The limbic system is a neuronal network that mediates emotion and motivation, while also playing a role in learning and memory Memory Complex mental function having four distinct phases: (1) memorizing or learning, (2) retention, (3) recall, and (4) recognition. Clinically, it is usually subdivided into immediate, recent, and remote memory. Psychiatric Assessment. The extended neural network is vital to numerous basic psychological functions and plays an invaluable role in processing and responding to environmental stimuli.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
The limbic system is a highly integrated system of structures with feedback mechanisms to appropriately balance the continuous stream of information that is received.
The limbic system is composed of several structures that produce subconscious responses to stimuli:
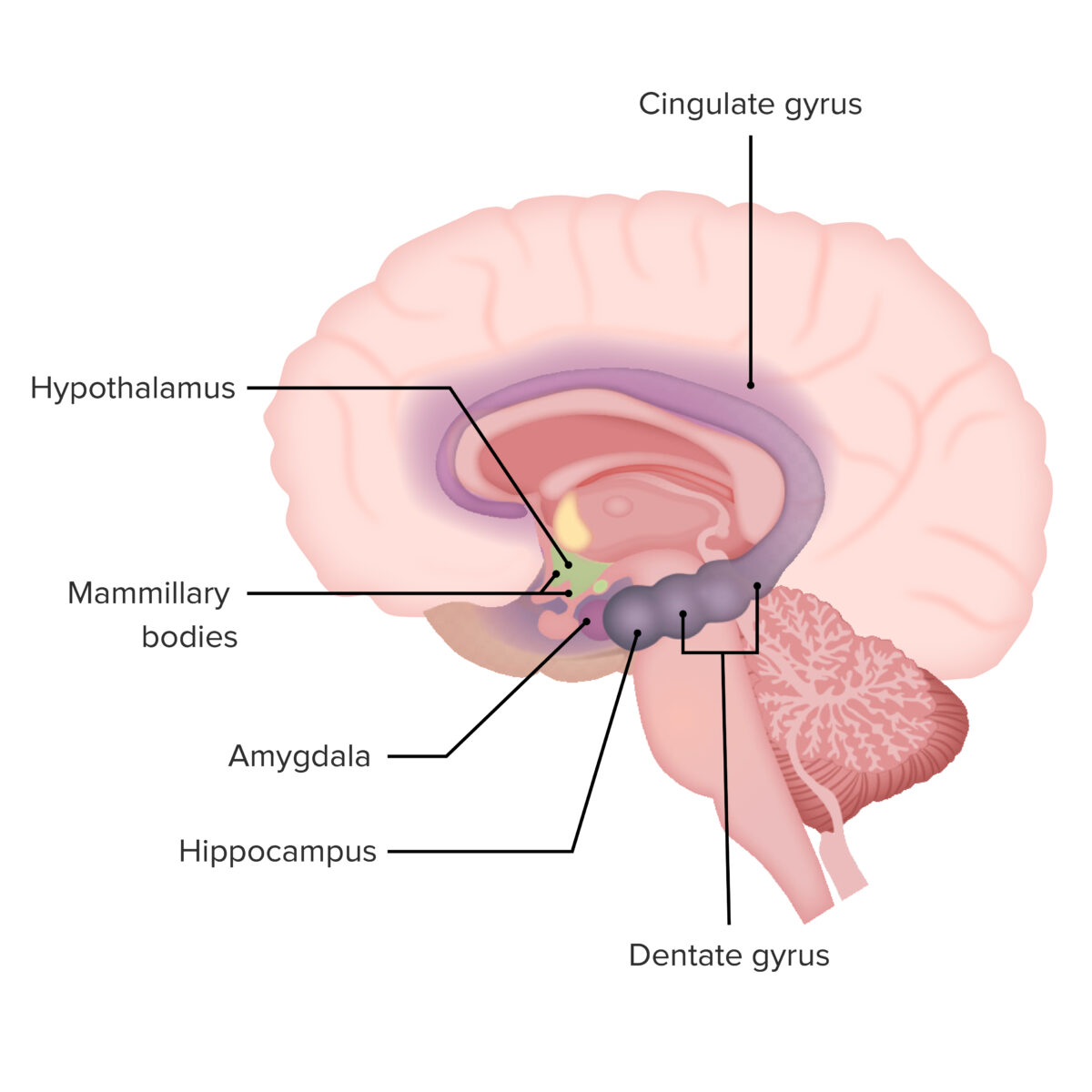
Primary components of the limbic system
Image by Lecturio.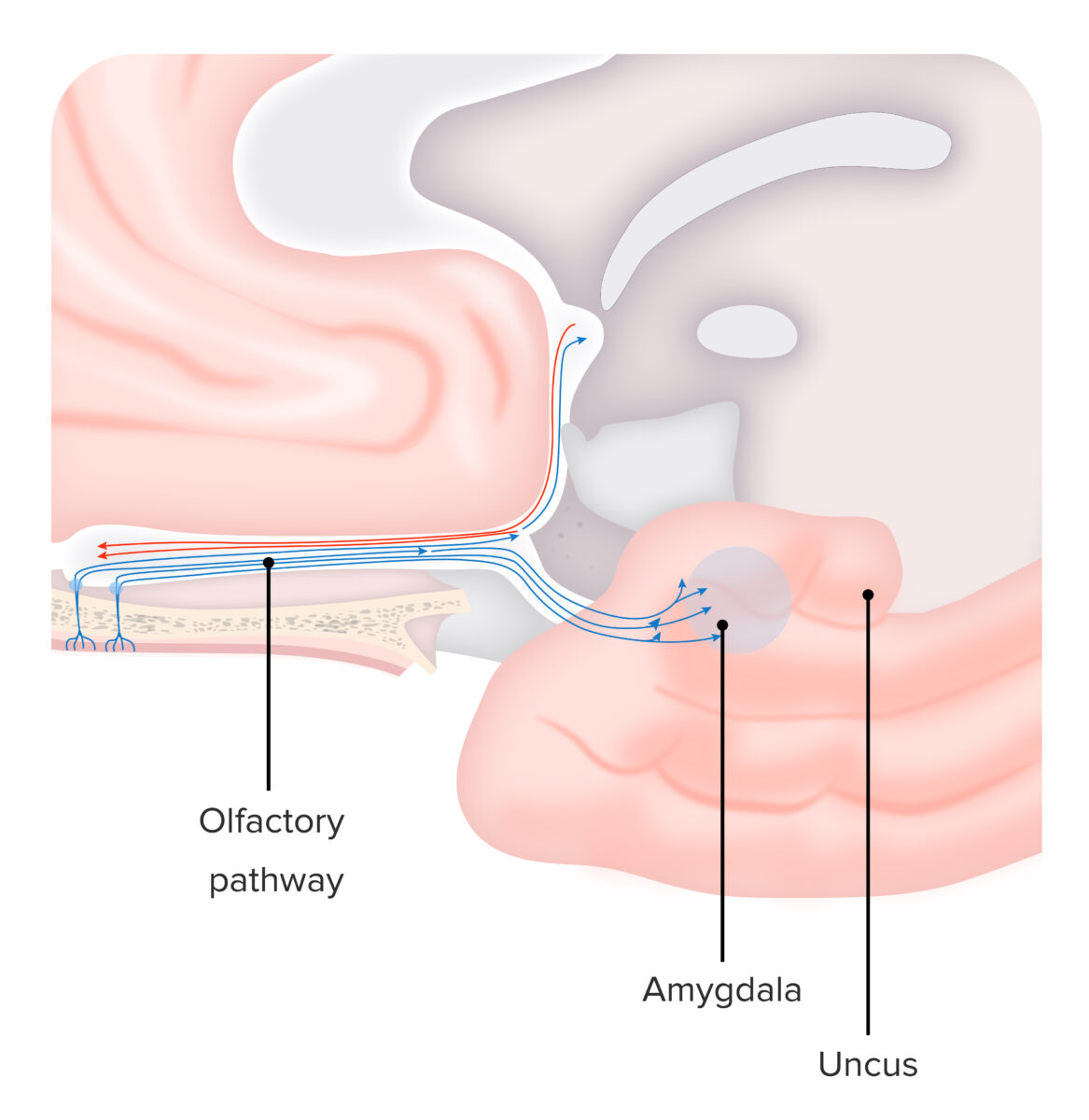
Image demonstrating the olfactory pathway. Note the direct input to the amygdala for emotional response and the direct input to the uncus, which permits the flow of information to the primary olfactory cortex.
