Leukocyte adhesion Adhesion The process whereby platelets adhere to something other than platelets, e.g., collagen; basement membrane; microfibrils; or other 'foreign' surfaces. Coagulation Studies deficiency type 1 Type 1 Spinal Muscular Atrophy (LAD1) is an inherited condition in which genetic mutations Genetic Mutations Carcinogenesis result in a lack of CD18 expression on neutrophils Neutrophils Granular leukocytes having a nucleus with three to five lobes connected by slender threads of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing fine inconspicuous granules and stainable by neutral dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation. These mutations lead to a decrease in the ability of neutrophils Neutrophils Granular leukocytes having a nucleus with three to five lobes connected by slender threads of chromatin, and cytoplasm containing fine inconspicuous granules and stainable by neutral dyes. Innate Immunity: Phagocytes and Antigen Presentation to migrate from the blood vessels to the site of injury or infection on recruitment Recruitment Skeletal Muscle Contraction. Patients Patients Individuals participating in the health care system for the purpose of receiving therapeutic, diagnostic, or preventive procedures. Clinician–Patient Relationship with this condition will have recurrent infections Recurrent infections Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID) and delayed wound healing Wound healing Wound healing is a physiological process involving tissue repair in response to injury. It involves a complex interaction of various cell types, cytokines, and inflammatory mediators. Wound healing stages include hemostasis, inflammation, granulation, and remodeling. Wound Healing. An elevated neutrophil count may be noted on laboratory evaluation. The diagnosis is confirmed with flow cytometry Flow cytometry Technique using an instrument system for making, processing, and displaying one or more measurements on individual cells obtained from a cell suspension. Cells are usually stained with one or more fluorescent dyes specific to cell components of interest, e.g., DNA, and fluorescence of each cell is measured as it rapidly transverses the excitation beam (laser or mercury arc lamp). Fluorescence provides a quantitative measure of various biochemical and biophysical properties of the cell, as well as a basis for cell sorting. Other measurable optical parameters include light absorption and light scattering, the latter being applicable to the measurement of cell size, shape, density, granularity, and stain uptake. X-linked Agammaglobulinemia demonstrating a deficiency in CD18. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation Transfer of hematopoietic stem cells from bone marrow or blood between individuals within the same species (homologous transplantation) or transfer within the same individual (autologous transplantation). Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation has been used as an alternative to bone marrow transplantation in the treatment of a variety of neoplasms. Organ Transplantation is the treatment of choice, and it can be curative.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
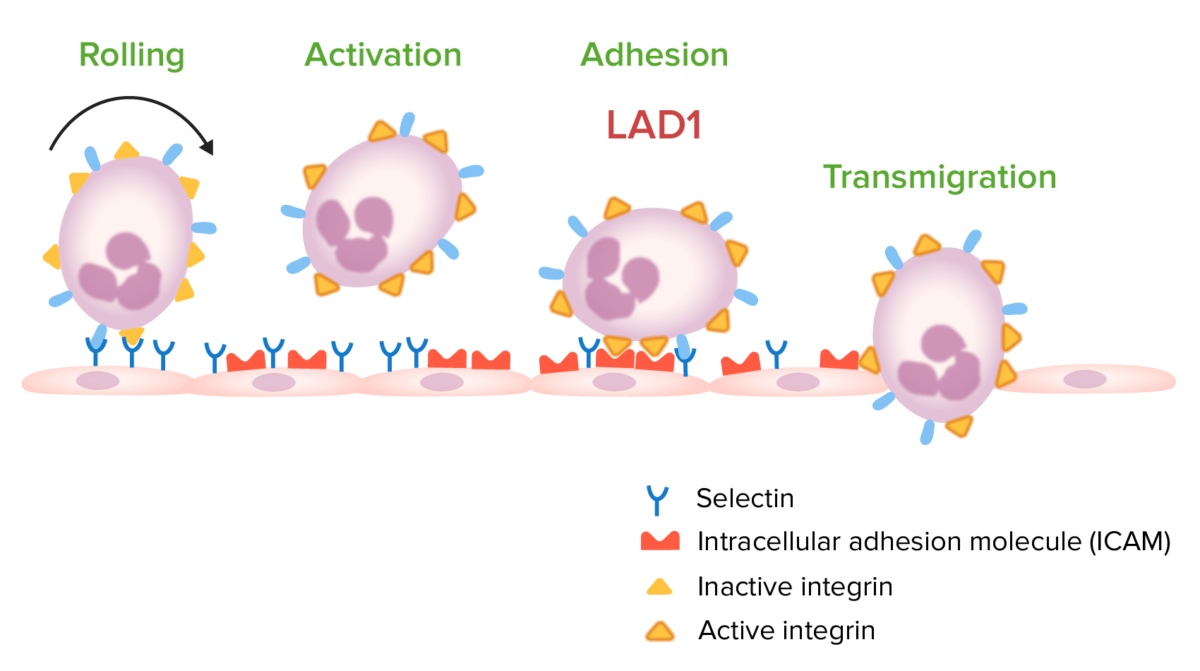
Steps involved in leukocyte migration:
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency type 1 (LAD1) occurs owing to a mutation in the gene encoding for CD18. This mutation leads to a deficiency of active integrins used in leukocyte adhesion to vascular endothelium, which prevents transmigration to the site of infection.