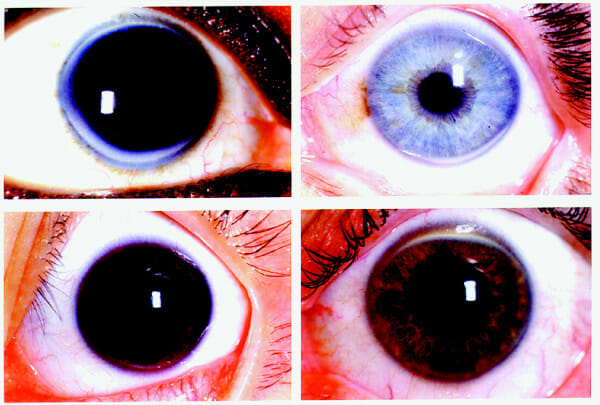
Four representative slides of corneal arcus:
Arcus deposits tend to start at 6 and 12 o’clock and fill in until becoming completely circumferential.
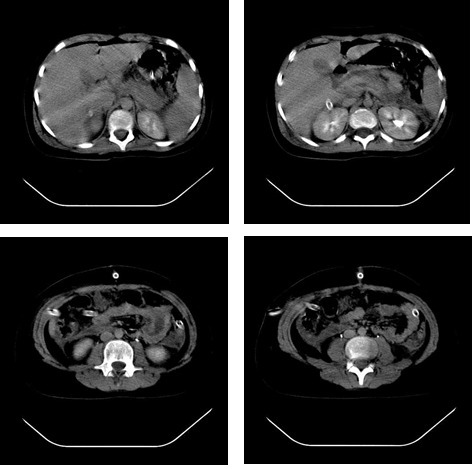
CT scan of acute pancreatitis secondary to hyperlipidemia in an 11-year-old girl: The scan shows a high-dimensioned pancreas, particularly at the head, with heterogeneous structure and peripancreatic collections.
Image: “Acute pancreatitis secondary to hyperlipidemia in an 11-year-old girl” by Department of Pediatric Surgery, “Grigore Alexandrescu” Clinical Emergency Hospital for Children, Bucharest. License: CC BY 2.0.| Lipid | Normal value |
|---|---|
| Total cholesterol Cholesterol The principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils. Cholesterol Metabolism | < 200 mg/dL |
| HDL cholesterol Cholesterol The principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils. Cholesterol Metabolism | > 60 mg/dL |
| LDL cholesterol Cholesterol The principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils. Cholesterol Metabolism | < 100 mg/dL |
| Triglycerides Triglycerides Fatty Acids and Lipids | < 150 mg/dL |
| Friedewald formula: LDL= total cholesterol Cholesterol The principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in animal fats and oils. Cholesterol Metabolism – HDL – ( triglycerides Triglycerides Fatty Acids and Lipids/5) | |
The aim of management is to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.