Image by Lecturio.The Papez circuit is an interconnected network within the brain Brain The part of central nervous system that is contained within the skull (cranium). Arising from the neural tube, the embryonic brain is comprised of three major parts including prosencephalon (the forebrain); mesencephalon (the midbrain); and rhombencephalon (the hindbrain). The developed brain consists of cerebrum; cerebellum; and other structures in the brain stem. Nervous System: Anatomy, Structure, and Classification that is associated with many emotional processes. The Papez circuit involves the hippocampus, mammillary bodies, thalamus Thalamus The thalamus is a large, ovoid structure in the dorsal part of the diencephalon that is located between the cerebral cortex and midbrain. It consists of several interconnected nuclei of grey matter separated by the laminae of white matter. The thalamus is the main conductor of information that passes between the cerebral cortex and the periphery, spinal cord, or brain stem. Thalamus: Anatomy, and cingulate gyrus.
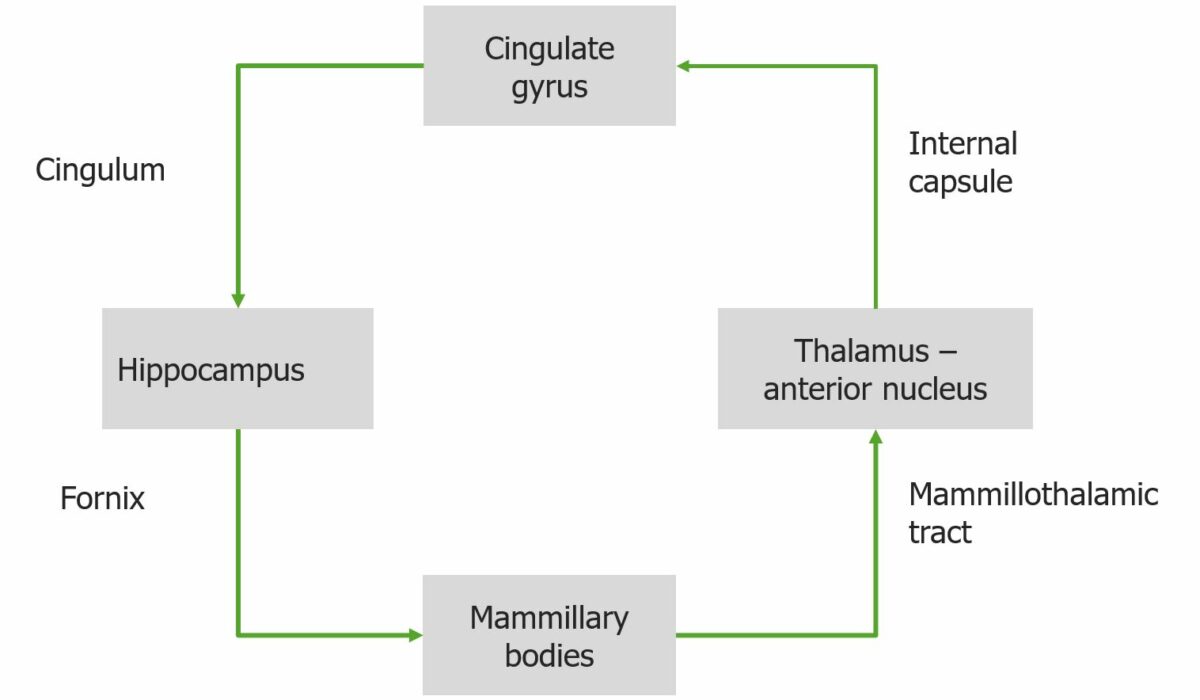
Circuitry of the Papez loop
Image by Lecturio.